Introduction
The assessments utilized in educational settings test diverse attributes exuded by learners. Instructors regularly assess learners’ understanding; furthermore, they judge instructional methods, adjust tasks, and re-appraise their instructional strategies. Administering these assessments is viable using certain teacher-developed or commercially produced assessments tools.
Language assessment emerges as one area in educational settings, which instructors’ accord attention. Assessments focusing on language are evident during program admission and assignment. The assessors strive to verify breaks in content familiarity and language ability. They gauge learner’s improvement and avail responses that facilitate students’ goal background. This term paper discusses a commercially produced assessment tool, BEST, which instructors use to assess adult English learners.
“Description of the intended audience and include at least one table or chart that summarizes demographic information.”
The audience that BEST appears to target include persons learning “English as a second language” (ESL) (Daugherity, 2008). The tool assesses practical language proficiencies for ESL. The tool regularly applies in learning settings and employment places. BEST emerges as a paramount assessment device that appraises ESL learner’s at grade ranks and adults at higher schooling levels. Notably, the BEST audience also entails diverse gender and age groups. It regularly applies to persons with a proficiency in a first language. These persons’ may include immigrants and refugees who decide to continue their schooling in America.
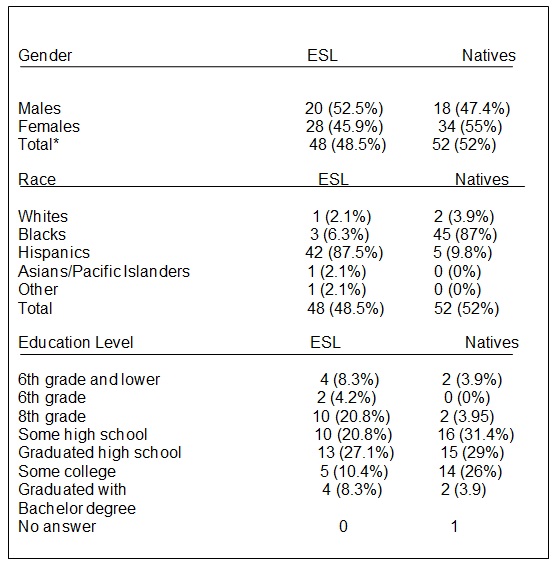
The following table outlines briefly the demographics for the BEST audience. The audience also includes the ESL learners. This study involved one hundred participants.
“Discussion of how the assessment tool has been used in at least three educational settings to obtain data on student achievement or improve instruction”
BEST has gained use in multiple educational settings. This tool has been utilized in schools for learners pursuing ESL. This enables assessors to determine learners’ capability before admission for programs (Daugherity, 2008). Correctional facilities also use BEST to determine the English proficiency of inmates originating from diverse regions. The administrators in charge of refugees also administer BEST to the immigrants thus attaining information on their language competence (Daugherity, 2008). In the workplace environment that uses English also administer BEST to potential recruits thus helping in determining the command for the language.
Characteristics of BEST
BEST is a standard tool for measuring listening conception, speaking, analysis, and lettering that applies to constrained English speakers in adulthood. These speakers appear to have studied ESL through capability strategy. BEST is characterized by 10-15 minutes personally taken interview that focuses on listening understanding and talking activities (CAL, 2008). The activities include telling time, inquiry and adhering to instructions, computing finances, and talking socially.
Notably, BEST entails two aspects including BEST Plus that regularly focuses on oral interviews. The oral interview remarkably entails assessing persons’ spoken English capabilities and mastery of the fundamental aspects of communication (CAL, 2010). The interview is regularly administered one on one. Further, it has BEST literacy that focuses on assessing the literary capabilities. These include details on persons’ skills regarding their knowledge content. Computerized versions of these tests also exist.
Establishment of Validity and Reliability While Using BEST
It emerges that attaining validity originates from achieving reliability. This is because validity remains superior. After all, it can occur through first attaining reliability. Establishing validity emanates from diverse tactics of attaining reliability (Hawkey, 2005). Then the results generated from reliability tests observed against the key reveals certain notions of validity. Ideally, validity also takes place central to tests because examinees may avail reliable responses, which may lack validity (Hawkey, 2005). The notable strategies for establishing reliability appear to entail correlation coefficients. The establishment of the BEST reliability occurs through test-retest that observes the links existing amid groups score administered at diverse times (Hawkey, 2005). Further, equivalent forms also establish reliability by availing a similar test to diverse groups on two forms. Split half also assists in establishing reliability by administering tests in halves to diverse groups.
Description of Scoring Procedures
Marking of BEST tests occurs through hand scoring. The procedure entails a physical evaluation of students’ rejoinders against the test key. It also entails the key that already contains certain numbers indicating scales of achievement simply help defines examinees’ responses (CAL, 2008). The key scaled beginning from one and ending at seven connotes that examinees feedback reveals certain competency when compared through using the keys. Therefore, peoples’ responses checked against the keys show their echelon of competency in the English language. Incompetent individuals regularly score diminished values starting from one (CAL, 2010).
“How you would use the results of the assessment to improve instruction and learning”
It appears that the results that emanate from the scored tests recorded as “students’ performance levels” SPLs indicate the achievement rates of learners’. The results also emerge from the ratings done through the “National Reporting System” throughout the ESL teaching (CAL, 2010). These results display individuals’ competency according to diverse scales. According to the capabilities of learners, as shown by the scores, instructors will enhance teaching methods thus bettering students’ abilities (Hawkey, 2005). The results also inform instructors’ content for coverage because results reveal knowledge gaps.
Assessment Tool and Scoring Procedure (or link to the tool)
BEST and its scoring procedure have certain links because hand scoring appears to focus on the details that already exist on the BEST test. The links that emerges between the two entails evaluating examinees rejoinders compared to the diverse aspects of BEST (CAL, 2008). The component of BEST that also indicates its linkages with scoring procedure entails the grading that BEST already contains. This indicates that comparison occurs using examinees feedback.
Conclusion
In summary, BEST emerges among the devices for assessment of diverse issues in educational settings. The device availed by commercial outlets attempts to determine the competence echelon of adult ESL scholars. The notable areas for evaluation include comprehension of elementary English, reading, and talking in social-based settings. The audience for BEST entails adults and insignificantly youths at diverse institutions. The notable characteristics of BEST include its two forms. These entail the interview-based BEST and literacy focus BEST. They also necessitate 10-15 minutes for applying the tool. Scoring for BEST takes place through hand scoring that compares examinees feedback with keys determined in BEST.
References
CAL. (2008). English Language Assessment Instruments for Adults Learning English. Web.
CAL. (2010). Important Information about the Basic English Skills Test (BEST). Web.
Daugherity, F. (2008). A correlative study of the International English Language Testing System listening test and a new repetition test. Michigan, MI: ProQuest Information and Learning Company.
Downey, La & Zun, L. (2007). Testing of a Verbal Assessment Tool of English Proficiency for Use in the Healthcare Setting. Journal of National Medical Association, (99), 7. pp. 795-798.
Hawkey, R. (2005). A modular approach to testing English language skills: the development of the Certificates in English Language Skills (CELS) examinations. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.