Introduction
The presence of business opportunities and potential markets has given rise to a lot of business opportunities that entrepreneurs are aiming to capitalize on (Dinkhoff 2009, 54). Therefore, entrepreneurs need to use innovative and creative business techniques to come up with superior products and services that are targeting specific needs of consumers in the various parts of the globalised world.
Entrepreneurs are required to be highly proactive and constantly study the environment so that they can identify viable opportunities that arise out of the situation. It is therefore necessary that entrepreneurs use their specific skills and core competencies so as to cope with the complex environment that always presents various complex challenges to entrepreneurs as they steer their organizations towards realizing the organizational goals and objectives (McDonald 2003, 45).
Consumer behaviors are not static, rather dynamic and will from now and then have a different set of demands which must be satisfied as they arise or else consumers may be forced to switch to the next best alternatives. It is therefore necessary that the entrepreneurs carry out continuous research that will gather relevant data and turn this data into useful information that will be used by entrepreneurs in the process of idea generation. Organizations and entrepreneurs who do not actively embrace change and idea generation may be faced out by much competitive entrepreneurs (Dupuis 1999, 15).
The idea generation process
The idea generation process is a highly mental process that requires individual’s to carefully study the environment so that they can come up with goods and services, which are creative. This process is very critical for any entrepreneur and if the outcome of this process is not considered successful then the resulting product that is pushed into the market. In today’s business environment competition between organizations demands that organizations come up with products and services that are highly convenient and efficient for the consumers, and therefore if an entrepreneur does not take consumer needs as the pivot of his all idea generation process then he/she may be laying ground for possible failure.
Ingvar Feodor Kamprad is a Swedish businessman and founder, IKEA a retail (specialty) company. Kamprad is an exceptional entrepreneur who started pursuing his entrepreneurial ambitions while still a teenager (Kotler 2003, 45). After evolving from a boy who sold matchsticks and low end consumer products, Kamprad decided to use the money that his father gave him for further studies to come up with his most successful idea, IKEA.
Kamprad believes that for every existing and aspiring entrepreneur the process of idea generation is very important. Kamprad believes that the challenges that arise out of the highly complex may at most likely threaten the peaceful existence of entrepreneurs and their ventures. It is therefore necessary for entrepreneurs to survive the dynamic business environment. Therefore, entrepreneurs have only one option which is either advance with the dynamic environment or else face extinction.
Entrepreneurs therefore should establish systems which will assist the organizations to come up with various techniques which will enable these organizations consistently and continuously come up with ideas which will assist the organization cope with complexities and ambiguities as they arise. Companies like Nike invest billions of dollars in the doing research and design, which focuses on coming up with new and high performance products. Nike has been able to adapt with competition by offering premium products that have come into existence as a result idea generation by the R&D department (Brigham & Houston 2009, 13).
Kamprad strongly insists on the importance of carrying out comprehensive SWOT analysis before pursuing any entrepreneurial and business ventures (Porter 1990, 103). An entrepreneur may come up with an idea that he/she may think is completely perfect and full proof but the truth of the matter the idea may be completely weak and unattractive. It is therefore appropriate for entrepreneurs to back their business ideas with sufficient proof that will ensure that their business ideas succeed. A SWOT analysis will therefore state the demerits and merits of the actual idea that need to be identified during the idea generation process. The best way to gather data pertaining to SWOT is by conducting comprehensive research.
Strategic objectives
When the idea generation phase comes into completion then the process of merging the ideas with strategies starts. A strategy is a blue print of comprehensive short run and long-term plans that an entrepreneur intends to apply to achieve the mission and goals of his venture (Torekull & Kamprad 2005, 89). Strategy therefore guides an entrepreneur by defining the path that his venture is to follow when his idea is turned into a full product or service and is introduced to the market. Strategy consists of elements such as vision, mission, program, tactics, budgets, and procedures that will generally guide the business which an entrepreneur intends to engage in (Paul 2008, 47).
The strategic process usually involves formulation of business strategy, implementation, finally evaluation and control measures. It is therefore very important that an entrepreneur gives full dedication to this process because if the business idea is wrongly executed when it enters the market then the full potential of the entrepreneurial idea may not be realized (Buckley 1995, 40). For instance, Coca-cola is highly respected for using superior strategies to enhance its global domination. Especially, when it comes to budgeting for advertisements/promotions and furthermore its distribution strategies are extremely effective making its products almost available in almost every nation.
Marketing analysis and research
Entrepreneurs must not ignore the importance of marketing in making entrepreneurial ideas successful. Products and services are made for consumers who have needs (Porter 1990, 10). It is therefore necessary that entrepreneurs come up with mechanisms that will help them package their products in a way that attracts the attention of consumers. It is therefore necessary that entrepreneurs design strategies go govern the 4 Ps (price, place, product, and promotion) of marketing. An entrepreneur needs to take a close look at how industry participants have packaged their products and what kind of marketing strategies that they have used. The outcome of analyzing how other industry participants can be used as input for the entrepreneur to formulate strategies that will govern the 4 Ps of the product (Casson 1982, 56).
Market analysis and research will therefore enable entrepreneurs to either serve the mass market or go a step further to segment or even target a particular segment of the market. Ryanair is an example of a company that generates business ideas targeting low end consumers by using a low income business model. It has then gone ahead to use marketing strategies that are in accordance with its business model (Wheelen & Hunger 2002, 49, Reynolds 2007, 43).
Understanding competition
Every organization is faced by the threat of competition from existing companies or new entrants. Competition can eat on a company’s market share and hence profits and if not well managed it can threaten its existence. This calls for every company to consistently and frequently conduct research to monitor competition. A company needs to evaluate the extent of competition in the market and know how to survive in the competitive business environment.
According to Thomas Wheelen and David Hunger, who are both gurus of strategy management, a company may choose a competitive strategy that either intent to serve a broader spectrum of the market or a narrow spectrum of the market while at the same time either choose to pursue either a low cost strategy or a differentiation strategy. Comparing Ryanair to a company like British airways or Virgin airline, Ryanair has chosen a low cost mass market approach which serves as the backbone of its competition strategy (Goodstein et al. 1993, 63).
Financial Planning
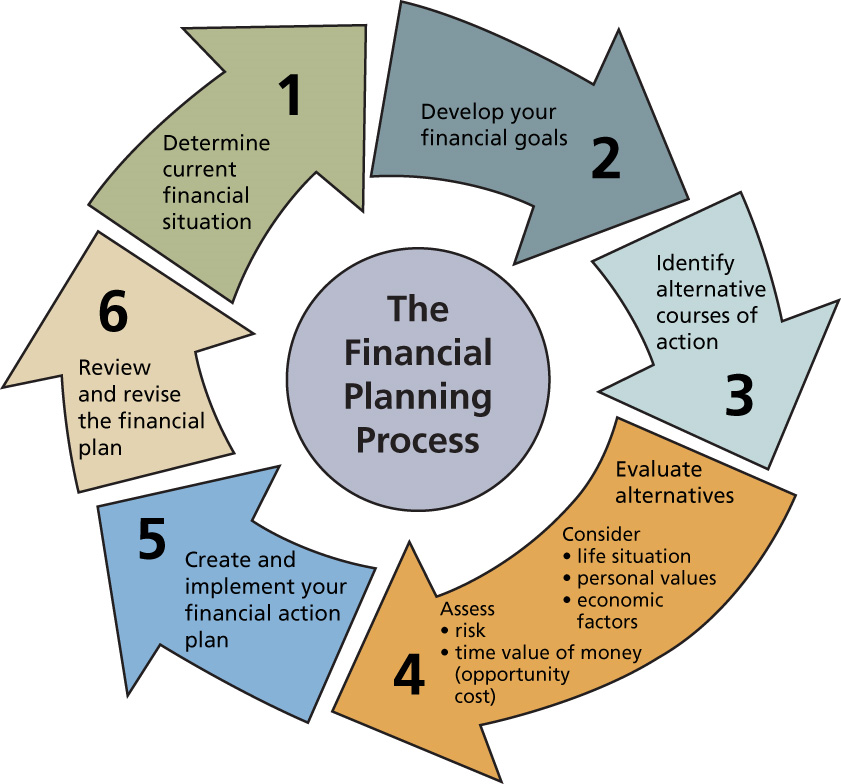
Financial planning is also a critical part of the entrepreneurship process (Reynolds 2007, 16). Entrepreneurial ideas involve pooling together many resources in order to be fully executed. Tesco mainly uses franchising to expand its business worldwide. A perfect financial therefore ensures optimal location or resources and also accountability. Tesco is an organization with a good financial system that uses superior financial planning techniques to support the ideas of various entrepreneurs who desire to join the Tesco franchise (Reynolds 2007, 54). Tesco’s financial department usually sends out assistants if necessary and maintains consistent communication with existing and prospective franchisees and then goes ahead to assist them in the process of financial planning within their franchises.
Entrepreneurial Skills
Introduction
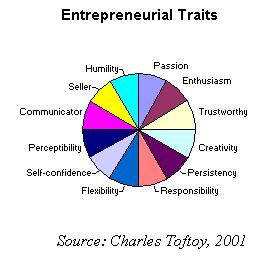
Not every individual in the society can be regarded as an entrepreneur. Entrepreneurs are persons who have a unique set of characteristics and personality traits that make them different from conventional businessmen (Gartner & Bellamy 2009 p. 2-12). Entrepreneurs are individuals who are considered to be highly creative and stubborn and therefore they come up with ideas and pursue them to the bitter end. Entrepreneurs are respected for their ideas and innovative nature that enables human life to be continuously improved by perfect business ideas that they are able to come up with that make life more convenient (Kuratko 2008, p.3-15).
While other individuals may operate businesses haphazardly entrepreneurs are individuals who have a passion for coming up with business ideas which are creative and furthermore at the sometime proactively improving these business ideas with an aim of maximizing profits and revenues from these business ideas while at the same time satisfying the needs of consumers (Kotler & Keller 2006, p.22). It is therefore true to say that a special pool of traits enable consumers deal with the complex changing environment together with various ambiguities that introduce themselves when entrepreneurs pursue their business ventures. Some of these traits include Entrepreneurial characteristics self-confidence, ambition, hard-work, commitment, Strong ego or a sense of pride and finally autonomy (Kuratko 2008, p.12-23).
Unique Characteristics of entrepreneurs
Ambitious
Ambition can be defined as a characteristic where entrepreneurs have a high affinity for personal achievement (Reynolds 2007, p. 22-34). Often ambition is regarded as a feeling which pushes an individual to make something out of nothing. It is therefore correct to say that entrepreneurs are usually individuals with a vision and therefore have long-term kind of orientation.
Entrepreneurs are highly imaginative individuals who are able to create a picture of what they intend to achieve and therefore go ahead to pursue their entrepreneurial ventures with an aim of succeeding and seeing their ideas come to pass. Carlos slim, the fourth richest man with vast interests in the telecommunication industry, finance and retailing, believes that unless an entrepreneur can have a dream and vision then he/she will most likely not be a successful entrepreneur (Torekull & Kampard 2005, p.31-32). It is therefore necessary that every entrepreneur becomes a visionary and thinks long-term in order to succeed.
Hardworking
Entrepreneurs are highly industrious individuals, this simply means that when an entrepreneur establishes his goals and objectives and has his/her venture running he/she goes ahead to give his all towards seeing the business succeed (Paul 2008, 79). Therefore entrepreneurs may often become addicted to their ventures and may even sometimes lack a social life and spend sleepless nights with an aim of seeing their ventures succeed.
Carlos Slim believes that it is best if entrepreneurs keep a close eye on their business ventures by ensuring that they invest a lot of time and effort in order to see them succeed (Torekull & Kampard 2005, 77). An entrepreneur cannot leave other individuals who did not nature the entrepreneurial idea run his/her business for them because these individuals may not share the same dream that the entrepreneur has as far as the venture is concerned. It is therefore better for the businessman offer his/her all to see his/her idea grow before delegating responsibility to others.
Self –confidence
An entrepreneur must be an individual who believes in him/herself. Entrepreneurs are people who have special skills and abilities which they must they themselves believe in. Entrepreneurs are people who have faith in their own capabilities; furthermore entrepreneurs also believe that their core competencies are enough to help them succeed within the business environment. Carlos slim is an individual who highly insists that entrepreneurs should never doubt what they are capable of, when events go bad it doesn’t mean that failure is inevitable but entrepreneurs may be required to use their gut and heart in perusing opportunities (Torekull & Kampard 2005 p.25).
Commitment
Entrepreneurs have the ability to set goals, objectives and strategies and guarantee that they will stick to them unto the bitter end come what may. Entrepreneurs treat their ideas as if they are their own brain child and therefore they do not jump ship when the times become rough and unpredictable but they instead go ahead to look for solutions which will better their own businesses and entrepreneurial ventures. Commitment can be further described as a situation where individuals are highly loyal to what they believe. Carlos Slim categorically believes that no one can achieve anything if they decide to quit, therefore entrepreneurs should find ways to face their challenges o generate solutions rather than quit, because nothing good comes out of quitting (Torekull & Kampard 2005, 2-30).
Autonomous
It is often assumed that entrepreneurs are individuals who desire to be free like birds. The venture theory of entrepreneurship suggests that entrepreneurs are people with free spirits who are highly adventurous and desire making decisions freely without undue duress, influence or pressure from other individuals. This characteristic of autonomy means that entrepreneurs are highly intrinsic and therefore look inside themselves to find motivation and make fully informed decisions (Casson 1982, 46). Business ventures involve consuming a lot of resources and furthermore very many variables influence the strategic path that is followed by businesses and therefore it is necessary that entrepreneurs are not subjected to peer pressure but rather make decisions which are solidly founded on logic.
Strong ego
Entrepreneurs believe that they are special and unique individuals who manufacture superb ideas that are a source of solutions to many people’s problems this is therefore why entrepreneurs have a strong sense of pride. Brigham and & Houston (2009, 106) notes that a strong ego simply means that entrepreneurs see themselves as highly unique and distinguished because of their specific capabilities which are not similar to anyone else’s.
Carlos Slim believes that he will remembered forever for his contributions in the technology communication industry because he has made it more easy for individuals to communicate with each other, he believes that his contributions are far much important and have improved the life of millions across the world (Cassanova 2009, 67-80). Carlos Slim believes that he is unique and different from any other individual due to a strong ego that he possesses.
Skills required by entrepreneurs
Effects of globalization and intense competition between corporations in the world have made business more complex and therefore it is not only enough to have necessary traits. Entrepreneurs who want to be in tune with changing times are required to go a step further and acquire the skills that will make them more superior and enable them incorporate superior strategies to boost their business ideas (Campbell et.al. 2002, 123). It is not enough for entrepreneurs to assume that the traits that they have are enough to enable them perform superiorly and succeed in today’s environment (Porter 1998, 54).
These skills that are gathered from numerous disciplines but are somehow interrelated and relevant to the success of all entrepreneurial ventures that individuals may decide to pursue. These skills include skills such as financial skills, accounting skills, planning skills, analytical skills, and also managerial and leadership skills that will enable them plan, control, organize, staffing and direct various activities that fall within their entrepreneurial ventures (Rogers & Makonnen 2002, p. 56).
The relevance of acquiring these skills are quite simple, entrepreneurs will be able to conduct continuous research and therefore gather data which will be turned into useful information to be used to formulate, implement and control organizational strategies. The business environment is highly dynamic; this means that entrepreneurs may be required to alter the various tactics that will either decide if their business ventures will fail or succeed, and this cannot be successfully achieved if entrepreneurs lack the necessary set of skills, which can be used to empower them and add more character to their traits (Reading 2004, p. 24).
Entrepreneurs who ignore acquiring such skills may find themselves lagging behind and doing not so well in the business environment. Carlos Slim believes that entrepreneurs should try as much to gather skills from various disciplines so that they can either be involved in every step of decision making and if not so then they can fully understand why it is necessary for certain decisions within the organizations to be made (Lida 2009, p. 38). This is because entrepreneurs are most likely to be motivated when there is information symmetry.
References
Brigham, E. F. & Houston J.F., 2009. Fundamentals of Financial Management. New York, NY: Cengage Learning.
Buckley, N., 1995. “People: Leahy rings Tesco’s tills”. Financial Times, p. 40.
Casson, M. 1982. The entrepreneur: an economic theory, illustrated edition, Manhattan: Rowman & Littlefield.
Dinkhoff, M., 2009. Business Valuation of Tesco: Calculation of Different Valuation Methods and Presentation of Differences Between Them. GRIN Verlag: Norderstedt.
Dupuis, M., 1999. European cases in retailing. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers.
Goodstein, K. et al. 1993. Applied strategic planning: a comprehensive guide. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Kotler, P., 2003. Marketing Insights from A to Z: 80 concepts every manager needs to know. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
McDonald, M., 2003. Marketing plans: how to prepare them, how to use them, 5th edn. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Paul, T., 2008. Innovation Management and New Product Development, 4th edn. London: Pearson.
Porter M.E. 1990.The Competitive advantage of nations, illustrated edn, Northampton, MA: Free Press.
Reynolds, P. D., 2007. Entrepreneurship in the United States. New York: Springer.
Torekull B., & Kamprad, I., 2005. IKEA: the story of Ingvar Kamprad & IKEA, the world’s leading home furnishing company. New York: HarperCollins.
Wheelen, T. & Hunger, D.J., 2002. Strategic management and business policy. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Campbell ,D., et.al., 2002. Business Strategy An Introduction, 2 edn, Butterworth-Heinemann: Banbury Rd.
Cassanova, L., 2009. Global Latinas. Palgrave Macmillan: Hampshire.
Charles W., et.al., 2009. Essentials of Marketing. South Western Cengage Learning: Natorp Boulevard.
Gartner, B. W., & Bellamy, G. M., 2009. Creating the Enterprise. Cengage Learning: Natorp Boulevard.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K., 2006. Marketing Management, 13th edn. New York, NY: Prentice Hall.
Kourdi, J., 2009. Business Strategy: A Guide to Effective Decision Making, 2 edn, Economist books: New York.
Kuratko D. F., 2008. Entrepreneurs: Theory, process and practice. South-Western Cengage Learning: Natorp Boulevard.
Lida, D., 2009. First stop in the new world: Mexico City, the capital of 21st century. Penguin group Inc: New York.
Porter, M., 1998. Competitive advantage: creating and sustaining superior performance: with a new introduction. New York: Simon & Schuster.
Reading, C., 2004. Strategic business planning: a dynamic system for improving performance & competitive advantage. New York, NY: Kogan Page Publishers.
Reynolds, P. D., 2007. Entrepreneurship in the United States. New York: Springer.
Rogers, S. & Makonnen, R., 2002. The entrepreneur’s guide to finance and business: wealth creation techniques for growing a business. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Torekull, B. & Kampard, I., 2005. IKEA: the story of Ingvar Kamprad & IKEA, the world’s leading home furnishing company. HarperCollins: New York.