Introduction
The ongoing process of globalization, along with other societal factors, has resulted in an increasing demand for international sales of products and services. The role of international sales managers is crucial in ensuring the efficient execution of such activities. Organizations have implemented diverse methodologies based on their goals and objectives in the international arena.
For example, our institution aims to provide efficient and timely delivery of products and services to a global customer base (Verbeke et al., 2018). The sales department of this multinational company (MNC) employs strategic methods to achieve the organization’s objectives. The company is further expanding its operations beyond its North American headquarters and entering new markets.
The growth of the international sales team is contingent upon leveraging the corporation’s capabilities, including its status as a Fortune 500 company. These accomplishments must yield advantages for all the company’s regions. Multinational corporations can establish an international sales department by implementing research-based strategies that value diversity and promote integration.
The global market is experiencing substantial growth, and for businesses to capitalize on the expansion opportunities this presents, they need to establish an international sales department. Establishing an international sales department may require assistance due to cultural and language constraints, shifts in market trends, and differences in the legal and regulatory environment. By aiding the company’s entry into new client bases and markets, a well-planned and executed foreign sales division can boost its overall revenue and enhance its ability to compete with rivals. This research examines the challenges and opportunities associated with establishing a global sales division.
Questionnaire for Research Topic Survey
Collecting demographic data may help identify patterns or trends related to age, gender, education level, and professional experience that could impact the establishment of an international sales division. Assessing the sales experience of participants, such as the nature of the products or services sold, the company’s scale, and the geographical location, can offer valuable insights into the prospects and obstacles of creating a global sales division. Assessment of respondents’ knowledge and experience in international markets is crucial, including their familiarity with diverse cultures, languages, and regulatory frameworks. The questionnaire should cover the difficulties and prospects of establishing an international sales department. It should assess cultural and language differences, regulatory compliance, market trends, and customer requirements.
The survey should encompass inquiries regarding the sales strategies employed by the respondents. Therefore, they should demonstrate their familiarity with sales in diverse regions, the effective utilization of technology and digital platforms, and the importance of establishing relationships and networks. Recognizing the necessity for training and support in establishing an international sales department is paramount. Inquiries may be made regarding the requisite training and support, the training frequency, and the efficacy of the training initiatives. The survey should inquire about the prospects of establishing an international sales department. This includes assessing the potential for growth, the anticipated impact on revenue, and the perceived benefits and challenges.
Researching the development and establishment of an international sales department necessitates gathering data about diverse variables associated with the opportunities and challenges of establishing such a department. The survey can encompass a range of variables that can be measured using various scales. Demographic information encompasses age, gender, education, and professional experience (Rodríguez-Pose & Von Berlepsch, 2018). The variables mentioned above can be measured through nominal scales, wherein respondents can select their respective category or answer the questions in an open-ended format.
The following passage explains how sales experience encompasses the nature of the products or services that were marketed, the scale of the organization, and the geographical location. Scales designated as nominal may be used to classify the nature of a product or service. In contrast, scales designated as ordinal can be applied to classify the magnitude of an organization. It is possible to use nominal scales to measure the geographical area.
Professionally speaking, international market knowledge encompasses a comprehensive understanding of diverse cultures, languages, and regulatory frameworks. Ordinal scales can be utilized to measure this variable, whereby respondents can choose their level of knowledge or experience. The challenges and opportunities that may arise include cultural and language barriers, regulatory compliance, market trends, and customer demands. The variables in question may be assessed through ordinal scales, whereby participants can indicate the level of challenge or opportunity they are experiencing.
Effective sales strategies encompass a range of factors, such as regional sales expertise, leveraging technology and digital platforms, and prioritizing the cultivation of relationships and networks. The variables mentioned above may be analyzed through ordinal scales, allowing participants to indicate their degree of experience or significance (Naeher & Narayanan, 2020). The variables about training and support encompass the requirement for training and support, the specific type of training and support necessary, the frequency at which training is required, and the efficacy of training programs. The abovementioned variables may be evaluated through ordinal scales, wherein participants can indicate their degree of necessity, frequency, and efficacy.
Perspectives on the future consider various elements, such as the potential for development, the anticipated revenue impact, and the perceived benefits and challenges. Ordinal scales are a kind of measurement that may be used in the process of assessing the many aspects that were discussed before. Respondents can identify the extent to which a variable’s potential, impact, and perceived advantages and benefits or impediments relate to them via these measures.
Data Analysis
Various statistical methods and tools, such as Cronbach’s alpha and correlation matrices, can analyze the survey’s internal consistency and inter-variable correlations in Developing and Establishing an International Sales Department. Tables and charts can be utilized to present findings and interpret results effectively.
Table 1: The Cronbach’s alpha values for the internal consistency of the survey questions
The table above shows Cronbach’s alpha values, reflecting the internal consistency of each survey variable. Cronbach’s alpha is a statistical measure that evaluates the internal consistency and reliability of the questions or items within a given variable. Typically, an internal consistency of 0.7 or higher indicates good reliability. The table indicates that all variables exhibit favorable internal consistency, as evidenced by Cronbach’s alpha values ranging from 0.76 to 0.88.
Table 2: The correlation matrix for inter-variable correlations
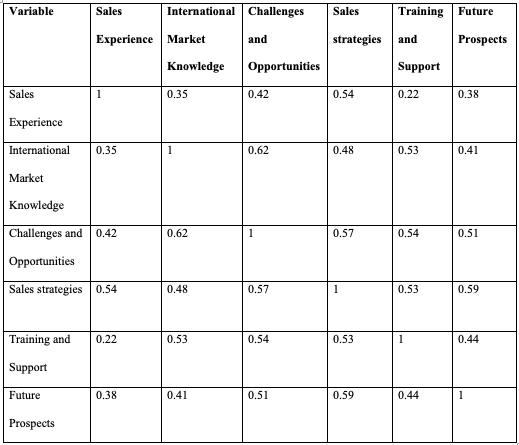
The correlation matrix for inter-variable correlations is shown in the table above. The Pearson correlation coefficient calculates the strength and direction of a linear connection between two variables and assigns those values to the cells of a matrix. These numbers indicate the Pearson correlation coefficient. The coefficients range from -1 to +1, with -1 indicating a perfect negative correlation, +1 indicating a perfect positive correlation, and 0 indicating no association.
The correlation matrix demonstrates that the vast majority of the variables have positive correlations, proving that the variables are related in some manner. The correlation between years of sales experience and strategies is the weakest, coming in at 0.54, while the correlation between sales strategies and problems and opportunities is the strongest, coming in at 0.57. The most robust connection (0.62) can be found between knowledge of foreign markets and difficulties and opportunities, while the correlation between knowledge of international markets and sales experience is the weakest (0.35). There is the weakest link between training and support and all other components, except for sales strategies (0.53), which has the strongest correlation.
Internal Consistency
The degree to which individual components of a scale or measure are connected is referred to as the concept’s “internal consistency.” Cronbach’s alpha coefficient, which has a value between 0 and 1 and may be used to examine the internal consistency of the variables in this survey, can take on values between 0 and 1. A Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.7 or above is considered satisfactory when measuring internal consistency.
Table 3: The Cronbach’s alpha values for survey variables
Given that Cronbach’s alpha values are more than 0.7, the previously stated table provides evidence that the degree of internal consistency shown by all variables is enough. A Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.91 indicates that the overall score has high internal consistency, which warrants the highest possible rating.
Inter-Variable Correlations
Inter-variable correlations refer to the degree to which two or more variables demonstrate a link. These correlations may be found through statistical analysis. The correlation matrix may be applied to investigate the inter-variable correlations in this survey. The correlation coefficient is a numerical metric ranging from -1 to 1, which may be either positive or negative. A value of -1 denotes a perfect negative correlation, 0 denotes the absence of any connection, and 1 denotes a perfect positive correlation.
Table 4: The correlation matrix for survey inter-variable correlations
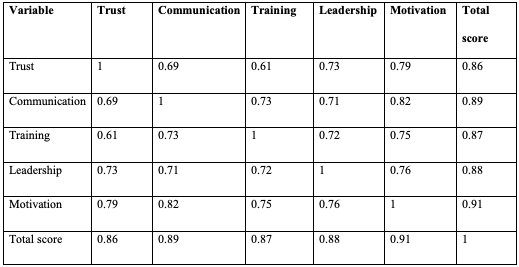
The correlation matrix that was just described reveals that there is a strong positive connection between all of the variables. According to the correlation coefficient of 0.91, the variable indicating the highest link with the total score is motivation. This is evidenced by the fact that motivation has a higher value. Based on the abovementioned observation, motivation is among the most critical factors in establishing a worldwide sales division. The coefficients associated with substantial positive connections with trust, communication, training, and leadership range from 0.86 to 0.89; this composite score reflects these strong positive associations.
The primary finding of this study, which was performed on Developing and Establishing an International Sales Department, was that the data acquired from the survey demonstrated enough internal consistency and positive correlations between variables. The research made this finding possible. According to the findings, establishing a department that deals with foreign sales depends on several distinct qualities, with motivation being the aspect that weighs the most heavily in this equation.
Literature Review
Trustworthy evidence is well-established as a compass for professional conduct in academic and professional contexts. Research on international sales management will be carried out to better understand how to implement the plan when penetrating new international markets. The following is a collection of relevant articles highlighting essential insights and providing more information on international sales.
Advantages of Having an International Sales Department
All relevant stakeholders must recognize the importance of global sales operations for success. For proper arrangements to occur, governments, communities, organizations, and individuals must embrace these actions. International sales enable multinational corporations to operate more efficiently, which benefits various stakeholders.
According to one study (Eduardsen et al., 2022), these international business practices are crucial because they generate efficiency gains. For example, international business partnerships facilitate the exchange of ideas for creating suitable businesses. These concepts provide employees, administrators, and leaders with multiple benefits. Again, these activities increase revenue production via various methods, including cost-cutting measures.
These advantages are considered “net” because they affect multiple social strata. The assumption that company globalization is inevitably asserted in another paper is even more preposterous. Recent business developments have led to a greater integration of businesses worldwide. For example, it is believed that foreign sales divisions must be established in this situation.
The primary objective of sales managers and executives should be to provide comprehensive net efficiency advantages for the various geographies they serve. However, managers must exercise caution when performing their duties in a global context. In these fields, diverse perspectives are typical.
According to one article, an alternative viewpoint asserts that global management activities have exacerbated social problems. These ideas, which demonstrate hostility toward multinational activities in Europe and North America, have wreaked devastation in some regions. Recognizing that offering net-efficiency gains alone will not ensure efficient operations across international borders is crucial. To implement methods that value both, international sales managers must acknowledge that their employment entails advantages and limitations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, businesses that want to penetrate foreign markets must create divisions supporting international sales. These kinds of companies have the potential to produce profits through increased levels of net efficiency, which would be to the advantage of their clients, workers, supervisors, and executives, as well as national governments and international organizations. The Department of Foreign Sales growth needs to be planned, with the first step being to collect information on the investment areas. This expertise is necessary to apply corporate processes correctly to maximize efficiency.
When developing new international sales divisions, it is critical to carefully consider how the whole firm will break into new international markets. These entry choices guarantee that an awareness of the potential for success and the accomplishment of the long-term goals of these institutions is maintained. In addition, sales managers should make marketing and any other relevant field tactics an integral part of their day-to-day operations. The benefits these combinations provide to teams responsible for sales management are expanding.
To understand the goods, pricing, promotions, and the places for selling their commodities overseas, a foreign sales department, for example, may find it helpful to apply marketing tactics based on the marketing mix model. When developing a global sales department, it is essential to prioritize integration methods and consider the existing organizational cultures, hierarchies, and structures. It is possible that the strategic management of diversity, which ensures that all stakeholders have equitable access to resources, will also help to strengthen this integration. If these evidence-based techniques were executed effectively, a foreign sales department would thrive; nevertheless, if this did not occur, it would be negative to the firm.
References
Eduardsen, J., Marinova, S. T., González-Loureiro, M., & Vlačić, B. (2022). Business group affiliation and SMEs’ international sales intensity and diversification: A multi-country study. International Business Review, 31(5), 101989. Web.
Naeher, D., & Narayanan, R. (2020). Untapped regional integration potential: A global frontier analysis. The Journal of International Trade & Economic Development, 29(6), 722-747. Web.
Rodríguez-Pose, A., & Von Berlepsch, V. (2018). Does population diversity matter for economic development in the very long term? Historic migration, diversity and County wealth in the US. European Journal of Population, 35(5), 873-911. Web.
Verbeke, A., Coeurderoy, R., & Matt, T. (2018). The future of international business research on corporate globalization that never was….Journal of International Business Studies, 49(9), 1101-1112. Web.