- Theory of moral unity
- Circumstances that results in the award of punitive damages to a plaintiff
- The golden rule of ethics in business
- Superfund
- Explain the environment protection agency (EPA) and its responsibilities
- Environmental Kuznets curve
- Four Major Sources of Ethical Values in Business
- Seven steps for an ethics program
Theory of moral unity
The theory of Moral Unity is amongst the fundamental opinions featuring within the age-old debacle of seemingly tolerant morals within the business environment. The theory is measured against communal or individual moral standards. Moral ethics within the business environment is measured based on collective moral norms found within the community as opposed to a unique collection of additional accommodative customs. Trade practices are compared with similar values as practices within other spheres of business conduct based on the presence of one moral benchmark.
Circumstances that results in the award of punitive damages to a plaintiff
Punitive damages can be defined as a form of additional award given to complement plaintiffs’ definite losses. Punitive damages are granted where there is proof of the existence of improper business practices. Damages are designed to curb impending mal-practices. It is argued that punitive damages should be valued proportionally to the firm’s malpractices. If business actions are judged by general ethical standards within any society and not a special set of more permissive standards then such a situation is described by the theory of Moral unity.
Example
One of the good examples is retrieved from the case of James Cash Penny who started from the butchery and developed several retail stores with the help of his mother. The previous proprietors who operated the business informed him that such business prospects would rely on orders from nearby hotels. To maintain his business transactions with the surrounding hotels, James was advised to purchase a bottle of whisky every week for the chef. For some time James Cash Penny adhered to such advice and made the weekly purchase of whisky for the chef but he soon developed cold feet and his business went under.
Afterward, James Penny invested in the Golden Rule Department Store within the same city and held to the opinion that his accomplishments were motivated through his value of integrity. This demonstrates that integrity is a crucial ingredient in the quest for achievement.
The golden rule of ethics in business
Golden Rule is a model established within major world religions and used in integral parts of life. The rule is recorded in major books used by these religions. The rule has acted as foundational teaching for a fairly long time. The rule applies principle denoted as “Do unto others as you would have them do unto you”. This principle incorporates the subconscious infliction of injury to other souls.
An administrator resolving a moral dilemma usually tries to place themselves in the position of those concerned with verdicts and as such consider actions that are more reasonable. A similar model known as ‘practical imperative’ was invented by Immanuel Kant. It states that “Act so that you treat humanity, whether in your personal or in that of another, as an end and never as a means to an end.” The rule advocates for the moral engagement of employers towards their employees. To fulfill the practical imperative and golden rule, an administrator is obliged to adopt the test of reversibility.
The principle of the golden rule (do unto others as you would have them do unto you) holds that a manager faced with a moral choice should act in a way that he or she believes is justified towards any person within a similar situation.
Example
The year 1990 was the time when Southern Pacific Railroad belonged to E.H. Harriman. This period was characterized by rail mishaps that claimed several lives between 5000 and 6000 people a year. While on an assessment circuit one of Harriman’s trains encountered a mishap and almost got off the track as a result of workers’ negligence. From this incident, Harriman was adamant about holding the entire team accountable and not the team leader.
Superfund
This was a central government plan established in 1980 to eradicate locations littered with poisonous substances. The concept was adopted from an account that was used to save money for the same venture to control pollution in River Hudson. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) intervened by announcing 197miles of the river, from the General Electric factories to New York which was considered an urgent superfund area. The superfund was initiated to regulate and offer solutions for a crime against the environment.
Explain the environment protection agency (EPA) and its responsibilities
The environmental protection agency is an administrative arm involved in establishing control. The agency was formed to merge all courses from the central government aimed at conserving the ecosystem. The agency was also endowed with the responsibility of safeguarding populations and environmental health. The EPA constitutes the majority of legislations involved in environmental conservation. EPA also presents one of the biggest control organizations within central administration. EPA stipulates exhaustive and precise regulations required for the successful implementation of environmental legislation adopted by congress. EPA issues policies that direct state control agencies on ways of implementing conservation regulations.
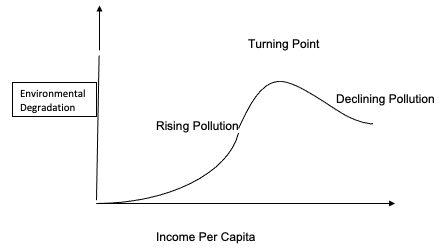
The slender margin atop the earth’s surface that supports life is called the biosphere. The environmental Kuznets curve is a (n) inverted u-shaped curve.
Environmental Kuznets curve
Four Major Sources of Ethical Values in Business
The four major stores of moral values that inspire administrators include Religion, Cultural Experience, Law, and Philosophy.
Religion
All major religions unite based on the conviction that supernatural desires create a clear distinction between virtues and vices within the business arena. These religions also concur on the composition of moral values within the community. They pay much attention to important virtues such as sincerity, justice, kindness, and accountability towards humans.
Philosophy
Administrators within various institutions at times rely on the philosophical analysis of morality that spans over 2000 years. This has formed the basis for a philosophy based on unethical and ethical practices within the business environment. As a result, new ideas have been developed and utilized in various sectors of life.
Cultural experience
Traditional customs are conveyed from one generation to another based on morals, regulations, and norms that form the basis for approved practices. This enables people to carry themselves acceptably within different societies. Societal evolution is a growing custom that has undergone three stages of transformation i.e. economic and communal organizations that have raised the special ethical standard.
Law
Legislation passed by parliament is meant to make an official moral code of conduct. The laws change with time as more regulations, decrees, and judgments define new moral expectations. Businesses and their administrators have adopted means by which to curb unlawful practices, instill discipline, and regenerate malpractices within business environments.
Seven steps for an ethics program
- Establishment of standards and procedures.
- Creating high-level oversight.
- Screening out criminals.
- Communication standards to all employees.
- Monitoring and setting up a hotline.
- Enforcement and standards and checking discipline violators.
- Assessing areas of risk and modifying the program.