Introduction
The University of BuProMan celebrated its centennial recently, and it has faculties such as Medicine, Arts, Engineering, and Management. The University has an excellent reputation and has always emerged top in the state according to university rankings. BuProMan University has had a tremendous and successful path as an organization, producing great people in the society including a Nobel Peace Prize winner in medicine, a highly competitive field. The recent university rankings rated BuProMan is at number four, and this has given the management, alumni, and even the current scholars a hard time. As a result of the University’s latest ranking, the number of students registering with the University for different courses, and enrollment numbers have reduced significantly. The university has also tried calling students for classes, but few are turning up, while many are opting to go to better high-ranking institutions. The main reason being everybody wants to be associated with success, and this means parents and students will prefer the top-rated universities for better reputation, gain, and education.
To salvage the BuProMan situation, the University under a new Chancellor has decided to take on their dreams of expanding overseas through offering online double degrees for postgraduates, an activity that will reward the university financially. The poor performance comes from poor marketing strategy to potential markets because students of high-caliber do not attend any university but that which is widely known and respected. The University under the new leadership of John Steward has already organized fundraising with alumni and large benefactors and promised that the institution should regain its position and its past glory.
The management of BuProMan’s processes is entirely manual thus causing difficulties in the retrieval of data and control of systems. Data errors such as double-entry of information and other inconsistencies have happened because of manual data entry. The organization under John Steward shall have reshuffled some employees and given them new roles as the old ones set new targets for the next three years. To help the institution achieve its new vision, they should introduce the BPM (Business Process Management) whose strategy should have futuristic goals. The plan should have a timeline through which the organization operates. In this case, the chancellor requires four years to provide a report to the stakeholders who took part in a fundraiser. The essential components of the organization include leadership; people change management and BPM project management without which the entire BPM activity should build on. The BPM project does not indicate that accountability is crucial, but the whole management endeavor requires responsibility.
The 7FE Framework
Organization leaders need to come up with an appropriate environment and high-level guidelines on how to execute the strategy of the organization. Alignment is one of the critical structures that a manager needs for achievement from the topmost to the lowest of the body as they allow the business strategy to lead them. The approach of an organization first requires the management to set rules that will govern the organization, known as the Business Operating Model (BOM) Dumas et al., 2018). The executed BOM needs further creation and development of business capabilities that drive the production of the components. The BOM however, contains the unspoken rules and codes of the organization; therefore, it is intrinsic to the way the University operates (Jeston, 2014). The BOM operates under the power of the business capabilities and components such as Processes, People, and Technology.
The people component carries human resource policies, roles and responsibilities, organizational structure, and reward structures. The process component needs several capabilities, frameworks, and governance including process groups and models, process assets, high-level value chains, and architectural framework. The BOM operates and drives the component of technology. Organizations need to implement a BPM project management system though it should stand on the three elements mentioned above. Without people, technology, and processes, the BPM strategy shall fail (Jeston, 2014). According to the 7FE approach, the BPM begins its operations after undergoing ten phases enveloped by three major essential components which include leadership, management change by the people, and BPM project management.
Mapping the 7FE Framework
The University of BuProMan requires a significant shift in its operations to regain its lost glory. This section shall use the Business Process Management (BPM) fundamentals majoring on the FE7 framework topics. The university requires a strategy that will address its current woes which including dropping its university rankings position and consequentially dropping the number of students willing to take courses in the university (Von Rosing, Zachman, & Scheel, 2018). The finances have as a result dropped significantly thus making it difficult for the organization to drive its agenda. The number one strategy that the university’s management shall implement is spreading it to other nations through an online degree platform for postgraduates. The framework consists of ten phases including foundations, enablement, launch pads, understanding, and innovation.
Under foundations, the university through its new management has established a solid base for launching the BPM activities (Vom Brocke & Mendling, 2018). The new chancellor, John Steward, has appointed people into leadership and given a time-work frame of three years to ensure everything runs usually. Through the appointed leaders, a working framework for the university shall save the situation and devise new ways of doing business. Other than implementing online programs, the university should investigate their marketing structures because lately, the university has failed in this area. The development of various strategies and working frameworks should bring fulfillment to the systems of management.
Foundation Phase
Upon taking the case of BuProMan University and after conducting the discovery meetings, some essential information on the University’s Vision, high-level value chain, the maturity level of the University’s Business Process Management, and other information of critical stakeholders was obtained from a series of discussion or the “Red Wine Test.” It is understood that BuProMan’s Chancellor Mr. John Steward has envisioned a new strategy for the University. The new vision is to make BuProMan the leading University in the State. The new strategy has rolled out some Strategic Objectives—or SOs (Jeston, 2014) and can be detailed as follows:
- SO1: Academic and Research Profile Improvement—through quality research publications and delivery of academic modules by leaders in the specialization.
- SO2: Partnership and Collaboration—with crucial Organizations across the States through joint research, internships, and guest lecturers.
- SO3: Regional and International Academic Outreach—through online postgraduate programs, expansion in Asia, the inclusion of inter-state high schools.
- SO4: Internal Operational Performance Improvement—by effectively observing Academic and Outreach results efficiently through the new Financial and Administrative solutions.
The new strategy and its’ SOs suggest that the University will drive a “Strategy-Led” project, consequently, it is “Critical” to start with the 7FE’s foundation and enablement phases and “Use” and perform all the steps in the LaunchPad phase to successfully roll out BuProMan’s BMP Project (Jeston, 2014).
For BuProMan’s BPM project to be a success, the business outcomes to be agreed upon from the stakeholders, who are required to ensure their dedication and allocate the time to initiate the BPM initiative, as well as to demonstrate their commitment to the whole University community. BuProMan’s BPM will require a Target Operating Model to ensure an ideal methodology of process operations in the University. To have a first start with the TOM, a workshop was planned to gather further information and data from the stakeholders. Despite the explicit instruction of this BPM requiring dedication and time from stakeholders, many of them could not join due to their busy schedules. This lack of dedication from the stakeholders is posing a risk to the foundation phase of BuProMan’s BPM project. Therefore, moving forward with this phase is put on hold, and the following risk mitigation measures have been put in place to guarantee appropriate BPM foundations are established:
- A high-level meeting with the University’s Chancellor discussing the risk and its effect on the establishment and progress of the initial stages of the project. A reminder of the promise given to external stakeholders, alumni, and fundraisers on the new Vision.
- Support the Chancellor with his communication strategy to buy-in the stakeholders and win their full commitment and time-dedication to BuProMan’s BPM Project.
The critical information obtained through face-to-face segregated meetings and interviews with vital university stakeholders has led to an understanding of the University’s organizational environment as well as the type and approach of BuProMan’s BPM project which our consultancy agency will be initiated in this Organization. Due to the University’s low level of process maturity, indicating a limited and challenging experience in university-wide and multi-faculty BPM initiatives (Jeston, 2014), and the form the separate meetings held with key personnel, the characteristics of the BuProMan’s BPM project were identified in Table 1 as follows:
Table 1: BPM Project Characteristic for the University of BuProMan.
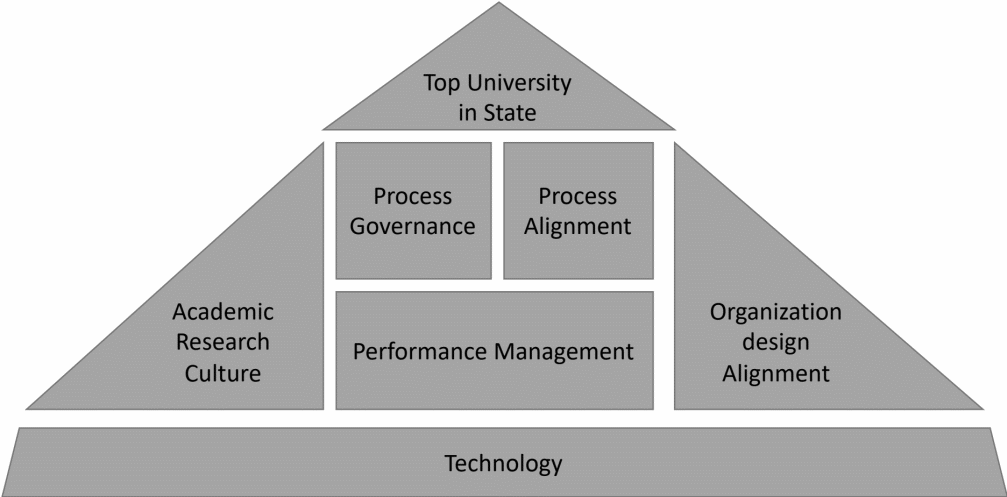
The Target Operating Model (TOM) for the University of BuProMan will set a high-level roadmap for the university’s future business operating model. Jetson (2014) has explained the core components of the TOM in a pyramid figure to ensure alignment and result achievement of BuProMan’s new strategy. Using the University’s BPM scenario characteristics and project approach, Jetson’s TOM pyramid can be adopted for the BuProMan University shown in figure 1. The suggested TOM for this initiative is creating the desired operations to transform BuProMan as a top-ranking university in the State. It is vital to ensure this TOM is communicated, explained, and understood by the Chancellor and University’s key stakeholders. The TOM explains how each of the Strategic objectives will be achieved through the existing value chain. The components considered for the University’s BPM initiative this includes process alignment with the new strategy, Processes governance, Performance management, Organization alignment, Academic & Research Culture, and technology.
The Chancellor, John Steward, shall announce this TOM the whole university emphasizing how this new process improvement initiative will affect current faculty staff. A press conference might be an effective medium to inform the fundraisers and prospective stakeholders on the new vision and strategy of John Steward the Chancellor of BuProMan University.
Enablement Phase
The proposed TOM for BuProman’s BPM is inspired by the below high-level value chain obtained during the first workshop with the key stakeholders.
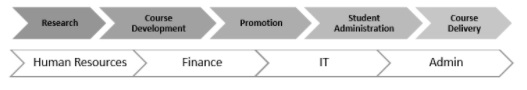
The second series of workshops conducted by Chancellor John Steward and the Operations Manager Pete Ant, to obtain further input and information on current operating practices and processes. This has led to an update to the original high-level value chain obtained from the first workshop and development of BuProMan’s Organizational Process Diagram. The updated high-level value chain is represented in Figure 3, with a second level value chain explained in Figure 4.
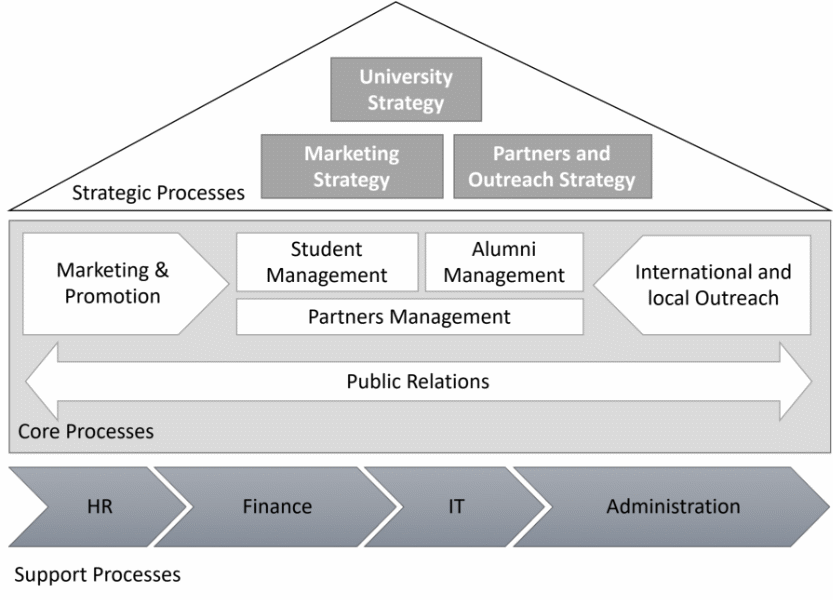
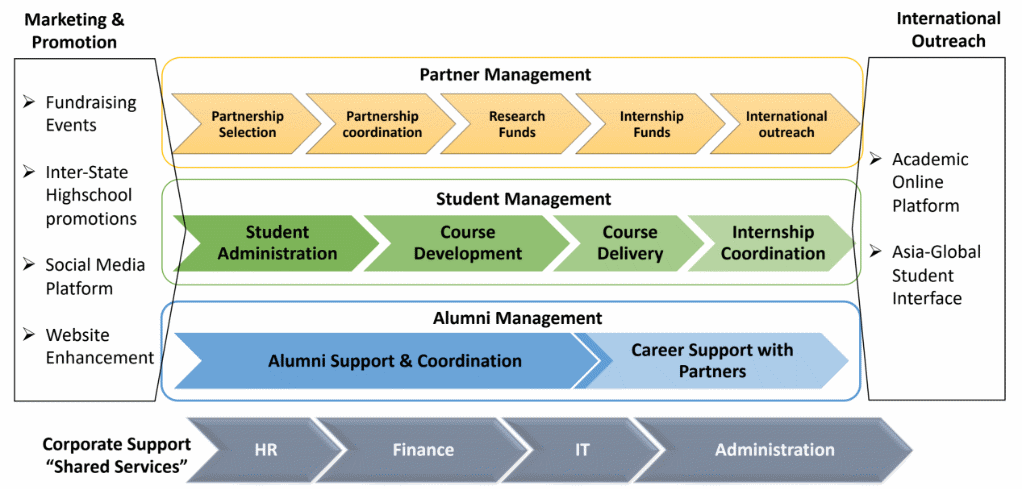
Referring to the figure 1—BuProman’s TOM, further dimensions can be further explained as follows: a) Process governance of the updated process framework for BuProMan University’s BPM will require management through identifying accountabilities, assigning responsibilities, and key performance indicators. Since BuProMan’s BPM program is a large-scale BPM, the Chancellor Mr. John Steward is the Project sponsor and ultimately accountable person for the success of the BuProMan BPM initiative, and since the process maturity is low. Pete Ant, the Operation Manager, will be accountable for and responsible for appointing appropriate Process Stewards of each of the Level 1 processes. Process owners and managers will be consulted in the case of change occurrences in the process. This division of roles and responsibilities will be taken into account in the performance review and management. To achieve an optimum level of accountability for process owners, BuProMan’s Chancellor will need to lead by example and determine the level of accountability he desires to observe from process owners and managers. Training and coaching of the process managers will be injected into their schedules to ensure proper process and consequently performance management.
Standardization and integration of the University’s business processes are required, and the level of standardization and integration will differ, using the figure of Business Capabilities delivered by a process developed by Ross et al. (2006) as cited in Jetson (2014), depending on the following university processes:
- Student Administration Process—this process requires full standardization for local and global students with a single interface for all students applying to BuProMan University. The standardization level is high, and the level of business integration is high. Thus, making the Student Administration process fall under the “Unification” category.
- Partner Processes—will be categorized as “Diversification” where there is a low level of process integration between BuProMan University and their current and potential Partners, and a low level of standardization considering the University and their Partners will have their unique business units.
- Research Processes—these processes will have a high integration level, but a low standardization where there is a need for a shared IT system to share and publish information, thus categorizing research processes as “Coordination.”
Launch-pad Phase
The lunch Pad phase is the how-to phase where BPM activities are identified, and project plans are initiated after extensive study for engaged stakeholder expectations and matching it with planned outcomes for PBM projects. For lunch, Pad is considered a critical stage that cannot be ignored in any BPM activity from strategy led BPM program to a small project. It forms the bassline for all initiated BPM projects within the organization. It consists of several steps that are required to guide the organization in determining the what efforts required, where and how to start BPM activities, and who will be involved to ensure its execution success and gain expected benefits (Jeston 2018)
As a result, from Lunch Pad activities, BPM scope, and goals will be identified; the project structure will be set up, and the team will be selected. Stakeholder engagement and expectation will have recorded, and high-level business processes and are analyzed and prioritized in the form of process selection and worth matrix. Lastly, a business case and project charter with a draft activities plan will be developed and documented besides the initial communication strategy.
The lunch Pad phase starts with initial interviews with key stakeholders of the University of BuProMan such as students, faculties, investors, partners, and heads of business units and their employees. The level of their engagement and expectations are identified and documented (Jeston 2018).
In the same manner, to understand business as-is, interviews with critical processes personals in each business unit to have an overview of an end to end business processes and understand how different business units’ interact with each other to identify similarities and differences.
For example, as each faculty in the university has its processes and business administration system, it is essential to interview each faculty head to understand how in processes are performed and interact with other faculties business processes to identify the bottlenecks and issues that affect its efficiency and effectiveness.
After collecting the required information through interview steps, BPM program leader ” Pete Ant,” senior management and business unit heads (see Figure 5: organization structure Chart) have to meet in one to two Executive Workshops. The purpose of this step is to discuss more defining the BPM activity scope and process goals, agree on the activity success checklist, identify and categorize stakeholders, list and analyze end to end and individual business process, agree on the implementation plan and defining processes governance ( roles and responsibilities ) and initiate a business case and draft project plan.
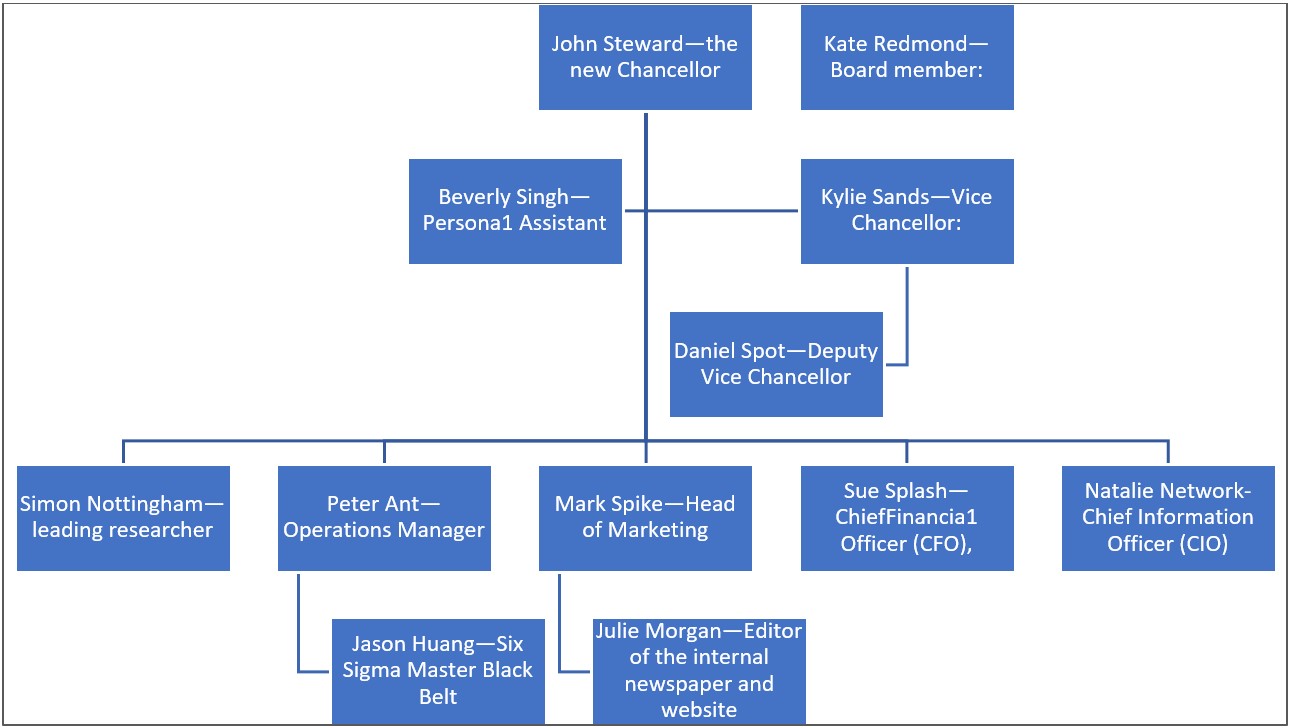
Seven people roles will be invited to the Executive Workshop are
Table 2: People roles.
Expected six outcomes to achieve from the workshop are
- Define BPM activity scope and process goals
- Stakeholder identification and categorization
- Process Selection and Worth Matrix
- Agreement on Success checklist
- An implementation plan with process governance for processes in the activity.
- Business case & Project Charter.
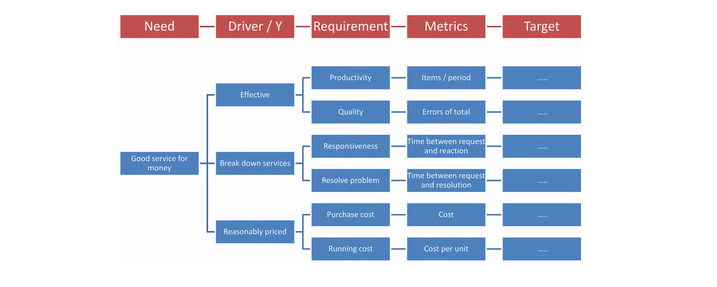
One of the deliverables that will be used in the understanding phase is the Process selection and worth matrix. University Executives can use Process Worth Matrix technique to categorize business processes based on its business value. So it will help them and help to identify the processes that should invest in and improve to generate the intended profit.
According to the table (1), Value chain processes are classified as per their importance to the University from a value /cost perspective
Table 3: Process Worth Matrix.
As shown above, student administration, promotion, research, and course delivery are classified as Identity processes that define the university identity and differentiate it from its competitors. Value chain core processes that include Student Administration and Promotion processes are considered asset processes as they support in creating economic value and profit for the university. While, Research and Course delivery are considered liability processes as required high investments and resource allocation from the university however the outcomes generate low economic values, but both processes play a vital role in differentiating the University in the market.
On the other hand, Course development processes that support course delivery processes are categorized as priority process but consume a lot of resources (financial and people) comparing to generated value.
Support processes that include HR, IT, Finance and Admin processes are considered Background and Mandated process that supports the daily activities of university operations but not visible to customers is essential to run the business but the value generated is less than resources and costs spent, they are classified as liability processes that management can outsource to reduce operation costs.
Once the Executives complete business processes analysis during the workshops; processes that create value for the University have been prioritized and selected for improvement and redesign. Executives have to develop a Business case to identify the business benefits that the University will gain by investing in process improvement projects.
Defined business Benefits of process improvement projects and activities should be measurable. So selected metrics can deliver quantifiable value
Accordingly, the intended business benefits that University Canceller would achieve by implementing the BPM program can use qualitative and quantitative measures. However, selected measures should be aligned to the business strategies such as improving operation by reducing costs through purchasing Student and Financial management solutions. So Cost of operation is considered the quantitative metric that identifies if the operation is already improved or not if the solution is purchased and implemented. Similarly, the student satisfaction rate is considered a qualitative metric that assesses if the student administration solution can fulfill student requirements and speed up admission processes.
Consequently, Processes high-level metrics that can be useful to measure expected benefits and manage improvement activities performance can comprise the following indicators
Table 4: Processes high-level metrics.
Understand Phase
The rationale for the Understand Phase
The understanding phase is necessitated by the four fundamental reasons surrounding the BPM processes, purpose, value, and change management strategy. For instance, about the BuProMan’s proposed BPM, it would be prudent for the activity team members to capture sufficient knowledge of the present business processes at the University. The team should also be in a position to carry out a comprehensive comparative analysis of the metrics of the new processes in the proposed BPM (Jeston 2018). This will enable the activity team to deliver the business value while clarifying the project functionality.
The understanding phase is also significant in baselining the skills needed to effectively execute the proposed current processes against future modifications for training purposes. Lastly, it is prudent to master the understanding phase to commence the personnel change management initiative (Gordon 2013). This means that the understanding phase is vital towards validating the current process reality within the BuProMan University to define the priorities for improvement as guided by the project scope. The understand phase ends at the point where all the stakeholders are made aware of the process involved in the BPM after which these activities are appropriately documented. However, for each process model, it is essential to building an agreement in the documentation for optimal project acceptance (Jeston 2018).
Projected Results of the Understand Phase
The primary results for a well-executed understand phase include documentation of the process models related to the current BPM processes and the development of enough metrics for establishing the activity baseline aimed at facilitating any future improvement measures. Other results are documentation of successes that are transitioned into the innovative phase, challenges, and missed opportunities (Kiran 2016). It is necessary to identify the quick wins that are implementable over a few weeks. The understand phase will be executed through building sustainable and acceptable consensus among the stakeholders of the BuProMan University to know what goes on through an integrated documentation process for reflecting the actual situation.
The process will be balanced to guarantee truthful reporting from point A to point Z of the current activities (Jeston 2018). Moreover, it is vital to understand the current risks facing the BuProMan to ensure that the process of stakeholder engagement is smooth and inclusive. Individually, using preset metrics would balance the group dynamics and create a systematic process for ensuring that the staff members of the BuProMan embrace the workshops. The understanding phase for the university will be set over a specific period of 6 months with specific milestones to be achieved. The milestones and timing will be tracked using the Pareto principle to gauge the success of the phase against the present point of diminishing returns (Jeston 2018).
Modeling the Understand Phase
The process modeling within the understand phase is significant in gaining consensus, demonstrating any shortcomings, supporting acceptance, allowing evaluation, and creating a baseline for managing inter- and intrapersonal relationships among the team. To effectively implement the understand phase for the proposed BPM management at BuProMan University, the steps to be completed include communications, scope revalidation, understanding workshops, complete metrics analysis, root-cause analysis, complete people capability matrix, identification of available information, process worth matrix, highlighting innovative priorities, focus on quick wins, and understanding phase report (Jeston 2018).
The communication activities will involve providing information to all stakeholders within the BuProMan University about the proposed BPM, its objectives, and their involvement. This will be achieved by creating a consultative, warm, and holistic atmosphere for ease of building consensus. At this point, the communication initiatives will be fully integrated into the BPM activity by balancing consistency and efficiency in passing information (Kiran 2016). The second step will involve the revalidating of the scope of the BPM activity on a continuous and systematic basis by leveraging the primary documents on process worth matrix and process selection matrix. The modeling will capture the interests of the various stakeholder groups such as students, teaching staff, and non-teaching employees among others. This step will enable BuProMan to understand the end-to-end processes for the useful, innovative outcome (Jeston 2018).
The third step is to ‘understand workshops’ to grasp the necessity of this phase. About the BuProMan University BPM activity, this step will create an inclusive environment for learning the current processes from the perspectives of success, stakeholder participation, and metrics guiding potential priorities and quantifiable benefits. The workshops will be scheduled conveniently and in time followed by the framing of the participants against set expectations. The workshops will be conducted in a controlled and structured manner to streamline attendees and agenda for active end-to-end processes (Jeston 2018). The fourth step will involve completing the metrics analyzing from the perspective of the targeted customers. These metrics form the standard for measuring the performance in any given process. Moreover, it facilitates the production of an analytical reflection of BuProMan University by allowing for benchmarking of any available process data such as volumes, task times, and cost implications against other similar campuses.
The process selection matrix will also be used to estimate the staffing levels, BuProMan sales volumes, and cost implications after which a specific process level will determine the measures for each processing time. For instance, the KPI and SLA would authenticate the measures against any bottleneck (Jeston 2018). These metrics will be measured at organizational and management levels from the workshops and periodic surveys. As captured in figure 6, the voice of the customer will be measured through qualitative and quantitative data available from BuProMan University to obtain measurable and tangible results.
Since BuProMan University is a complex organization, the understand phase will also involve a comprehensive root-cause analysis for potentially non-performing processes. This approach is critical in understanding errors and their sources, the accuracy of information being received, and the capacity of the university to meet the desired standards. Through the use of the Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA), it will be possible to establish the process reference, failure mode, cause, failure effect, residual risk, and severity on the total score (Jeston 2018). This will be followed by People Capability Matrix to gain useful information on the future and current environment. In performing the People Capability Matrix, it will be essential to examine the current capacity as a function of future needs at the organizational level to identify the high levels for reviewing competency enhancement requirements (Daft & Marcic 2016).
During the identification of available information step, a process selection matrix will be developed for the BuProMan University as part of the BPM activity. As captured in figure 7, information identification will be made via the workshops, human resource archives, and interaction with different stakeholders (Jeston 2018).
The primary documentation that will be gathered includes IT architecture, annual strategic plans, system interface, communication landscape, and management strategies. After gathering the relevant information, it will be necessary to revisit the process worth matrix to overlay the metrics of the understanding phase effectively. As captured in figure 7, the identification of innovating priorities would determine if a process should be improved, abandoned, innovated, or outsourced by prioritizing the processes (Jeston 2018).
The quick wins will then be identified via workshops to validate any feasibility of the proposed BPM activity. After validating the implementation, considerations will be given to creating a sub-project team tasked with the duty of implementing the quick wins. The understanding phase will end by reviewing the process report regarding findings for the current processes, metrics, identified quick wins, and potential risks against mitigation strategies (Jeston 2018).
Innovate Phase
Rationale and Projected Results for the Innovate Phase
This phase will present an ideal opportunity for the quantification of benefits associated with the proposed BPM plan. To effectively maneuver the dynamics within this phase, a series of documentation will be generated and integrated to foster creativity and complete commitment. These documents are aimed at redesigning the process models, clarifying any high-business need, and simulation of activity-based details of costs. Moreover, the innovative phase will address the capacity planning, review of alternatives against stakeholder expectations, and capturing the process gap report (Jeston 2018).
Since this phase integrates the people’s value in implementation, the plan will schedule the personal development needs and present a detailed cost-benefit analysis of the BuProMan University BPM activity. The plan will frequently be updated on a need basis to quantify the costs and benefits from the assessment of the project’s impacts, regarding intangible and tangible gains. Also, this phase will outline the steps to be taken, alternatives considered, comprehensive analysis, results, and recommendations. Since BuProMan University is a complex organization, the innovative phase will be accompanied by a presentation to the management on the proposals and direction to be taken to turn the campus around. This will be realized through the development of an improved communication plan from the understanding phase targeting all the stakeholders (Jeston 2018).
As a strategy for countering the common misconceptions about innovation, this phase will be developed through the integration of workshops in each process. Each workshop will be structured differently through upfront planning. Individually, each training session will internalize the process being adjusted until it is completed using the end-to-end meter. Since BuProMan University has many departments, the workshops will be organized by crossing the departmental boundaries for effective integration (Jeston 2018). Moreover, the innovative workshops will be created in a way that they are not limited by BuProMan University’s current organizational structure. The process will be flexible, expansive, and inclusive to guarantee stakeholder support.
As part of the critical thinking strategies, the proposed innovate phase for the university will involve aligning the perceptions of the stakeholders into the right-thinking frame for active involvement, implementing the innovative or creative activities through the engagement of the current employees, and determining and preparing the course of action against solutions proposed (Jeston 2018). These suggestions will be executed through a streamlined approach and subdivided into another phase for ease of control. As captured in figure 9, to make the innovate phase relevant to BuProMan University’s BPM activity, the process will include an innovative progress redesign matrix for tracking potential opportunities tied to different innovative alternatives.
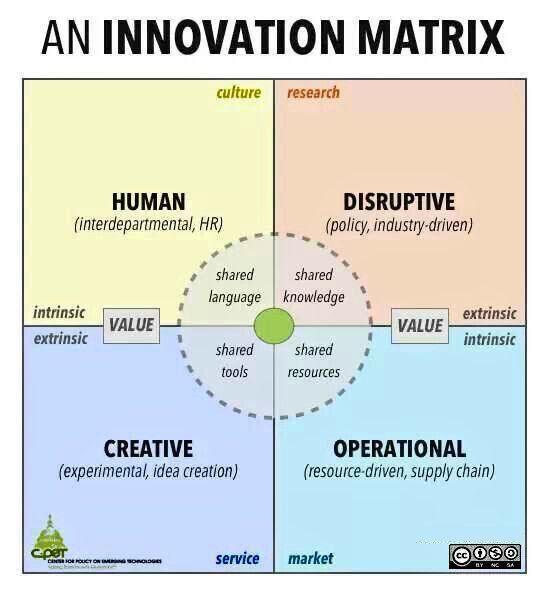
The opportunity redesign matrix will be laden with a stable process innovation process that balances the way transactions are processed and the conventional structure of the university. Just like any other higher education learning institution, BuProMan University is a vertical organization organized into departments with work that is processed horizontally. Therefore, an improvement will involve the introduction of end-to-end process modeling to provide extensive opportunities for process improvement.
Before implementing the workshops, it will be necessary to understand the required innovation and the best strategy for internalizing the needs of stakeholders. As a result, the innovative processes will achieve high useful service and satisfaction levels. Therefore, ideal process management should be controlled using the end-to-end perspective to interface areas of the activity that are deemed to have significant improvement opportunities (Jeston 2018). The proposed project innovative phase will attempt to balance the impacts of different levels of customer satisfaction through improved service excellence. For instance, through optimizing the zone of margin effect, it will be possible to avoid the irritation level by creating a line of absolute indifference that transition towards the wow zone (Daft & Marcic 2016).
It is the process that will matter in executing the innovate phase through understanding the variations between customer satisfaction and excellent service. For instance, a wow factor could be quickly eroded by consistent poor service charter. Thus, the hygiene factors will be adequately taken care of before integrating the wow factors in the effectiveness charter. For instance, this phase will be modeled around the elimination of irrational factors to improve customer satisfaction and higher service levels. Therefore, the innovative phase will be accompanied by a series of research activities to facilitate the direction and appropriateness of the proposed BPM activity at BuProMan University.
Modeling the Innovate Phase
As captured in figure 10, the innovate phase of the proposed BPM activity at the BuProMan University will consist of 18 stages: communication, executive kick-off workshop, update innovation approach, external stakeholder focus groups, internal mobilization, robotics process automation, prepare for innovation workshops, innovate workshops, future process metrics projections, simulation, update people capability matrix and capacity planning, workshop proposed solutions, demonstrate and validate feasibility proposed solutions, process gap analysis, identify benefits and update business case, report and presentations, approvals, and business requirements (Jeston 2018).
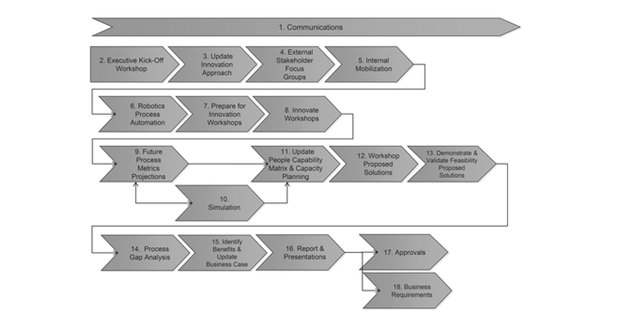
The communication stage will involve informing stakeholders about the scope, options, and status of the BPM activity. This stage will integrate the input of the stakeholders to gain an understanding of the choices and objectives of the activity. The executive kick-off workshop stage will be integral towards knowing the goals associated with the proposed BPM activity for the BuProMan University regarding timeframes, strategy, planning, constraints, successes, and process optimization among others. The third step will involve updating the innovation approach by reviewing the present BPM plan against standards for the right personnel in the workshops (Jeston 2018). The updates are necessary for tracking different scenarios associated with implementing a complex project such as the proposed plan. The next step will be gathering and establishing consensus among the external stakeholder focus groups to capture their insights in the workshops. The fifth step will be the internal mobilization of innovative ideas by focusing on quality instead of quantity of the suggestions. This process will be implemented through a competitive approach to collecting surveys, outcomes, and previous activities.
The robotics process automation (RPA) will be incorporated through the use of consistent, repetitive rules, unambiguous roles, and strategic decision-making. For the proposed BuProMan University’s BPM activity to be productive, the RPA will be part of the IT-aided section of the system (Jeston 2018). As a result, the innovative phase will be characterized by reduced cost, improved quality, and consistency with the compliance needs of the university. Preparing the innovative workshops and their implementation will be performed by the expected outcome. Since the plan intends to improve on the quality of education, future process metrics projections will be used to understand the operations costs, and additional opportunities or benefits of the project (Battor & Battour 2013).
The simulation stage will be performed to determine the efficiency and feasibility of the proposed adjusted process options. Through a detailed metrics analysis, it will be possible to quantify the potential budget. Among the workshop, proposed solutions will include an update of the people capability matrix, process gap analysis, and demonstration of the proposed solutions’ feasibility (Jeston 2018). The benefits will then be identified and reported to the stakeholders, and their approvals will transform the proposal into a viable project. The business requirements such as realized value and output will provide the matrix for measuring success or any need for further adjustments.
People Phase
Most of the time organizations blame the lack of performance on their people. However, it may have a multi-approach that affect the processes. BuProMan University’s BPM framework for the people phase will approach the processes, structure, and people to have its improvement program. By the processes of the workflow, it meant to examine whether the process is adding value to the organization and it is efficient and effective. Moreover, the structure is to check that the processes structure is right or near to the right roles and structure to processes. After the employees get to know and train to the new processes and the roles and responsibilities (new structure), it will go down to the people phase, and a person’s performance can evaluate it.
The detailed steps of the people phase proposed to BuProMan University consist of 8 steps that describe the impact of the BPM approach with the external culture activity; which started with communications which are noted as the primary step to achieve the best outcomes by involving the people of the university. The Communications step will start and will continue until the end of the people phase in parallel with the developing phase.
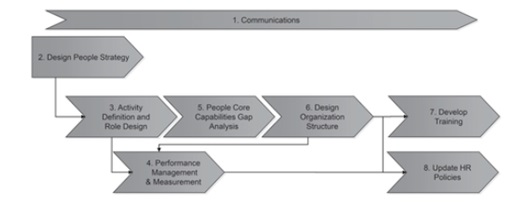
Starting with the second step of design people strategy, BuProMan University HR department should be involved in this step. The team of BMP Project for BuProMan University and the HR will start structuring the people’s responsibilities and roles after the finished the understanding and innovative phases which described the current working scenarios and the estimated scenarios for the future. This step will engage the staff of the university and will include learning and development. Also, it will guidelines the structure of the organization of the hierarchy levels and team sizes. Which will present the leadership and management of the university and the resources of role to be fulfilled by employees or contractors. Also, the design people strategy should have a place for rewording and recognition, and the policies of recruitment and retrenchment.
By agreeing on the designed strategy of people it should be undertaken by the BPM activity, after that, it should be appropriately documented and signed off by all stakeholders. The stakeholders are the people themselves in this case faculties, students, it may concede the suppliers and the leadership and management.
Step 3 is designing the role of activity, and it is the definition of a process that can be a multiple or collection of tasks. Which will be presented as a hierarchy job activity and structure creation. By placing the process which consists of a group of tasks in the bottom linking it with the activity definition which some tasks can be shared between two or more activities. Then it should be gone under the role and job of the people who are part of a workgroup as shown below in the figure.
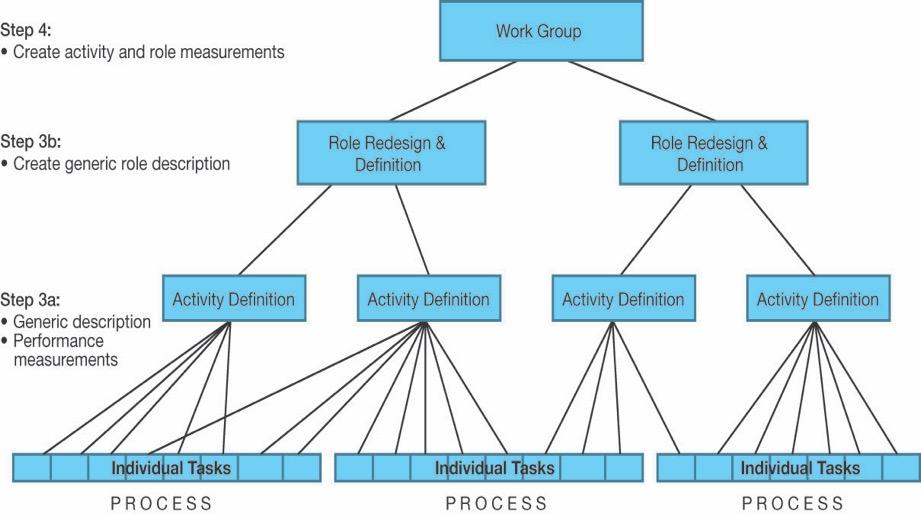
By describing the critical roles of an on-boarding student and required skills we propose, step 4 which is a must in every phase of the BPM project from the very beginning. Performance management and measurement, after declaring the processes it should be apparent to everyone within the university their role, and it will be measured. In the understand phase the project is measuring the current process while in the innovate phase it targeting the future process performance for this phase of people it is positioning the performance measures. It should be updating the HR policy when the design is ready.
While stabilizing and designing the tasks, process, roles, and responsibilities there may be a gap between the roles and the responsible students, in other words, the skills required for the redesigned processes from the innovate phase required training and adopting of new processes which are a necessary action to analyze the students’ capabilities gap. The recommended training will be using Microsoft office programs to deal with all files and emails coming through outlook and word documents attached. Moreover, training on the system that will be developed to register and admission from the contractor himself.
By recognizing and structuring all the possible people’s processes the development needed will be discussed in the developing phase. People and innovative phases are impaling the core processes to start the next phases to develop, implement, realize the value, and sustainable performance.
Develop Phase
After all, preparation was made in all previous phases to perform the BPM project by the BPM activity team. It is the time to produce the solution prepared which placed the development phase in parallel with the people phase. New system development requires care and sufficient flexibility that can adopt any near future change by meeting business change.
As we are in the developing phase, we have a full picture of a redesigned project that has been developed with the BPM activity team. As most of the phases start with communications the development phase. There are two possible proposed ways to develop a BPM solution which are the traditional way of software development life cycle (SDLC) which is also known as a waterfall or Rapid Application Development (RAD) which is known as iterative and agile. As for BuProMan University, the team proposed that it is an agile way of development. Because of the short time provided for three months and possible to correct things as we move on. Also, it helps by giving priorities and change them along with the go of BPM activity, which releases the small scope and guides the people to concentrate. As is known, it is a university with low income so if the BPM activity terminated it will save the highest value and will support in case of budget cuts. The three recommended IT components are:
- The reliability of the system
- Students are applying to the university but don’t get admission
- University providing wrong data
- Conflict-free
- Ask for data entry multiple times
- Don’t take-up the student offer
- Security check
- There should be a secure channel to apply for university
- The university is dealing with fees and online payment.
Implement Phase
As a BPM project team, it seems that the system approach is business issue-led. It driven by operational or business issues such as wrong submit of the admission form. Also, it is a combination implementation as there is no IT system changes and no time for that which is used to enroll new students. The period is also three to four months which makes it so hard to start from zero or to try something new. There are one or more fully informed and undoubtedly committed to implant the BPM within the university. That is online to use in the case of the system to be on for users. After sometimes the implementation will be used proposed change until it reaches the business as usual.
A combination of the relay, parallel, and big bang will be the implementation scenario. That provides roll-out to a specific situation that helps the university to provide an inflexible and manageable way. The risks that will challenge the proposed changes are the lack of communication which is rational or chaotic. It is helpful for a small project which is needed to have a testing plan and after that to enlarge the process shortly.
The traditional way to communicate with the stockholder in the university was an announcement through the system portal that was used by faculties for the students. The communication with stakeholders will be as training in the classroom that will accommodate a large number of people in one session. Moreover, it helps in grouping them up and perfume teamwork assignments and Appling change management activities. It may have a disadvantage of expensiveness. However, the location is available as we are in the university, and the trainers are the two managers that have a full picture to adopt BPM which will reduce the cost of the training.
The pilot and the complete business test can overcome the risks of implementing the proposed system. To mitigate risks, the BPM project team proposed the following essential to minimize the risks:
- Involves students and suppliers
- Give the testing steps its time and period with strong management
- Easy to use the feedback system
- Obtains testimonials form faculties, students, and suppliers.
- Celebrates success and reward the team.
Ensuring that the old processes vanished and roll-out the new processes effectively. Moreover, a mechanism to continue improving and mentoring. Also, there should be a handover in case of leaving the organization someone should take over the BPM team.
Realize Value
Realizing the value of the University of BuProMan is a progressive business process (Jeston, 2014). Figure 14 shows the realize value phases. Each of the steps should be executed effectively and efficiently. In step 1, the University of BuProMan requires active communication channels and processes throughout the BPM activities, so all realize value phases benefit, and it can be achieved.
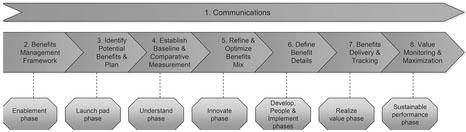
The enablement phase can be achieved with standards and templates from the benefits management framework. The University of BuProMan identifies various benefits so the relationship can be created with the organizational strategy. These benefits are measured and defined with specific responsibilities, roles, and ownership, planning procedures, guidelines, and creation of benefits register. Potential benefits registered planned and identified so the launchpad phase can be achieved.
The University of BuProMan analyzes business processes while confirming with BPM activity progresses. Once the benefits plan is done, then it can be achieved. BPM activity shall deliver the benefits, and they should be monitored and updated. The achievements made measured and reported with a comparison of the University of BuProMan case. Throughout the BPM activity, the benefits register must be updated continuously and continuously with all the new information and insights (Trkman, 2010). In the understand phase, it is to establish baseline and measurement of the comparison made and should be aligned with the University of BuProMan. The techniques for baseline measurement should be agreed with all the University of BuProMan levels. All changes and improvements should be captured every month with a comparative assessment to analyze changes in costs and expenses.
The innovative phase can be achieved with the processes being redesigned as per criteria with an estimation of processing efficiency, processes calculations, and new redesigning with an executive workshop. The benefits confirmation is depending on the original baseline measures for validity and accuracy. They are updated with the latest costs and expenses that the University of BuProMan experiences.
In the people, develop and implementation phase, the marketing plan should be done and enforced with the integration of academic services improvement and development. The people should get the opportunities to develop knowledge, skills, and abilities so new strategic objectives and goals of the University of BuProMan can be achieved under the leadership of John Steward and newly appointed people.
The implementation phase shall include strategies implementation with aggressive marketing of both on-campus courses and online courses with sales target for each of the marketing group with assigned geographic location. The incentives will be linked to employee performance and student enrollment. When there is a low number of student enrollment, then staff members shall earn fewer incentives. In this way, the costs will be reduced while boosting revenues from increased student enrollment. Benefits tracking and delivery are possible by monitoring the value and maximization of performance. It can be done with internal audits of checking compliance. The process of audits shall find any minor or major problems and help in the improvement of a business process with changes and developments required.
Benefit Summary Plan
Throughout the BPM activity, the benefits register must be updated with the new information. The benefits realized are for students so student enrollment can be increased for each of the semesters and made sure that there are good attendance and participation level. The benefits realized shall benefit college students, lecturers, and the University of BuProMan as a whole. The benefit amount is zero-based budget and depending on the quotation from developers for installations. Therefore, the costs are as per pricing from potential suppliers and strategic partners. By the next academic year such as March 2019, the benefits are to be rolled out, and it shall include all semesters including summer semesters as well. The majority of the benefits depend on significant stakeholders of the University of BuProMan.
There are no project activities without risks so, in BPM activities, there shall be risks as well. However, the process managers and leaders of the University of BuProMan shall make use of risk alteration strategies to minimize the adverse effects of these risks on the realized benefits. All the risks in the following table can be mitigated with reminders for the student to bring student cards for attendance and participation marks, fixation or replacement of damaged cards, and maintaining ID card reader. After data entry, all the data and information should be double-checked to reduce increased errors and mistakes. All missing information and data can be added and checked by double-checking by various employees and team members of the University of BuProMan. For all network connection errors, the IT should have a backup network connection and servers to reconnect immediately. Due to errors in the system and online, the manual system should be available for the continuation of academic activities and initiatives.
Sustainable Performance Phase
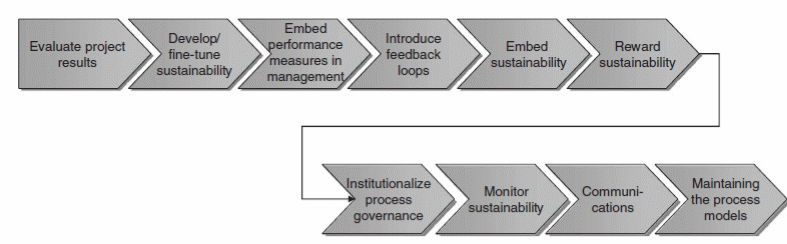
Evaluation of Project Results (New Student Enrolment)
New student enrollment can be delivered based on mechanisms and also depend on improved and managed enrollment processes. The evaluation process (see Figure 2; Jeston, 2014) comes with the development of sustainability of performance that is embedded with measurement of performance in the management of the University of BuProMan management. With the feedback loops, it becomes possible to embed sustainability and reward sustainability. Once these steps are completed, the next steps are institutionalizing process governance so sustainability can be monitored with proper communications. Accordingly, the University of BuProMan should maintain the process models for new student enrollment after the evaluation of the project results.
The evaluation of project results can be done as per statistical data on some new student enrollment for every semester and compared with the data in the past. The newer students are enrolled then; the more results are achieved. The process of new student enrollment should take 15 minutes in admission and registration that includes enrollment in each of the courses as well. All registration processes should consist of less than 20 percent errors and rework.
The new student enrollment process should be efficient and practical enough for both parents and students that they do not need to visit the registration office frequently. The process should be efficient for both the registration office, parents, and students. They should be able to share and provide all the information and details that the student requires to be enrolled such as student packet of information.
By the end of the new student enrollment process, the should conduct and compare the student satisfaction rate and compare it every semester. The satisfaction measurement rate should also include employee satisfaction measurement, and improvement should be made on a semester basis. Once satisfaction measurement is done with the comparison, the results should determine whether there is an improvement in satisfaction level or declined satisfaction rate. Depending on the results, there is a need for necessary actions to ensure the increased satisfaction of both employees and students. As per the cost-benefit analysis, there should be more benefits than costs. It is to make sure that the University of BuProMan is not going on loss and the benefits are flowing the same as expected with the achievement of more new student enrollment. The University of BuProMan should make changes and improvements in the current environment based on improvement areas identified about any shortcomings.
Process Governance: Student On-Boarding Process
Process governance is an essential and significant requirement for many business communities and organizations so they can manage, control, and report processes within their organizations (Jeston, 2014). The process of student onboarding should be transparent, and there is a need for accountability for all individual processes with the need for reporting.
The student onboarding process should be appropriately followed with the identification of any undesirable and exceptions, so the process manager of the University of BuProMan tackles those. The University of BuProMan considers many process governance points during the student onboarding process. They shall keep measuring student enrollment and onboarding process with the expected outcomes and measuring such progress with the achievements made. All lessons learned should be recorded and maintained so future projects can make use of these lessons during application and evaluation.
Managers at the University of BuProMan should divide the leadership with a delegation of responsibility so all the student onboarding process can be taken care of by admission and registered professionals. In this way, all the responsible staff members will be accountable for managing the process effectively. The most important thing for the University of BuProMan is the selection and use of governance structure without giving preferences to any specific or particular ones. It is not about the selection of conventional or fashionable governance structure but the one that helps in meeting the objectives of the University of BuProMan.
Managers should encourage and support staff members so they can do student on-boarding process correctly with appropriate measures and steps with recognition and incentives. With proper performance reviews, the process of student onboarding became more comfortable and done rightly with the right behavior. There is no need for excessive control by the management of the University of BuProMan. Therefore, there is a need for delegation of control similar to the delegation of leadership so control measures shall become a central part of the University of BuProMan working environment. The governance structure should be kept simple and straightforward and models prepared should not be too complicated and complex or else it will lead to complications. It indicates that governance structure and process shall become less effective due to complex models.
Recommendations
As evident from the case study that the University of BuProMan has low process management maturity. However, the new canceller has set a new optimistic strategy; university operations struggle due to the lack of linkage between business vision and its processes.
So, an essential recommendation that leadership has to ensure closing the gap between strategy and operation through an agreement with all business levels to establish Target operating model. The aim of TOM is bridging the gaps through strategic alignment and governance of the value chain activities and underlining components which are people, processes, and technology, and ensure effective and efficient execution and deliver intended value to all stakeholders.
Business Process management as usual practice enables the organization to adapt and adopt changes either in the internal or external environment, demands, technologies. So, the university management needs to keep monitoring market trends and apply required changes and improvements in its business processes to satisfy students’ needs, attract high-rank students and sustain its competitive position in the global academic and research domain.
An important aspect the university leadership needs to ensure to guarantee successful ongoing business process management is executive, and business unites commitment, support full engagement as they represent the key for convincing others in the organization to adopt the recommended changes in business processes.
As a result of leadership commitment to BPM, the effect will cascade to all employees who will boost creating process-oriented organization culture where all participate and hold the responsibility of executing assigned activities effectively and efficiently to meet associated strategic goals.
Besides that, another critical aspect that considers a success factor for BPM is a communication strategy that should be enabled on all management and none management levels and allow feedback and feedforward with all business processes concerned stakeholders.
However, the marketing department in the university is responsible for arranging market research to analyze the market and students’ demands; research results need to be communicated to top management to reflect that in university strategy and accordingly will feed as input for relevant business processes.
Another aspect that university management need to tailor while planning its strategy and BPM activities is establishing a performance management framework that enables management on all levels to monitor and control the execution of business processes through a set of smart goals and key performance indicators and applies corrective actions once process outputs are not meeting targeted goals. A balanced scorecard can be a useful strategic tool to support top management vision and give a balanced view of the four main perspectives that they are looking to achieve which are the stakeholder, financial, improvement, and growth and shareholders.
Within the business performance framework, business core processes governance need to identify the accountability and responsibility framework of each aspect of the processes activities and involved individuals and its execution results that feed as input for performance management processes to achieve intended business continuous improvement and sustainability.
Achieving operation efficiency and effectiveness with limited resources can be maintained through adopting strategies that accept outsourcing some functions, such HR which university can hire talent acquisition and recruitment agency that can help provision highly experienced faculties and employees to enable the university in achieving its competitive advantage factors.
In addition to that, strategic joint ventures with international universities and technology companies such as IBM, Apple, GE, and Cisco can be valuable options to exchange experience in technology and innovation research arenas, skills and allow for benchmarking and improve its business processes. As well can offer graduate students to employment opportunities in these companies with continuing their academic studies and gain funds for their academic researches to meet the University objectives.
Conclusion
Every project under the BPM strategy should have futuristic goals. The plan should have a timeline through which the organization operates. In this case, the chancellor requires four years to provide a report to the stakeholders who took part in a fundraiser. The essential components of the organization include leadership; people change management and BPM project management without which the entire BPM activity should build on. The BPM project does not indicate that accountability is crucial, but the whole management endeavor requires responsibility. Every leader needs to account for their contributions to the achievement of the set priorities and goals. The group of leaders chosen under John Steward should consider for their work in the view of the set strategy. Individuals like Peter Ant who have served in the university for more than fifteen years with the zeal for change should report the support they need from the executive and remain accountable for the duties he has. Every person in the new management panel has excellent plans which require continued support from the top leadership and accountability will either motivate the executive or demotivate them to support the projects. Since the chancellor has an international consulting background, the university is set to not only become top in the state but also known internationally through its merit.
References
Battor, M & Battour, M 2013, ‘Can organizational learning foster customer relationships? Implications for performance’, The Learning Organization, vol. 20, no.5, pp. 279-290.
Daft, R & Marcic, D 2016, Understanding management, 10th edn, Cengage Learning, London.
Dumas, M., La Rosa, M., Mendling, J., & Reijers, H. A. (2018). Process Redesign. In Fundamentals of Business Process Management (pp. 297-339). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Davenport, T.H., 1993. Process innovation : reengineering work through information technology. Harvard Business Press.
Gordon, J 2013, Project management and project planning, Prentice Hall, New York, NY.
Kiran, D 2016, Total quality management: key concepts and case studies, Elsevier Science, New York, NY.
Jeston, J 2018, Business process management: practical guidelines for successful implementations, 4th edn, Routledge, New York, NY.
Jeston, J. (2014). Business process management. Routledge.
Trkman, P., (2010). The critical success factors of business process management. International journal of information management, 30(2), pp.125-134.
Vom Brocke, J., & Mendling, J. (2018). Business process management cases. Digital innovation and business transformation in practice. Cham, Switzerland: Springer (Management for Professionals).
Von Rosing, M., Zachman, J. A., & von Scheel, H. (2018). The Complete Business Process Handbook: Extended Business Process Management (Vol. 2). Morgan Kaufmann.