Abstract
The purpose of this piece of assignment is to investigate and determine the causes of cost fluctuations. Conversely, fluctuation effects on prices that leads to customer complaints. Additionally, the paper thoroughly investigates inter departmental crisis and the solution.
Causes of costs fluctuations
For most businesses, managerial accounting plays a particularly crucial role. As a management accountant, one has the responsibility of keeping the CEO aware of the financial status of the company. Managerial accountants together with other financial consultants are the sole decision makers of the business enterprise. The direction that the business takes heavily depends on them. The Pine Products Company works with a job order system. There have been some ongoing arguments between the sales and production departments (Drury, 2000).
The conflict concerns the TC-1 outstanding order products, manufactured in batches of 1000 units sold at a cost plus a mark- up 40%. The fluctuating production units adversely affect the selling prices (Pratt, 2011). These cause difficulties for sales department to set up prices. As a result, it causes excessive customer complaints. This causes a considerable loss to the TC-1 orders. The stand of the production department is that each job order must be fully cost on the basis of the incurred cost within which the produced goods. According to the personnel department, the real solution to this ongoing crisis is to increase sales in slack periods for the sales department. (Horngren et al, 2006). The company president as requested the accountant to collect past year quarterly data on TC-1. The following are the main findings from the cost accounting system. Used the data below:
Quarter
What manufacturing cost element is responsible for the fluctuating units costs? Why?
The fluctuation of unit cost can be caused by any of the elements in the quarterly data. The following costs can be examined to determine the cause of fluctuation of the unit costs.
Direct materials
Determination of cost per unit for direct materials = total cost of direct materials / number of batches =$100000/5= $20000
First quartile: 20000*5=$100000
Second quartile: 20000*11=$220000
Third quartile: 20000*4=$80000
Fourth quartile: 20000*10=200000
If production of 5 batches in the first quarter is $100000, then the costs of direct materials in production of one batch is $20000. In the second quarter, production of 11 batches is $220000. In the third quarter, the cost of direct materials determined as $ 20000*4=$80000 while the fourth quartile given as $20000*10=200000. This means direct materials are variable costs, hence cannot cause the fluctuation of costs.
Direct labor
Determination of cost per unit for direct labor = total cost of direct labor / number of batches $60000/5=$12000. If production of 1 batches is $12000, then in the first quarter we determine the cost of direct labor for the 5 batches by: 5*$12000 = $60000. The second quarter the cost given by: $11*$12000=$132000. The third quartile; $12000*4=$48000. Fourth quartile: $12000*10= $120000. This means that direct labor costs cannot cause the fluctuation of costs as they are variable costs.
Manufacturing overheads
Determination of the cost of manufacturing overheads=total over head costs/number of batches $105000/5=$21000, therefore, as we compare with quarter table above, we see that the costs are different as follows;
First quartile: $21000*5=$105000
Second quartile: $21000*11=$231000
Third quartile: $21000*4= $84000
Fourth quartile: $21000*10=$210000
This means that manufacturing overheads are semi- variables. Therefore, the overheads do not depend with the number of batches produced. They are incurred irrespective of the number of units produced. Therefore, the overheads are the cause of fluctuation of the unit costs (Pratt, 2011).
What is your recommended solution to the problem of fluctuating unit costs?
In my opinion, I recommend the company to produce equal 10 batches 3 times annually. As a result, more savings of the semi variable manufacturing overheads would be realized. The condition is that the products are not perishable. This would solve the problem of fluctuating costs as the new cost per batch will be $44500. The overall selling price will also be stable after adding a mark up of 40% on cost. Therefore, there will be no more customer complaints (Drury, 2000). Additionally, the conflict between sales and production departments gets solved.
Restate the quarterly data on the basis of your recommended solution?
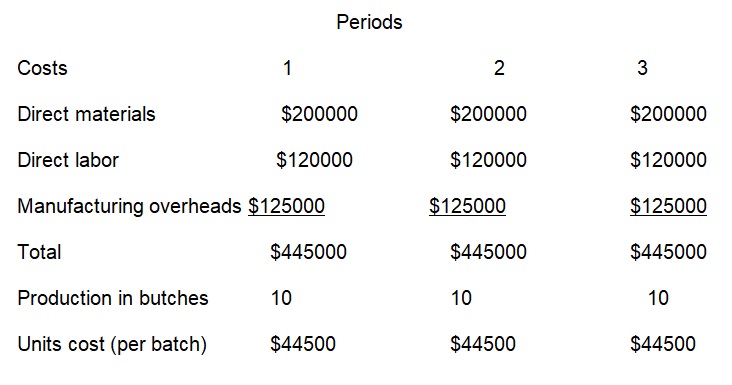
The company should spread out the batches produced within the three periods each producing 10 batches to save on the semi variables manufacturing overheads (Pratt, 2011).
In conclusion, for the companies to avoid inter departmental wrangles, as well as customers complaints, it should come up with sound cost policies and strategies. The policies should aim at avoiding extra costs and the overall price fluctuations (Kieso, 2012). The policies and strategies should be formulated by management accountants and other financial advisers or business stakeholders. By doing so, this facilitate profit maximization and, at the same time, reducing costs and other factors that may cause price to fluctuate.
References
Drury, C. (2000). Management & Cost Accounting (5th ed.). London: Thomson Learning.
Horngren, C. T., Datar, S. M., & Foster, G. (2006). Cost accounting(12th ed.). Upper Saddle River (N.J.): Prentice Hall.
Kieso, D. W. (2012). Study guide to accompany Managerial accounting (6th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Pratt, J. (2011). Financial accounting in an economic context (8th ed.). Hoboken (N.J.): Wiley.