Introduction
Over the years, sophistication of business models has been embraced. These business models are dependent of technology which is vital in accentuating the accessibility of business to their customers. Mass customization is a key strategy that pools efforts and focuses on flexibility in a production process.
The ability to produce at minimum levels, a guarantee in quality, and little or no disruptions during production is among the key sought features in mass customization. This aims to build business models upon mass customization.
This is fundamental as it turns customers’ diversification into opportunities to maximize profits. Profit maximization in business settings is the ultimate goal. Addressing the present trends of the prevalent business models in the lead of mass customization is highly credible.
Research Methodology
A research methodology entails four concepts; the activity in question, manner to proceed, measure of precession and what comprises the test. The credibility of building business models upon mass customization is tricky hence requires a thorough analysis of the current businesses and their degree of success in terms of operational excellence.
This research was entirely done with the help of online books, rich internet sites, journals and magazines. Personnel in the business field through their knowledge and expertise in the field amplified the fact that it is highly credible to build business models upon the principles of mass customization.
The mining of information from these sources aided the test of businesses which incorporate business models as their strategic fit with those that do not. The process of accomplishing the task of highlighting the key concept of business models is vital as it shows competence and profoundness in the research.
Aims and objectives
The aims and objectives include understanding:
- The concepts of business models and mass customization.
- The credibility of building business models upon the principles of mass communication.
- The relationship between these two concepts and customer satisfaction, quality, profit maximization and operational excellence.
- The connections between mass customization and open innovation.
- The concept of mass customization in relation to product development, efficiency in time and cost.
Business Model Concept
The concept of the business model is becoming more acceptable in the business field. In the creation and designing of businesses, models used are likely to be vital factors in ensuring success. The business model thus explains the plans put in place by a company to spawn revenue and maximize the profits from its operations.
The business model constitutes the elements and roles of the business as well as the proceeds it generates in relation to expenditure incurred. Business models are thus used to correspond to the core elements of a business.
These constitute the strategies, organizational architectures, operational processes, purpose, trading practices and corporate social responsibility (CSR). This concept of the business model dates back to the ancient days. It simply illustrates the manner in which a company is designed to make money (Hansen & Mladenova 2001, p. 450).
Thus, it can either be simple or complex in nature. Simple business models entail the production of goods and services by a company to sell to its customers. Depending on the strategies implemented, the revenues from the sales overpower the operational costs hence realization of profits.
However, other models are complex and intricately knit. This entails a number of parties in the channel of distribution, that is, the stages the products or services pass through right from the initial production until the delivery to the consumers. Whether a simple or complex business model is implemented, the platforms for value creation, mechanisms, delivery and strategies engaged by the businesses should be reinforced.
The fundamental nature of business models is that they lay down the ways in which businesses relinquish value and quality to customers, persuade them to make payments for the worth of goods which in turn translates to profits. Business models also play a key role in the management inside the companies to survey chances for future growth and development (Baytendijk 2010, p.5).
Considering the convolutions of products, the internal and external environment in which the firm conducts its operations and the markets, only a few individuals wholly understand the organization in relation to task relationships and roles. The business models thus seek to link the technical professionals and the business connoisseurs.
Role of the Business Model
There are various concepts of business model. Value proposition is a concept that describes clearly the problem statement and the causes of the customer problem. It also illustrates the worth of the product in relation to the customer’s point of view. Market segment entails a niche or group of the customers to aim at or target. This is done through a clear analyses and understanding of their needs and expectations.
The values chain structure entails the position of the firm, its operations and measures it will put in place to annex the value or worth created in its chain. The fourth concept is that of competitive strategy. This explains the ways in which the company will implement in order to come up with sustainable competitive advantage.
Competitive advantage can be accentuated through product differentiation, low cost strategies and niche strategy. Business models thus spell out the exact position of the business in the value chain. It points out to the concepts of customer needs assessment, operations, finance, economics, strategy and entrepreneurship. All these work together to ensure sustainability of the business in the market (Fogliatto 2011, p. 5).
A system approach of business modeling
The concept of a business model is more vital in cases of new businesses. It is essential for new businesses to ascertain positive response sphere, for instance word of mouth which has to be effectual. Consequently, customers need to recommend other customers on the goods and services of the company in question. This is vital in creating awareness of the products available in the market.
In cases of inexistence of this hastening, a business may never get off from its initial stages. The modeling approach is beneficial as it clearly lays down the processes, traces and checks them in cases of alteration and modifications. Complex stages may further be broken down into simpler stages where each stage can be assessed individually enhancing suitability (Kreutter et al. 2004, p. 240).
Mass Customization
Mass customization is a strategy that is streamlined in suggesting swiftness and elasticity in a production process. It enhances production at minimum levels, high quality products at higher levels with little or no interruptions.
Products that are mass customized compete in relation to standard goods offering a company a competitive perimeter by having the ability to produce unique, special and customized products at very high speeds, cost and quantities. Mass customization is inclined towards high levels and quantities incorporating flexibility in the process of production.
It holds in cases where a high degree of specialized, unique and customized goods are released to the market to give a competitive edge. This concept of mass customization calls for a swift supply chain to operate effectively and at optimal levels.
Understanding and realization of the customer needs, expectations and desires is pertinent in ensuring their acquisition, retention and satisfaction. Achieving customer satisfaction is paramount thus a swift and flexible supply chain should be reinforced (Macaskull 1972, p. 425).
Many manufactures can therefore benefit from this concept of mass customization. Strategies have been put in place to assure manufacturers produce innovative and mass customized products which in turn drive the sales up. Companies too are guaranteed of a competitive edge through the principles of mass customization.
Production strategy aims to create any disparities in a product group on demand in regard to economy. It ensures these products are created in elastic processes without high costs setups and that ultimatums are met.
The supply chain strategy seeks to ensure that all components, materials and sections are always accessible to increase efficiency and effectiveness during production. The design strategies entail the outline of the products in a more unique, special and customized way (Moser 2007, p. 206).
Building business models upon the principles of mass customization is that vital as it ensures customer integration. Many companies are up to date feeling the need of understanding the growing individualization of the demand. This has built up the pressure to achieve competitive advantage through the strategies put in place to foster this competitive edge.
These strategies reinforced have made companies embrace the relationship with customers by offering them quality goods just in time as they (manufacturers) uphold on factors of efficiency, effectiveness and operational excellence. This principle of customer driven value creation has effectively been created through mass customization.
Mass customization is a thoughtful approach that managers can use to build their business models. Strategies, methods and organizational transformations needed to create process and release to the market individually and unique customized goods can help mangers tell if they should make a shift to mass customization (Pine 1993, p. 6).
Mass customization therefore depends on a company’s ability to create customized goods based on the developments. Building business models upon mass customization ensures innovation that drives up the revenues of the companies, value creation and economies of integration. Economies of intergration get deeper than just the differentiation pros of manufacturing through customization as denoted by the price premiums.
This concept looks deeper into the efficiency as portrayed by a firm in its quest for knowledge in the environment and creates processes that uphold value to get rid of wastes at all the production levels (Pinno & Wilhelm 1997, p. 260).
Business model build upon principles of mass customization can be simplified by the following model of value creation.
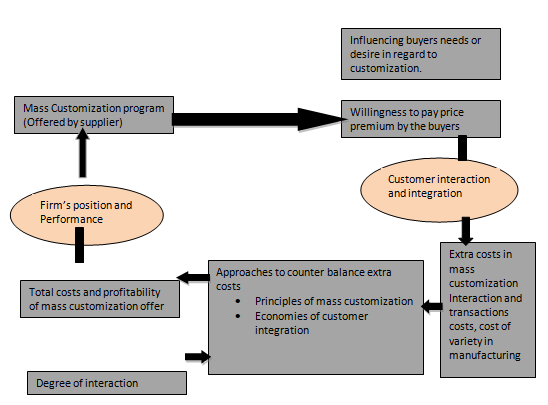
Source: Author
Figure: A model of value as created in mass customized systems
Conclusion
Business models translate innovation to the economic worth of the business. A focus on the customer needs ensures exceptional offering of services to the customer which in turn results to customer loyalty, retention, acquisition and satisfaction, which is key in guaranteeing higher profitability.
Business models are becoming more and more sophisticated in nature as entrepreneurs feel the need to incorporate them as once implemented, they are likely to drive the revenues a notch higher. There is always a start in the business modeling approach. The model seeks to foster the key features that make it work and make changes to the ineffective one (Rosenberg & Ziegler 1992, p. 480).
Building business models upon the principles of mass customization accentuates value creation, customer integration and economies integration. Open innovation and mass customization fosters innovative business models. This is depicted by the prosperity of Spreadshirt and Cafepress.
These companies have incorporated open business models that make it easy and accessible for everyone to co-create their personal business, interact, share outlines for growth and developments and gain tangible knowledge from the experiences of successful entrepreneurs.
Applying methods and concepts of mass customization in the business models is effective and vital as it has the improvement in the development process of products, ensured they are produced at lower costs and within minimal periods of time (Seelman 2002, p. 150). Companies can also create tailor made products on request by individuals. This key concept ensures industry attractiveness.
Most customers want to feel the value for their money. Companies can gain identity through this approach. Spontaneous supply chains are also reinforced through these mass customization principles.
Mass customization is thus in unswerving resistance with ancient and rigid manufacturing approaches. It yields high inventory, higher quantities, economy in order quantities and high capacity utilization. It is thus highly credible to build business models upon the principles of mass customizations.
List of References
Baytendijk, F. 2010. Dealing with dilemmas: where business analytics fall short. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons Publications.
Fogliatto, F. S. 2011. Mass customization: Engineering and managing global operations. London: Springer Verlag Publications
Hansen, P. and Mladenova, N. 2001. Variable neighborhood research: principles and applications. European Journal of Operational Research, 130, 449-467.
Kreutter, G. et al. 2004. Auction based variety formulation and steering for mass customization. Electronic Market, 14, 232-242.
Macaskull, J. L. C. (1972). Productive line balances for mixed model lines. Management Science, 19, 423-434.
Moser, K. 2007. Mass customization strategies. London, UK: Klaus Moser Publication.
Pine, J. B. 1993. Mass customization: the new frontier in business competition. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press.
Pinno, A and Wilhelm, W. E. 1997. A family hierarchical model for the design of deterministic assembly system: International Journal of Production Research, 35, 253-280.
Rosenberg, O. and Ziegler, H. 1992. A comparison of Heuristic algorithms for cost oriented assembly line in balancing methods of and models of operations research. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 36, 477-495.
Seelman, R. 2002. Moving into Mass customization: Information systems and management principles. Berlin: Springer Verlag Publications.