Introduction
Cardiomegaly is a health condition that poses a serious threat to life since it affects the heart. Patients suffering from such conditions have an enlarged heart. The enlargement is caused by the extra job that the heart has to do to pump blood to the whole body. It is rated at an increase of the ratio of cardiothoracic increase. The increase is attributable to a number of causes and the common cause is a cardiac failure. The enlarged heart condition is becoming a common heart disease. Some causative factors are more prevailing than others, hence prevention can target reducing these factors. Cardiomegaly is associated with other cardiovascular conditions among them congestive heart failure and hyperthyroidism but it’s not in its entirety caused by these conditions.
Cardiomegaly Symptoms
Changes in the physiology of the human body like pregnancy or suffering chronic medical problems, then the heart is forced to work harder than it should normally do. This way, the heart enlarges. The physician can make use of X-Ray and other diagnostic test for a better diagnosis of the condition (Díaz et al, 2006, p. 123).
The common symptoms include enlargement of the heart and this way the patient experiences trouble when breathing, the patient also experiences fatigue, dizziness and coughing that is persistent.
Other symptoms that come as a result of enlargement of the heart include edema of various body parts like the ankles. The patient can also experience irregular heart pulse (Kahan et al, 2008, p. 52). On the examinations by a cardiologist, there is the possibility of diagnosing heart murmurs because the heart valves are unable to close well in some cases. The American Transplantation society has claimed that in some cases, the patient can experience loss of appetite and stomach upsets. Potential patients are advised to seek attention first when they notice these signs since they could signal a risk of heart attack (Díaz et al, 2006, p. 123). These include chest pressure, breathing difficulty, or spells of fainting.
Severe Signs depending on what side of the heart is enlarged; one can develop critical complications when the condition is untreated. Left ventricular enlargements could mean a greater risk of heart failure. Cardiomegaly increases the possibility of clots which could cause blockages. Severs conditions can result in abnormal heart rhythms and this affects its pumping capability (Díaz et al, 2006, p. 123). The risk is that the heart can develop sudden cardiac arrest which could be lethal.
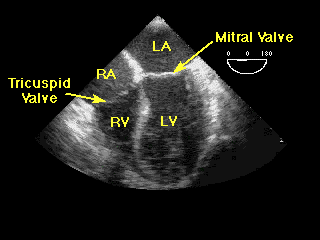
Types of Cardiomegaly
There are two types of cardiomegaly, the mild and hypertensive one. Mild cardiomegaly is described as a slight increase in the size of the heart. Hypertensive cardiomegaly on the other hand is the increase caused by high blood pressure.
Diagnosis
The physical usually check for history of the following conditions;
- Chest pain which could be due to ischemic heart problems
- Rheumatic fever (Kahan et al, 2008, p. 52)
- Family history of heart disease
- Drug or alcohol abuse (Kahan et al, 2008, p. 52)
- Congenital heart problems
Other symptoms include syncope, fatigue, palpitations, and dyspnea. These are not positive tests but they show the great possibility that it could be cardiomegaly.
Physical examination of the heart is carried out and appositive indications are a downward and leftward movement of the heart. In normal conditions, the left border of the heart is not displaced this way.
Laboratory findings carried out following the medical history and physical examination could have the following as a guide for diagnosis. The complete blood count is carried out to exclude anemia; tests for thyroid-stimulating hormone and creatinine n are also done. On rare occasions, a calcium test is done to exclude hypocalcaemia, test for magnesium to exclude hypomagnesaemia and sedimentation rate of erythrocytes to assess autoimmune causes (Díaz et al, 2006, p. 123).
Electrocardiographic tests are also done and g waves are an indication of MI and account for the enlargement. ST-elevation is an indication of possible myocardial infarction. EKG could be an indication of enlargement of the left atria or right atria.
The X-Ray tests are used to calculate the cardiothoracic ratio. Viewing the heart on the AP film, the heart is seen to be enlarged. Other diagnostic means include a pharmacologic stress test, pathologic tests, and ultrasound.
Understanding the Echocardiogram
Diseases that affect the heart are usually assessed by measuring the electrical characteristics of the heart, this is whereby the echocardiogram from echocardiography is used to draw conclusions found (Michelena & Melduni, 2008, p. 1443).
Heart size: results from echocardiogram can explain heart. Various causes can lead to enlargement including hypertension of destruction of the valves.
Heart potency: an echocardiogram graph can show the pumping capability of the heart. In this manner, the ejection fraction is the term that describes the strength of the heart of the ventricles for every pulse (Kahan et al, 2008, p. 55). Cardiac out is a tool that is used to gauge the amount of blood that can be pumped out each minute. In event that the heart is found to have inadequate strength, then the patient has a higher risk of heart failure.
Heart damage: the outcomes of the echocardiogram can reveal information to the physician of any damages to the heart that could be present (Kahan et al, 2008, p. 55). There are various tests that help physicians in assessing and determining whether every part of the heart can function correctly. Any unusually movement of the heart can be a revelation of coronary heart disease, possible ischemia or several health problems. Therefore, if the damage on the heart is discovered it can be corrected by surgery or medication.
Heart valves: the job of heart valves is to open and close as the heart pumps, result of an echocardiogram can reveal problems of their functionality when they do not open wide enough or they do not close properly (Michelena & Melduni, 2008, p. 1444). When valves of the heart do not open properly during pumping, the heart is overworked. This way the blood flow is slows and this in turn decreases the amount of oxygen reaching the heart muscles. Heart muscles can be severely weakened by this. Correction may be by surgery (Michelena & Melduni, 2008, p. 1444). General defects: the echocardiogram can be used to detect congenital heart defects. The defects could be affecting valves, the heart muscles, and chambers. Such defects can be life threatening.
Treating Cardiomegaly
Most of the causes of Cardiomegaly are preventable. However, management of the condition can be effective when the root cause is known.
Diuretic medication: when enlargement is as a result of cardiomyopathy and the heart enlarges and becomes thick or becomes weak, drug of choice include diuretics. These drugs reduce the amount of sodium ions that the body absorbs. Lasix can relieve the chest pressure build very fast and therefore minimizes heart tissue scarring (Kahan et al, 2008, p. 55).
Other medications: other drugs used include Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitors, B blockers, digoxin and ARBs. The ACE lowers the blood pressure and enhances pumping capacity of the heart. Beta blockers also lower the blood pressure. digoxin alleviates the probability of hospitalization. Atrial fibrillation surgery is critical because fibrillations can affect the pumping of the heart and this can result in complications like stroke or enlarged heart. Is this is the cause of enlarged heart, and then surgery can regulate its rhythm (Michelena & Melduni, 2008, p. 1444).
Heart valve surgery; sometimes the valves can be the cause of enlarged heart. If this is the case, They can be removed and replaced by normal ones from another animal or use artificial ones. Transplant is necessary in severe cases. for instance when various medications have been applied and even other treatments have failed to achieve the desired outcomes. the last option is a heart transplant.
Conclusion
The implication of the increases in the size of the heart, especially its muscles is basically determined by the causal pathology. Effective treatment is also based on the cause. However it’s critical to avoid habits that can cause any heart problems.
Reference List
Díaz, A.G. et al, (2006). Correlation Between The Chest Radiography And The Echocardiogram To Evaluate Cardiomegaly In Patients With Systemic Arterial Hypertension, Arch Cardiol Mex; 76 (2) Pp 123-134.
Kahan, S., Miller, R & Smith, E. (2008). In A Page Signs & Symptoms, Hagerstown, Maryland; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, pp 50 – 62.
Michelin, H & Melduni, R. (2008). Right Ventricular Plasticity, Internal Medicine, Vol. 47, No. 15 Pp. 1443-1444.