Introduction
In the modern world, Bank is an essential and useful financial service organisation for people. The globalisation and competition of the banking industry have increased because of the growing importance of banking in the marketplace. Therefore, providing only financial services is not limited to financial instruments but also involved in various non-financial instruments and services. For this reason, banks can be described as:
- serving economic functions,
- serving customers through various offers, and finally,
- existing as a legal entity.
According to customer demand, various types of banks are formed, like commercial banks, money centre banks, merchant banks, insured banks, virtual banks and many more. These banks differ from country to country. After 1975, central banks of G-10 nations set international governance standards for financial institutions according to Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. These regulations improved global banking regulations until 2005 to prevent financial instability and legislation. However, Germany was under controversy according to the Basel II proposal in 2001; and these consequences have affected the German economy, and costs of credit have increased in German industrial and banking sectors. From the viewpoint of Lichtblau, the transitions of banking in Germany are in a complicated position, which increases equity to open themselves to the rest of the world, but they cannot survive with a complete change in the thinking process of them.
Analysis of Problems
Problem Identification
The problem of this case is mainly focused on the difficulties of banking in Germany, like whether they were value-oriented according to Anglo-Saxon style for capital markets and shareholders, their profits, and losses. The decisions of Basel II and the EU for public sector banking and capital markets may hamper the relationship of the banking industries of Germany. The regime of Basel II mainly emphasized the norms and criteria of banking sectors, rather than profit orientation. The decisions of customer orientation and their satisfaction are dependent on the development of banking services to satisfy customers properly. The classical banking system has to be reformed as relationship-oriented commercial banking in Germany.
Environmental (PESTLE) Analysis
The banking environment is very sophisticated to be flexible, which is true for any region’s banking industry. For Germany, it is also obviously true for the banking industry. When the Basel II and EU had changed decisions on changing the style of the banking industry in Germany, the environment has affected much on these issues. The following figure will show the environmental factors, which has an impact on Germany:
- Political Factors: The main factor, which is affected most in the banking industry of Germany, were political factors of the banking environment. When the proposal of Basel II was being controversial to Germany according to changing the style of commercial banking, then other regions of different states were being agreed with the decisions of EU and Basel II, which was hampering the relationship of Germany with other states. However, very badly, these states are major sources of financing on the banking of Germany. Therefore, these political issues were impacted negatively, when German banking has accepted and received new styles so easily.
- Economical Factors: All knows that banking industries are mainly holding the economic conditions of any region. However, when the industry is being controversial, then economic conditions are also being hampered for not only banks but also the whole of Germany with high records ever made. The life cycle of the banking industry is also being lowered than before without the help of possible outsourcing of financing. These banks were also being unable to supply secured short-term and long-term loans to public sectors and government organisations.
- Social Factors: Basel II and the EU have implied relationship consumer banking, rather than commercial and profit orientated banking. When the German banking industry was unable to develop these new banking systems, it was being anti-socialism to the consumers in a commercial banking environment. Therefore, not only is profit orientation is the success factor of business, but also socialism and relationship build up between organisation and customers are also important for running a successful and smooth business.
- Technological Factors: The new Anglo- Saxon style is a part of modern banking for its consumers according to commercial and personal financial services. This new system is developed based on transparent, favourable equities, value orientation for shareholders, external ratings and is easily accessible to capital markets. These issues are implied with the blessing of technological advancement. However, as Germany’s banks were unable and not agreed with these systems of modern banking according to Basel II and EU, so they are lacked behind in technological issues.
- Legal Factors: Basel II and EU are regulatory and governing bodies of Europe and other states’ banking services and organisations. However, the German banking industry is not accepting the new banking system regulated and developed by these two legal and governing bodies. Therefore, they are not maintaining legal issues of the environment.
- Ecological Factors: German banks are successful in maintaining loans and capital requirements of various organisations and enterprises of Europe and other states’ customers. These organisations and enterprises are given huge employment opportunities to the general people. High employment is obviously a good sign of the stable economic condition of a country. Therefore, the German banking industry perfectly maintains the ecological balance in the economic condition of the country.
Market Analysis- Five Forces Model
Market analysis is another important issue to be discussed for critical analysis and technical issues. Michael Porter is developing a model, which is called Porter’s Five Forces Model, describing some forces that affected the industries. As, Germany’s banking industries are in vulnerable positions, so it should also develop market analysis discussions for affected and potentially affected areas of the banking industry. With the following figure, Porter’s model is described briefly for the banking industry of Germany:
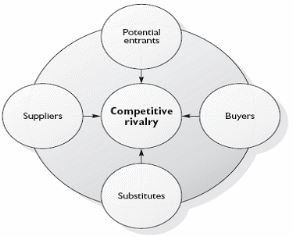
Bargaining power of Buyers
Customers of any industry are being favoured by flexible and different services in the marketplace with various offers and pricing systems. The new banking system developed by Basel II and EU is based on a relationship-orientated and modern baking system, so customers of banks are very fond of this new system. However, the problems are started when the German banking industry was not followed the new modern banking for them. For this reason, the bargaining powers of buyers or customers are getting too much higher than ever.
Bargaining power of Suppliers
When the German banks were getting unable to accept a new banking system for themselves, then potential sources of financing, like capital and loan arrangements from outsourcing from different sources were being stopped. These industries were facing too much trouble for their bad loans and damaged balance sheets. Some of these banks were being bankrupt, which is also being impacted negatively in the environment and others are compared as bad banks to the marketplaces. Therefore, for these reasons, the bargaining powers of suppliers are also being high in the banking industry of Germany.
Threats from Substitutes
When the banking systems of Germany was being rigid, and then other state banks were taking advantage of the inability in banking industries. When the performances of Germany’s banking were lowered in terms of new economic systems, then most of the other European countries were presented Germany’s banking system as a sick man of Europe with a rigid and old banking system to its customers. As a result, threats from substitutes or other banks are also too high in banking marketplaces
Threats from Potential Entrants
The banks of Germany are already in a vulnerable situation. The banks are not followed a new economy banking system with proper customer services, business management and information technologies (Rose & Hudgins, 2008). Most banks are bankrupt in 2003, and others are being unsuccessful to operate their businesses. Therefore, this industry is not lucrative at all for new banks. Therefore, potential entrants to this banking industry are low.
Threats of Competitive Rivalry
When German banks were being unable to meet the loans and capital arrangements for their own industries and governmental organisations, then according to the new economic system, the capital was arranged from other European banks, which was very harmful to them to survive in their own country. Therefore, competitive rivalries from other countries are being high in the banking industry in Germany.
Internal Analysis- SWOT Analysis
There are some internal issues, which are affected by the banking industry of Germany. Internal issues are discussed and focused on by another model, which is called SWOT analysis. This analysis is emphasised on internal and external factors of industry, which can work as S-strengths, W- Weakness, O-Opportunities, and T-Threats for this industry, shown below with the help of figure:
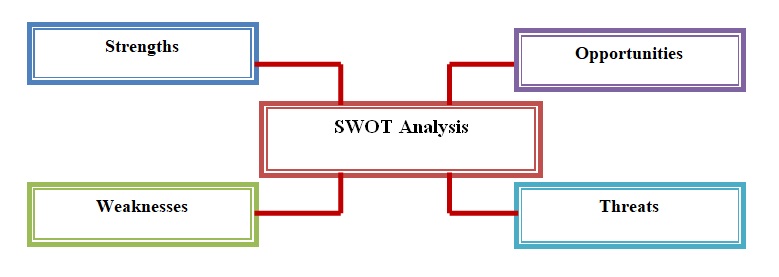
Strengths
A major strength of the banking industry in Germany is to be stable in its system in any situation. They are proven themselves rigid and unsuccessful to provide capital requirements for other industries and enterprises of Germany, like Mittlestand. Most of the employment opportunities are provided by these organisations in Germany, which is about 42% of all jobs (Fear, 2003). Bank loans are also meet the need of short-term loans, as well as long-term loans to modern capital markets and various enterprises. Strong positioning is the major strength of the banking industry in Germany.
Weakness
The banking industry in Germany has various weaknesses in terms of rigidity and inaccessibility. As, banks play crucial roles to meet up capital requirements of Mittlestand firms and other organisations, so it has to be flexible with the change of environment and other conditions. However, these banks are unable to change themselves as the modern banking system and make good relationships with their customers. These banks are also carried social risks of various organisations by keeping up more than 57% of shareholders’ value of the market. On the other hand, the equity levels of these banks are lower compared with other state’s banks in Europe and international marketplaces, which was 20%.
Opportunities
Germany’s banking industry is not limited to providing banking and financial services to customers in marketplaces. It is also proving consulting services, like arranging contacts, recognising potential joint ventures and alliances, organising education centre, managing export markets, financial management and technological development and alteration in banks and other industries. Therefore, they have huge opportunities to expand themselves as various services providing organisations in the market.
Threats
Basel II and the EU have been developed a new commercial banking system with relationship orientation to its customers, not only profit maximisation is the only goal of banking services. German banks are maintained good relationships with their customers. However, they are also rigid and unable to accept the new banking system, which has very negatively impacted the banking industry of Germany. Other states of Europe have taken advantage of this issue, they termed German banks as bad banks to the market, and they also take most of the market share of banking services, although they are not localised to Germans and their environment.
Recommendation
According to the case analysis and conclusion of this analysis, it is needed to have a proper recommendation for the banking industry of Germany. There are some models, which are used to develop some strategies according to the problems and have proper solutions to the problems. Porter’s generic strategies are one of them, which has three major parts and any single issue or strategy should be selected to give a solution. The following figure will show the true picture of generic strategies and be discussed thereafter:
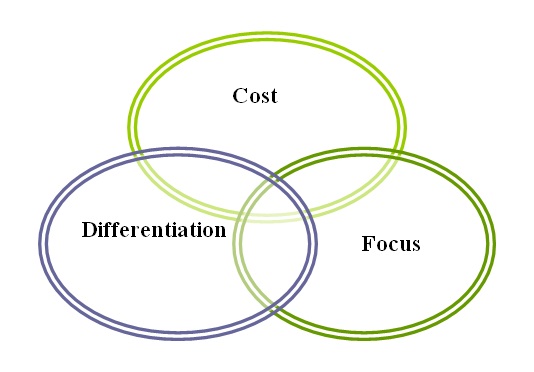
- Costs: When the industry is emphasising cost minimisation and being a cost leader in the market with low costs products and services, then the strategy is based on costs. For the German banking industry, cost minimisation is not an appropriate strategy. If the costs would lower, the services would also provide at low costs. Low costs services are low quality and assumed low value to the customers. Therefore, they should not follow this strategy.
- Differentiation: Differentiation is having different and uncommon services in the market and to its customers. This strategy is also inappropriate for the banking industry of Germany, as all banks of different states are providing almost the same services to their customers. They are being differentiated with their relationship and values are given to their customers. However, it would not recommend following as a strategy.
- Focus: The controversy of this case is mainly on legislation problems between German banking and Basel II with the adoption of a new system. The German banking industry was successful in providing its services to its customers. However, the problems occur when they are showing their inability with the new and modern banking system. Therefore, they should focus on their rigidity and be capable of changing the environment and system in the market. As German banking was successful in providing three pillars of services, so, they should continue their services with the new system, like saving banks, people’s banks, and private commercial banks. So, it is recommended to be a focus on the new modern banking system.
Conclusion
From the above case analysis on the banking industry of Germany and its controversy with regulations of Basel II, it is clear that, as Basel II is a legal and governing body for all banks, it is better for the German banking industry to maintain the newly developed banking system. On the other hand, a relationship orientation banking system would also satisfy customers in terms of flexibility and relationship build up between the customers and banking organisations. It also assures that a good banking industry is a good sign for the economic conditions of a country. Therefore, if the banking industry of Germany were stable and flexible with the legislations and relationships, it could have brought good results not only for customers and banks but also for the whole state.
Reference List
Fear, J, Banking on Germany, Harvard Business School, 2003.
Rose, PS & SC, Hudgins, Bank Management and Financial Services, 7th ed, McGraw- Hill, 2008.