Introduction
One may wonder why organizations take their time to come up with employee motivation strategies, but the objective is to retain the employees. Employees are a vital asset of any organization and if they fail to commit themselves to organizational goals, it means that the organization does not offer them some incentives.
A study by Ramlall in 2004 found that at least 86 percent of institutions work hard to attract new employees and 58 percent of the organizations encounter difficulties in retaining their existing staff.
According to Millette and Gagné (2008), whenever an organization loses ten employees, the affected organization loses millions of dollars. Besides the financial loss, the organization also loses the expertise and knowledge the employees may have, which comprises one of the valuable assets of any employee.
Employee motivation could facilitate in avoiding chances of an organization incurring these costs.
There are numerous reasons for emphasizing on employee motivation. Among the reasons include making sure that the employees accomplish organizational and personal goals (Shanks, 2007).
There are significant differences between traditional and motivating companies with respect to how the two handle the issue of employee motivation.
Traditional companies use their management teams to identify the staff to recognize while the motivating companies consult their staff when making decision on the employees to recognize. Using the motivating factors, organizations come up with various methods of employee motivation.
Some organizations work to enhance the relationship between the employees and their -supervisors (Millette & Gagné, 2008).
A healthy relationship between employees and supervisors contributes to job satisfaction, which in return enhances employee performance. Other organizations exercise employee recognition to motivate their staff. Employee recognition makes them feel valued, which in return enhances their commitment.
Organizations benefit from employee motivation in different ways. One of the ways is that it promotes customer satisfaction and loyalty. Motivated employees offer quality and efficient services.
Therefore, they meet customer needs leading to their satisfaction. Another benefit of employee motivation to organizations is that it helps the organization to circumvent costs associated to employee turnover. Employees like working in organizations that encourage growth and development.
Hence, failure to motivate employees leads to organizations losing their skilled personnel. Replacing these employees is expensive for an organization. Labor costs are other organizational costs eliminated through employee motivation.
A motivated workforce operates under minimum supervision and is efficient, cutting down on labor costs.
This paper will focus on employee motivation, theories of employee motivation, and the benefits of employee motivation to an organization, giving real life examples of employee motivation in contemporary organizations.
Comparison between tradition and motivating companies
Traditional companies refer to companies that observe a hierarchical structure with respect to employee management, decision-making processes, as well as employee motivation. Such companies exhibit bureaucracy in all the operations (Reichheld, 2001).
On the other hand, motivating companies refer to companies that exercise high level of employee empowerment (Reichheld, 2001). In motivating companies, decision-making processes are decentralized and all employees participate in making critical decisions on matters affecting their organization.
There is a clear difference between traditional and motivating companies. Both the traditional and motivating companies practice employee motivation. Nevertheless, their approaches to employee motivation differ significantly (Reichheld, 2001).
For traditional companies, the management is responsible for implementing employee motivation. Therefore, the management team identifies the employees to recognize without taking into account the contribution of other employees. This form of employee motivation has numerous limitations.
One of the limitations is that the approach demotivates those employees the employees that do not receive recognition (Shanks, 2007). They perceive the management as biased, and this affects their performance.
In addition, the approach leads to the motivated employees feeling manipulated, controlled, and overpowered as their seniors make the recognition decision. It might affect the relationship between the employees with the staff that is not recognized declining to cooperate with the recognized staff.
Motivating companies understand the dangers of using biased motivating methods. Moreover, they appreciate the contribution made by every employee in the organization. Consequently, they seek the opinion of every employee within the organization when selecting the employees to recognize.
Motivating companies treat their employees as valuable business associates, rather than seeing them as, “traditional input resources needed to accomplish tasks and goals” (Baldoni, 2005). Motivating companies have a well-established employee recognition system, which motivates the employees to work harder.
Today International Business Machine (IBM) Company is one of the information technology companies with a strong and dedicated workforce. The reason behind this is that the company exercises an all-inclusive system when recognizing its employees.
The company has given its employees the power to make decisions on employees to recognize (Doyle, 2004). This promotes cooperation between all the employees since they all feel to be part of the success the company makes.
Another distinction between traditional and motivating companies comes from business ownership. In traditional companies, the management owns the business and all the decisions made within the business have to come from the management.
This underlines the reason why traditional companies exhibit poor growth. Motivating companies are employee-owned. They exercise high level of employee empowerment allowing the employees to make critical decisions within the companies.
The idea behind employee empowerment in motivating companies is that making employees feel to be part of the company enhances their commitment. Employees strive to see that the company that they partly own prosper.
According to Abbasi, Hollman and Hayes (2008) “No one that owns a company wants to see their assets dwindle due to poor work relations and personal drive.” (55). Motivating companies involve all employees in selecting the management team to run the company.
Therefore, they do not impose leaders on their employees. This promotes cooperation between the employees and the management team.
Benefits of employee motivation
For decades, organizations have encountered a major challenge in attracting and retaining employees with skills relevant to their operations. The economic crisis witnessed in 2001, made this challenge severe as many organizations had to layoff most of their qualified employees as a way of cost cutting (Mitchell, 2002, p.77).
In the United States, the companies did away with over one million jobs leading to employees losing faith in the companies. In addition, the move led to increase in employee distrust and reduction in employee productivity.
Employee creativity and morale tumbled while the stress level went high leading to increased cases of absenteeism. Today, organizations are predisposed to an awfully vibrant and impulsive work environment characterized by continued instability in the economy.
Managers encounter challenges in their bid to motivate and retain employees in a working environment full of uncertainties (Mitchell, 2002, p.78). Now, new jobs are emerging at an unprecedented rate, which is happening at a time when workers are scarce, particularly in the medical field.
In a bid to make sure that organizations do not lose their employees to rival companies, organizational leaders are turning to employee motivation as the last resort.
Organizations understand the cost incurred whenever employees leave an organization due to dissatisfaction. Hiring new employees is always expensive in terms of training. Organizations end up investing heavily on the new recruits to equip them with the relevant skills since it is hard to get staff with the required expertise.
In a bid to avoid these overheads, organizations opt to motivate their staff as a way of encouraging them to remain in the organization and to direct all their attention to organizational goals. In the modern unstable workplace, a committed workforce becomes a critical competitive advantage for an organization.
Companies with unstable workforce end up spending thousands of dollars in training, supervising, orienting, and recruiting new staff (Reichheld, 2001).
In a bid to continue enjoying a close relationship with customers, organizations require motivating their employees. Employee motivation contributes to the continuity of an organization. Failure to motivate the employees affects their performance, which in return affects the continuity of an organization.
In the end, it erodes consumers’ loyalty rendering the company uncompetitive in the marketplace. Ambrose (1996) posit, “Arguably, the most valuable (and volatile) asset is a stable workforce of competent, dedicated employees” (p.13). Once a company loses its qualified employees, it becomes hard to replace them.
In a bid to maintain their performance, organizations are forced to hire staff with less skill who in most cases fails to fulfill customer expectations. The customers leave the company and look for others that would meet their expectations, affecting the cash flow of the affected company.
Employee motivation helps the company maintain its cash flow and profit because it promotes employee efficiency, which in return leads to customer loyalty.
Employee motivation facilitates to curb employee turnover. Reichheld (2001) posits, “Employee voluntary turnover is a persistent phenomenon that produces a serious problem for organizations” (p. 115).
Organizations lose skilled and qualified staff because they do not encourage innovation and competitiveness, which in return, affects the quality of services they offer. In the health industry, employee turnover leads to organizations incurring huge costs with respect to recruiting, hiring, and training new staff (Abbasi, Hollman, & Hayes, 2008).
In Italy, the issue of employee turnover in the nursing industry is rampant. In 2009, the country had a shortage of over 40, 000 nurses.
Abbasi, Hollman, and Hayes (2008) argue that as many nurses left their institutions in pursuit for others with attractive working conditions, the affected institutions recorded poor performance, loss in employee morale, and more turnovers.
Employee motivation helps health institutions shun cases of dysfunctions that might arise due to high turnover.
A research in the Journal of Management posited that a health institution with about 300 employees and an annual turnover rate of two percent, incurs a cost of approximately $2.8 million trying to replace the employees who leave the institution.
The turnover cost related to a single health worker is at least $10,000, which underlines the reasons why health institutions require establishing superior employee motivation policies if they wish to reduce this cost (Richer, Blanchard, & Vallerand, 2002).
In the state of Karnataka (India), transport companies use employee motivation to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Companies that own fleets of busses know that employees like the drivers come into direct contact with customers daily.
Therefore, the companies’ ability to enhance customer satisfaction or to offer quality services lies on their drivers. Hence, the companies strive to have highly motivated drivers and other staff as a way of making sure that they offer quality services to their customers.
Among the strategies that these companies use include improving the working environment and offering competitive remuneration packages to their employees.
Southwest Airline is one of the companies that utilize employee motivation to enhance its profit and competitiveness. Today, competition in the airline industry is extremely stiff, calling for companies to come up with strategies for enhancing customer loyalty.
In a bid to achieve competitiveness, Southwest Airline focuses on the pillars of employee motivation. It enhances employee relations in a bid to encourage them to commit their energy to organizational goals.
The current success in the airline company is attributed to its employees who offer quality services to their customers at a low cost. According to Southwest Airline’s policies, employees take the first priority. The company commits to offering stable working environment to its staff.
It encourages employee growth and development, which in return contributes to innovations within the organization. As Herzberg puts it, employee growth and development are some of the motivating factors.
Encouraging employee growth and development spurs employee creativity leading to an organization realizing novel innovations that not only help it cut down on operations cost but also improve its competitive advantage.
Organizations that promote entrepreneurship and independence have employees that are willing to take risks and to come up with novel innovations at all levels (Ahmad, Wasay, & Malik, 2012). Internal competition is normally high in such organizations.
One of the methods through which Southwest airline motivates its employees is through the promotion of entrepreneurship and autonomy. In the company, every staff has the freedom to share their opinion. The company calls on every employee to take leadership duties in their areas of work.
The company also motivates its staff by tolerating failure. By exercising tolerance to failure, the company nurtures an innovative environment where employees feel free to pursue their dreams. These motivation factors are the reasons for the current success of the Southwest airlines (Gittell, 2006).
According to the Innovation Index, Southwest airline is among the top ten innovative airline companies in the world. Between 2003 and 2005, the airline’s revenue went up from $5.9 billion to $7.6 billion.
Besides, the value of the company’s stock has continued soaring. Through employee motivation, the company is currently one of the airline firms that offer quality services at low cost. The company records the lowest number of customer complaints among all the domestic airlines (Gittell, 2006).
Employee motivation helps in the enhancement of organizational efficiency. In organizations that value employee motivation, managers meet with their employees to deliberate on methods of enhancing their performance. In return, this aspect encourages employee feedback.
Employees identify areas that cause deadlocks in organizational efficiency and relay the information to the management for it to respond appropriately (Richer, Blanchard, & Vallerand, 2002). Eventually, it facilitates in streamlining operations within the organization, thus, enhancing its efficiency.
Besides, the employees volunteer to participate in tasks outside their job descriptions just to see that the organization achieves its goals. Failure to motivate employees discourages volunteering.
In return, an organization faces challenges in addressing certain issues that arise outside the job descriptions of their employees. For instance, an organization may want to organize for teambuilding activities but fail to meet this objective due to lack of volunteers.
Despite how efficient an organization is, it is hard to manage labor costs. Organizations that do not operate on a fully automated system record labor cost as the biggest chunk in its total operating costs. Conventionally, labor cost is split into two: direct and indirect.
Direct labor costs emanate from the employees working within an organization while indirect labor costs emanate from customers and people affected by the institution’s operations (Shanks, 2007).
To reduce labor costs and enhance organizational profit, organizations ought to focus on their employees. They ought to motivate their employees in a bid to boost their commitment.
Organizations that do not motivate their employees incur high labor costs.
In such institutions, employees respond to certain activities only when asked to do so by their supervisors, which implies that such organizations require having supervisors in all their departments to facilitate in monitoring the operations (Tzeng, 2002).
The main reason why organizations motivate their employees is to reduce labor costs. When employees are intrinsically motivated, they do not require supervision. Therefore, rather than monitoring the employees organizational managers can spend their time doing other productive activities.
Employee motivation helps institutions to run efficiently with fewer managers. One of the factors that contribute to labor costs within an organization is hiring of numerous managers to facilitate in the management of different tasks.
Motivating employees avoids the need for having numerous managers and, it makes it possible for an institution to run with fewer managers. This move saves the institution the cost of paying the salary of many managers (Tzeng, 2002).
Tesco uses employee motivation as one of its strategies of cutting down on labor costs. To cut down on operations costs, the company undertakes to nurture a motivated, well-trained, and flexible workforce.
The company works closely with it staff in their different departments to help them develop vital skills in customer assistance. Besides, Tesco equips its staff with diverse skills to facilitate in employee rotation (Tzeng, 2002). Job rotation is one of the strategies that organizations apply to minimize labor cost.
It entails assigning employees to different duties on different occasions. In the process, they expand their skills, therefore allowing them to fit in various departments within the organization. The move adds to job satisfaction. Furthermore, it contributes to employee motivation.
Through this strategy, Tesco has been able to cut down on labor costs. Whenever one of the employees is absent, the organization always gets another one to stand for him or her.
It helps in reducing the operations cost since the company does not have to hire another employee whenever one goes for sick or maternity leave (Tzeng, 2002). Besides, the employees work under minimum supervision, saving the company the cost of hiring numerous supervisors.
Employee motivation leads to improved productivity and triggers an inherent desire to put effort on a particular activity with limited supervision. According to McNerney (1996), employee motivation “promotes and encourages a dedication by every staff to cooperate with other employees” (p.17).
In other words, motivation encourages the culture of teamwork within an organization. In return, it enhances the employees’ willingness to participate in different projects within an organization. Source posits that there is clear link between motivation and productivity.
Employee motivation benefits the organizations in the sense that it improves the organizational performance (McNerney, 1996). Motivated employees are loyal to an organization and willing to help an organization pursue its objectives.
In spite of the current advancement in project management technology, employees remain the primary factor that determines the success of any project.
They are responsible for setting the project goals, organizing for project implementation, monitoring, and coordinating the project, among many other responsibilities (McNerney, 1996). Motivated employees direct all their energy to organizational projects helping in the improvement of productivity (Herselman, 2001).
One of the industries where employee motivation facilitates to improve the organization productivity is in the construction industry. In South Africa, the construction industry is a major contributor to national economy. The industry offer employment opportunity to the local community (Herselman, 2001).
According to Statistics South Africa, in 2006, eight percent of the total employment opportunities in the country came from the construction industry. In spite of the industry being one of the major contributors to national economy in South Africa, it is yet to meet its full potential.
The industry’s productivity is low with the main reason for poor productivity being poor employee motivation (Gruneberg, 2005). Majority of the people with experience in construction industry prefer working in other industries or looking for employment in foreign countries to working in South Africa’s construction industry.
Majority of the construction companies in the country lack capital to enhance the working conditions. This aspect demotivates the skilled personnel prompting them to look for employment elsewhere. Today, the South Africa’s construction industry experiences shortage in the number of skilled personnel.
In a bid to enhance its productivity, the South African Institute of Civil Engineers believes that the industry will have to hire experts from foreign companies (Gruneberg, 2005).
Only through hiring experts from foreign countries would the industry manage to restore sanity therefore encouraging local engineers to work within the industry, which would significantly facilitate in improving the productivity of the industry.
Employee motivation not only facilitate to enhance organizational productivity, reduce the rate of employee turnover, enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, but also facilitates in enhancement of the organization’s fiscal profit through enhanced quality of products and services (Gruneberg, 2005).
Employee motivation makes staff invest their brainpower, effort, and time into enhancing the quality of the products and services they offer. Motivation triggers creativity within the employees.
In return, they come up with novel ways of producing goods and services, which are efficient and cost effective, which adds to the organization’s profit by reducing the operations costs and increasing the sales volume of the respective organization (Gruneberg, 2005).
Whenever employees are motivated, they take delight in their accomplishment, implying that they ensure that the company’s brand name stands out in the market. In a bid to achieve this goal, they strive to come up with superior products or services.
On the other hand, demotivating employees leads to majority of them exerting little effort.
Eventually, the quality of the company’s products or services get compromised leading to majority of the customers leaving the respective company and looking for an alternative one that offers quality products or services, which affects the profit margin of the affected organization (Gruneberg, 2005).
Employee motivation has helped Afroze Textile Industries Limited in Pakistan make significant progress. The company started in 1973. Initially, it operated as a towel manufacturing company. Nevertheless, as time went on, the company diversified its products to manufacture other textile products.
Afroze Textile Industries uses numerous methods of employee motivation (Muhammad & Memon, 2012). One of the methods is enhancing working environment. The industries’ management is conscious of the employees’ health and safety.
Hence, it takes them through safety training and supplies them with tools for safety (Muhammad & Memon, 2012). Besides, the company enhances job satisfaction by giving its employees the freedom to make decisions on matter affecting their areas of operations.
This has facilitated in bridging the gap between the management and the employees, thus creating an environment that encourages teamwork.
Majority of the organizations fail to offer quality products and services due to lack of cooperation between different departments within an organization (Muhammad & Memon, 2012).
Cooperation between the departments and employees helps to streamline operations, therefore improving the quality of products or services. Through job satisfaction, Afroze industry has witnessed significant innovation within the industry earning the company a good reputation across the globe.
Today, the company is renowned for quality and reliable products. Besides, in 2001, employee motivation helped the company come up with novel process integrated unit.
Today, the industry is popular for products like Woven Fabric, Knitted Hosiery, and Terry Towels (Muhammad & Memon, 2012). Besides, the company has used employee innovation to cut down on the operations costs. This has helped in profit maximization.
Conclusion
Employee motivation is a vital element in enhancing organizational performance. Toady, competition is high with every organization trying to outdo its rivals. Organizations constantly fish skilled personnel from their rivals.
Hence, to remain competitive, organizations require coming up with strategies for attracting and retaining competent employees. Enhancing employee motivation is the best strategy for attracting and retaining skilled personnel. There are distinctions between the traditional and motivating companies.
In traditional companies, the management makes the decision about who to recognize in the company. Therefore, this leads to majority of the employees feel unvalued. Conversely, in the motivating companies, the management involves all the employees in deciding on the employees to recognize.
This promotes cooperation between the employees since they feel to contribute in decision-making processes. Organizations use employee recognition, improved employee relation, remuneration, and growth and development to motivate their staff. Employee recognition leads to job satisfaction.
Besides, it triggers a healthy competition among the employees, which enhances organizational performance. Improved employee relation contributes to job satisfaction and employee commitment.
Additionally, employee growth and development helps employees meet personal goals and the unsatisfied needs. In the process, it strengthens employees’ commitment to the organization since they perceive the organization an appropriate vehicle for helping them meet their life dreams.
The benefits of employee motivation are innumerable. It helps organizations to reduce costs associated to employee turnover and labor cost. Whenever employees feel dissatisfied with their jobs, they leave the organizations and look for others that offer satisfying jobs.
In a bid to ensure the organization continuity, the affected organizations look for alternative employees to replace those that leave. Since it is hard to get other skilled employees easily, the affected organizations end up incurring high costs in hiring and training new staff.
Apart from reduction in turnover and labor costs, other benefits of employee motivation include increased customer satisfaction, innovations, enhanced organizational performance, and increased organizational profit.
The majority of the organizations turn to employee motivation as their strategy for enhancing organizational performance.
For example, Southwest Airline employs employee motivation to encourage innovation and improve organizational efficiency. Today, Southwest Airline is among the most innovative airline companies in the world.
Charts on factors of employee motivation
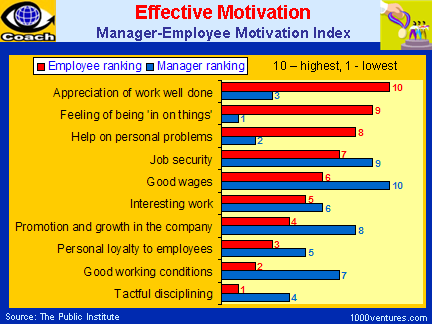
Source: (Doyle, 2004)
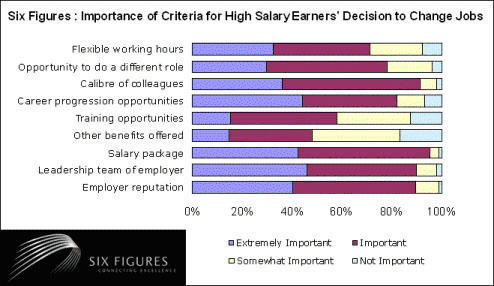
Source: (Baldoni, 2005)
Reference List
Abbasi, S., Hollman, K., & Hayes, R. (2008). Bad bosses and how not to be one. Information Management Journal, 42(2), 52-56.
Ahmad, M., Wasay, E., & Malik, S. (2012). Impact of employee motivation on customer satisfaction: study of airline industry in Pakistan. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 4(6), 531-536.
Ambrose, D. (1996). Healing the Downsized Organization. New York, NY: Three Rivers Press.
Baldoni, J. (2005). Great Motivation Secrets of Great Leaders. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Doyle, S. (2004). The manager’s Guide to Motivating Employees. Amherst, MA: HRD.
Gittell, J. (2006). The Southwest Airlines way. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Gruneberg, S. (2005). Construction Economics. New York, NY: Palgrave Publishing.
Herselman, S. (2001). Performance, motivation among employees of a wholesale company. South African Journal of Ethnology, 24, 1-10.
McNerney, J. (1996). Employee motivation: Creating a motivated workforce. Human Resource Focus, 73(8), 14-19.
Millette, V., & Gagné, M. (2008). Designing volunteers’ tasks to maximize motivation, satisfaction and performance: the impact of job characteristics on the outcomes of volunteer involvement. Motivation and Emotion, 32, 11-22.
Mitchell, L. (2002). Corporate Irresponsibility – America’s Newest Export. London, UK: Yale University Press.
Muhammad, G., & Memon, U. (2012). Determinants of employee motivation – A case study of Afroze Textile Industries Limited, Karachi, Pakistan. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 4(3), 22-25.
Reichheld, F. (2001). Loyalty Rules! How Today’s Leaders Build Lasting Relationships. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press.
Richer, S., Blanchard, C., & Vallerand, R. (2002). A motivational model of work turnover. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 32, 2089-2113.
Shanks, N. (2007). Management and Motivation. Burlington, Ontario: Jones and Barlett.
Tzeng, H. (2002). The influence of nurses’ working motivation and job satisfaction on intention to quit: an empirical investigation in Taiwan. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 29, 867–878.