
Towards 2025 is a program promoted by the Government of Hong Kong to help all citizens to learn and develop a healthy lifestyle and prevent and overcome overweight and obesity as risk factors for developing other diseases (“Change4Health: Home page,” 2019; Department of Health, 2018).
Since many guidelines on healthy eating and lifestyle are available for pilots, the aviation weight management and lifestyle modification program should be based on an individually tailored lifestyle modification intervention suggested in the context of Towards 2025. The components of this important intervention are:
- Healthy eating: an individualized diet based on counting the calorie intake to develop appropriate eating behavioral patterns and control weight (“GovHK: Healthy eating,” 2019);
- Increased regular physical activity and exercise;
- Stress management based on breathing exercises;
- Behavioral change is based on self-monitoring and goal setting.

Behavioral Change and Self-Monitoring
To be motivated throughout the overall path of changing behavior to focus on healthy lifestyle habits and control weight, it is necessary to apply self-monitoring forms and goal-setting techniques (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2015). The following steps should be completed to succeed in modifying pilots’ lifestyle:
- Step 1: Goal setting. Specific, measurable, achievable, and time-dependent goals need to be set by a person regarding keeping to a diet, exercising, and losing weight (“Nutrition education resources and materials,” n.d.).
- Step 2: Selection of a lifestyle modification program – an individually tailored lifestyle modification intervention for pilots associated with Towards 2025 objectives.
- Step 3: Filling in self-monitoring forms every day during the active stage of the intervention and flights (See page 7).
- Step 4: Consulting a supervisor and evaluating the outcomes of adhering to the intervention.
Healthy Eating
Objectives: to reduce fat and sugar consumption, increase calcium and fiber consumption.
Diet design:
- calculating calories – 1500 calories per day;
- reducing fat consumption;
- developing an individualized meal plan;
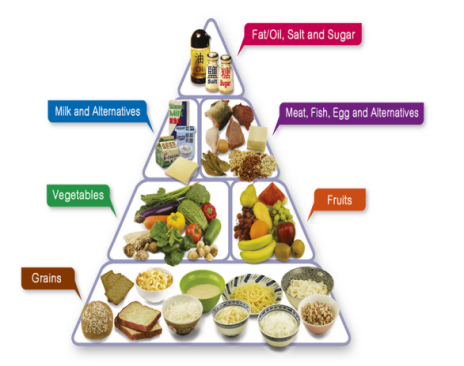
- using a food pyramid:
- taking mostly grains (3-8 bowls);
- taking more vegetables and fruit (2-3 servings);
- taking enough milk, fish, and meat (1-2 servings of each);
- taking less sugar, salt, and fat (Centre for Health Protection, 2017).
Teaching focus:
- diet principles – low-calorie intake;
- food choices – eliminate saturated fats and sugars (“Change4Health: Healthy diet,” 2019);
- menu and food preparation – choose low-fat methods of cooking;
- portions – control sizes of portions at home and public places (“About the campaign,” 2019).
Physical Activity
Pilots’ regular physical activity leads to overall health benefits, reducing weight, lowering risks of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes, reducing risks of depression, stress, and sleep problems (“Change4Health: Physical activity,” 2019).
- Aerobic physical activity: walking, running, cycling, playing basketball, football, swimming, and dancing – 150-300 min/week (moderate intensity) or 75-150 min/week (vigorous intensity).
- Duration of aerobic activity in bouts: minimum 10 minutes.
- Muscle-strengthening activity: exercising with resistance bands, lifting weights, carrying heavy loads, calisthenics – 8-12 repeats/exercise, 2-3 sets of different exercises, 2-3 days a week (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019).
- Additional exercising: flexibility and stretching activities, warm-up and cool-down exercises.
- Worksite physical activity: regular exercising during breaks.

Stress Management and Breathing Exercises
The profession of pilots is associated with high levels of stress experienced by these people regularly because of the tension they feel in their practice.
Symptoms of stress to pay attention to
- headaches;
- sleeping difficulties;
- loss of appetite;
- depressed mood and frustration;
- stomach ache and back pain;
- poor concentration (Centre for Health Protection, 2018).
Stress management
- identifying the source of stress and eliminating its effect;
- sharing thoughts and problems with partners, relatives, friends, and counselors;
- regular exercising and physical activity, including walking and jogging;
- keeping to a healthy and balanced diet;
- following a sleep schedule (7-8 hours of sleep);
- avoiding alcohol, cigarettes, and coffee;
- using relaxation techniques (massage, yoga, meditation, breathing) (Centre for Health Protection, 2018).
Breathing exercises
- Belly breathing: sitting and putting a hand on a belly, breathe in deeply through a nose, letting a belly push a hand, and breathe out through lips (3-10 times).
- 4-7-8 breathing: sitting and putting one hand on a belly and other on a chest, breathe in slowly counting to 4, hold a breath counting 1-7, breathe out counting 1-8 (3-7 times).
References
About the campaign. (2019). Web.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2015). Losing weight: Getting started. Web.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). Division of nutrition, physical activity, and obesity. Web.
Centre for Health Protection. (2017). The food pyramid – A guide to a balanced diet. Web.
Centre for Health Protection. (2018). Men’s mind – Stress. Web.
Change4Health: Healthy diet. (2019). Web.
Change4Health: Home page. (2019). Web.
Change4Health: Physical activity. (2019). Web.
Department of Health. (2018). Towards 2025: Strategy and action plan to prevent and control non-communicable diseases in Hong Kong – Summary report. Web.
GovHK: Healthy eating. (2019). Web.
Nutrition education resources and materials. (n.d.). Web.