Introduction
Business Intelligence (BI) is an umbrella term used for various mechanisms that provide solutions to various business problems (Whitehorn 1999, p. 11). According to Marr (2012, p. 1), the term Business Intelligence refer to tools that are utilized to support the decision making process in organizations.
Typically, the use of BI tools simplifies the decision making process and greatly improves performance as the decision making process is speeded up and business concerns are addressed much faster. Although the term Business Intelligence is frequently used to denote application software used to analyze a business enterprise’s data, it is rather elaborate (Marr 2012, p. 1).
This paper presents a discussion on two Business Intelligence tools. One is by International Business Machines (IBM) while the other one is a product of SAS. As can be seen from figure 1, Business Intelligence includes a number of components.
Figure 1: Components of Business Intelligence
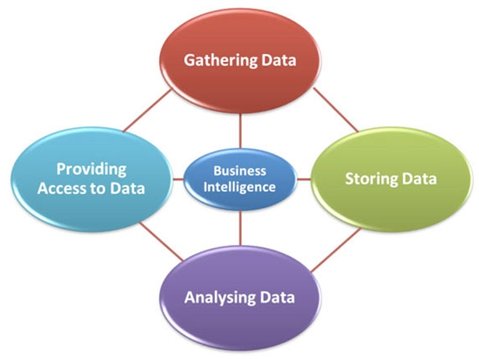
From the figure, it can be seen that a BI tool must be able to support data gathering, analysis, and storage. In addition, the BI tool must provide access to business data. With the help of Business Intelligence tools, business enterprises are able to solve a whole range of problems that afflict those who use data within an organization.
IBM’s Business Intelligence Software
One of the most powerful Business Intelligence tools offered by IBM is Visual Warehouse. Among other things, this BI tool makes it possible for users to create, manage, and automate a data ware house. A data ware house is an off line copy of an operational database, usually held on a totally separate machine.
Off line in this case implies that people are no longer adding to, and altering the data. To a large extent, the tool simplifies the work of dealing with complex queries that require a large proportion of the records. It is also possible to customize data in order to meet specific needs.
Another major advantage of Visual Warehouse has to do with the fact that it can enable a business enterprise to optimize the structure of its database to suit its customized business requirements. Despite the fact that the optimization exercise can take a variety of forms, it might as well involve reducing the detail in the stored data.
For example, rather than storing all the details of every sale made over the last five years, a business enterprise may choose to store only the weekly totals for each product. Another key feature of the Visual Warehouse is that it does not restrict the user to a single source of data. It facilitates the use of data from disparate databases.
Visual Warehouse provides the user with all the tools required to set up and maintain the data warehouse. Further more, it provides all sorts of additional features that make automating and controlling the data warehouse easier.
Using SAS Strategically
According to Aanderud and Hall (2012, p. 3), SAS Business Intelligence solution makes it possible for users manipulate and analyze data in a very simplified manner. Using the tools available through SAS, users can access any kind of information for almost any business needs without having to go through so much trouble. The power of SAS Business Intelligence is in reducing the data gatekeeper’s role in the business so that each person can freely interact with analytic results.
Ordinarily, SAS Business Intelligence makes it possible for business enterprises to address issues at different levels of the organization. Essentially, there are three broad groups of SAS Business Intelligence clients. One group includes the tools required to create reports. The second group allows users to view the reports, and the final group offers the ability to address data management and administration needs.
Typically, organizations grant each user community access to one of these groups. SAS reporting tools include SAS Enterprise Guide, Add-in for Microsoft, Web Report Studio, and SAS Stored Processes. Viewing tools are SAS Business Intelligence Dash Board, and Information Delivery Portal. Finally, SAS administration tools include SAS Information Map Studio, OLAP Cube Studio, and SAS Management Console.
Similarities and Differences between IBM and SAS Business Intelligence Solutions
As can be deduced from the preceding discussion, both the IBM and SAS Business Intelligence solutions have a variety of benefits to offer to business enterprises. Both have the capability to simplify the complex process of data management and analysis. With the help of these Business Intelligence solutions, therefore, business enterprises have a great opportunity to improve efficiency and general business performance (Shmueli et al. 2011). However, each of these Business Intelligence solutions has a number of distinguishing characteristics.
One of the joys of IBM’s Business Intelligence software is that it is very adaptable and highly scalable. One feature that helps to provide this adaptability is that the various components making up Visual Warehouse can be installed in a multitude of different places.
One can, for example, Visual warehouse itself on one machine, the actual data contained in the data warehouse on another and he or she can sit at yet a third machine driving the whole system over a network. The level of adaptability associated with Visual Warehouse guarantees users with a very flexible solution.
Even though SAS is structurally complex, business users of SAS Business Intelligence, only require a basic understanding of the system’s architecture to operate. When compared to IBM’s Business Intelligence software, SAS appears to be more superior and offers a great number of features that make data management and manipulation quite simple.
Conclusion
Clearly, a number of benefits can be realized by incorporating Business Intelligence solutions within a business enterprise’s operations. Among other benefits, there is improved transaction efficiency, ability to integrate internal operations in order to have a seamless operation, back office process automation, transaction status visibility, and reduced information sharing costs.
The primary motivation for the acquisition of a Business Intelligence solution is better control over more efficient day to day business operations (Williams & Williams 2007).
As has been discussed in this paper, Business Intelligence solutions provide a business enterprise with an opportunity to improve business operations and offer excellent services to clients (Rud 2009, p. 24). However, it is important to note that business value of any Business Intelligence solution lies in its use within management processes that affect operational processes that drive revenue or reduce costs.
It is also worthwhile noting that the benefits that accrue from the use of Business Intelligence solutions are directly linked to the way such solution s are aligned with a business enterprise’s operations. Without properly aligning Business Intelligence solutions to business operations, the benefits of using BI solutions may be outweighed by the drawbacks.
Reference List
Aanderud, T & Hall, A 2012, Building Business Intelligence Using SAS: Content Development Examples, SAS Institute, Cary, NC.
Marr, B 2012, What is Business Intelligence (BI)?, <https://www.bernardmarr.com/default.asp>.
Rud, OP 2009, Business Intelligence Success Factors: Tools for Aligning Your Business in the Global Economy, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey.
Shmueli, G, Patel, NR, & Bruce, PC 2011, Data Mining for Business Intelligence: Concepts, Techniques, and Applications in Microsoft Office Excel with XLMiner, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey.
Whitehorn, M 1999, Business Intelligence: The IBM Solution, Springer, Bromyard, UK.
Williams, S, & Williams, N 2007, The Profit Impact of Business Intelligence, Morgan Kaufmann, Oxford, UK.