A logic model is a strategy for providing an idea of how stakeholders or investors would nurture a program, taking account of the resources, impacts, and outputs. It is a strategy that gives an approach to fostering investment in a program. The plan addresses the following questions using its six primary components: the reason for the program, its activities, output, the impacts of the program, and its conditions (Wisesa et al., 2020). Following on from the information offered above, the illustration that can be found below shows an example of a logic map developed by Apple stakeholders.
Logic Model for BPI Strategy Implementation
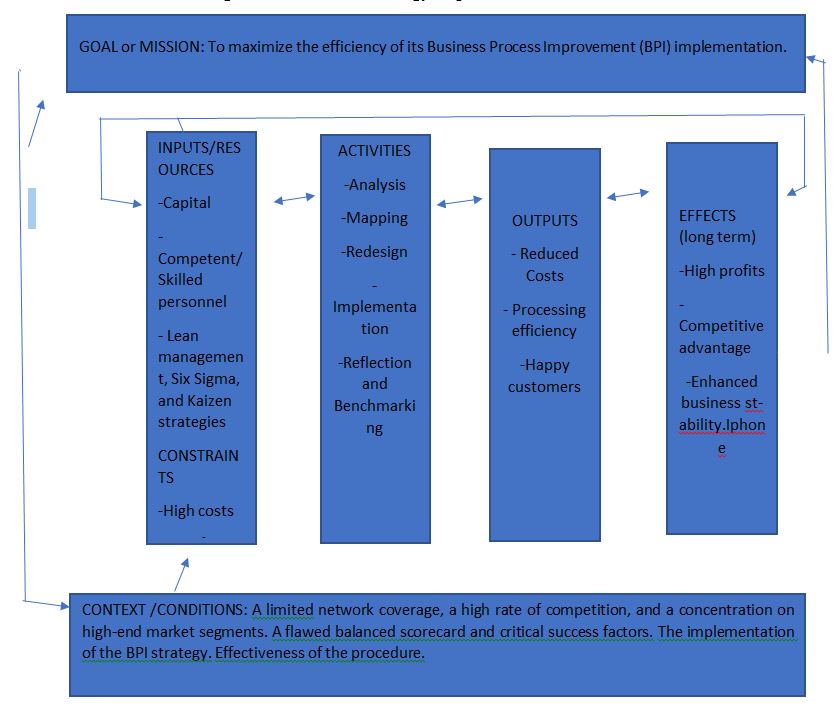
Mission/Goal
This model aims to demonstrate how the management team at Apple Inc. may successfully implement the BPI management strategy inside the firm. It demonstrates how resources will be utilized in the development of the project, which helps develop considerable projections to reduce waste and increase revenues through increased production efficiency.
Resources/Inputs
This section provides an overview of the organization’s resources to execute the system successfully. In this particular scenario, the workforce is the essential resource. The management team at Apple would begin by recruiting or hiring employees with an extensive background in this strategy to assist the corporation with the process of putting it into action (Wisesa et al., 2020). Aside from that, the organization can also provide training to its current employees to assist in implementing the strategy. Second, the business would look for adequate funding, although the entire process would be completed without outside financial assistance.
Constraints
This section discusses the many obstacles that may need to be overcome to implement this method successfully. The first problem is that the implementation and management are quite expensive. The installation of BPI can need a significant amount of capital, which might affect the company in the short run. If the company is serious about participating in this system, it can seek additional investors and funding from various sources (Bernhardt, 2017). Fear of change is an additional obstacle that could hinder success. Often, managers and employees are afraid to implement changes because they fear unknown consequences. Taking safeguards before putting this step into effect is the quickest method for ending this illusion.
Activities: The implementation process begins with mapping, an important step that significantly assists in determining the weak spots of processes to find a solution to the problem. The second step is analysis, in which the cost or profitability of BPI is determined. After that comes implementation, and finally, reflection, in that order.
Output: This output would result in lower costs, increased process efficiency, and increased customer happiness. Because it places a significant emphasis on making improvements and alterations to reduce costs and maximize the level of satisfaction that customers can provide, the BPI implementation’s primary objective is to maximize efficiency.
Effects: The following are some of the effects of applying this measure. These are increased financial security and a competitive edge are both benefits that emerge from the ineffectiveness of the procedure.
Context/Condition: The present state of affairs at the company is described in this section. Because of the limited locations, Apple is at risk of a lack of supplies. Besides that, Apple’s iPhone sales are restricted to a select group of customers, particularly those in the middle and upper classes. Keeping the merchandise out of the hands of others (Bernhardt, 2017). Before BPI, the company used a Balanced Scorecard to manage costs, but it ran into problems. Hence, the management turned to other methods, such as BPI, which focuses on production efficiency.
References
Bernhardt, V. L. (2017). Data analysis: for continuous school improvement. Routledge.
Wisesa, O., Andriansyah, A., & Khalaf, O. I. (2020). Prediction analysis for business to business (B2B) sales of telecommunication services using machine learning techniques. Majlesi Journal of Electrical Engineering, 14(4), 145-153.