Introduction
The case study is based on an entrepreneurial venture called the Chainaya Lozhka belonging to the fast food restaurant chain of Russia. The company has been doing well in the highly competitive Russian fast food market, and was now planning to expand its operations. The decision to expand was initiated when the two founders of the company saw that the organization’s annual sales figures and saw that it has gained immense success in St. Petersburg.
However, expansion required a lot of changes that had to be ushered into the company, which so far was being run from a two-man decision-making level at the top. The changes that will have to ushered may change the whole culture and structure of the organization, and if not successfully implement, may cripple the future of the company. Therefore, it was important to understand the steps and strategies that the company can take in order to go ahead in the path of expansion, if at all they should expand.
It is believed that there are both “strengths and weaknesses in the expansion” of a firm (Kaufmann 1972, 85). Therefore, expansion for any company is important in a competitive environment in order to grow. Therefore adopting expansion and hence, change is important for Chainaya Lozhka. However, most change management endeavours become ultimate failures (Aiken 2009). As research by Kotter suggests, only 30 percent of the change management initiatives succeed (cited in Aiken 2009) therefore, making a change management initiatives even more difficult and risky affair.
In case of small entrepreneurs, it becomes even more difficult as there is a change in the way the whole company works. Therefore, in this case study analysis, some issues and challenges related to expansion and change are discussed, along with a few possible solutions for the company to go ahead in its expansion plans.
Issues related to Chainaya Lozhka’s Future
Some of the problems that are foreseen as possible issues for the company in its operations as well as expansion plans in the food industry in Russia are discussed. A few of the environmental issues affecting the company are discussed in this section. Russian fast food industry is at a nascent stage. The growth of the fast food industry in the country and its yet unexploited potential has attracted many international fast food giants like KFC and McDonalds in the country.
As has been mentioned in the case study, the main fast food demand in the Russian market is of pancakes. The unsaturated Russian market in Moscow could be around 25 percent in outside Moscow at 15 percent. Fast food market comprised of the large chunk of the restaurant business in the country. Therefore, fast food industry was one of the quickest growing market segments. Further, the restaurants in Russia showed a tendency to flow from cities to suburban areas.
The reason for this is the increase in the income of the people living in the suburban areas. Further, the problem of commercial real estate in cities pushed the restaurants to the suburban areas and in malls and arcades. Further rents in the cities were higher than in the suburbs. Therefore, due to low profitability for smaller chains in the cities, a move towards the suburban areas was a better proposition. Therefore the infiltration of the American fast food chains in the Russian market could be reduced through the development of small establishments, at a cheaper and more affordable prices, in the suburban areas where the bigger chains had not yet approached, was a possible issue that faced the Russian fast food restaurants.
Another issue that was a problem for the Russian fast food restaurants was the menu option that could be offered to the customers. The American fast food chains offered pizzas, burgers, and hotdogs. Therefore, the issue faced by the Russian fast food retailers was what menu choice they could offer to the customers. Pancakes were a possible option as pancakes was a local food with different variants available, and could be easily served with tea or coffee. Therefore, a market research conducted by the company confirmed that the serving could be pancakes. The main idea for a good fast food retail was to serve a basic menu item which was inexpensive, and the items were desirably close to the Russian tradition.
Apart from the menu issue, the other issue was to develop an ambience for the restaurants. This related to the interior furniture and building the ambience of the restaurant. Further creation of additional value to the customers was another issue that was faced by the company. Thus, as in the menu, even the restaurant ambience captured the national style in a futuristic traditional design. The other issues that were considered were the table turnaround time that should not be too high for fast food restaurants. Further, many of the fast food sales were more impulsive than planned; therefore, display and customer attraction tactics had to be employed. Further identification of the target market as well as the menu and tea quality acceptance for this group was another issue that had to be answered.
As the company aimed at becoming a tea house, and there were many impediments in its operations, therefore it was important to understand what role an expansion and change would do to the company. The main issue faced by the company was expansion and change, therefore, the management had to plan strategic change implementation, rather than ushering in an unstructured change process in the company. Therefore, the main issues related to the change process are related to planning the change.
Most companies undergo change without planning for it (Robbins 2007, 383). Therefore, the issue related to the change management process was to plan the change process. The aim of planning the change process is to keep the organization sustainable and viable. In order to grow in business, change in inevitable and leading the organization through the right change process is important (Coulson-Thomas 2009, 33). For a change management process forces the organization to undergo change in the culture and working practices. Further expansion would imply that the company must undertake standardization and specialization in order to deliver same quality throughout its chains. Given these issues, it is now important to understand the challenges ahead of a change management in the company.
Challenges in Change Management
Most of the change management initiatives are a failure (Aiken 2009). Kotter (1996) has pointed out the reasons why firms fail in change management processes. One of the main challenges for change management is too much of complacency (Kotter 1996, 4). This actually results when organizations plunge in to a change process without establishing the required background study for establishment of the change process. This implies that the “transformations always fail to achieve their objectives when complacency levels are high” (Kotter 1996, 4). This is a challenge for Chainaya Lozhka as the company has been doing very well in its current form, and a sudden change into a wider and bigger chain may cause problems for the company and endanger its survival.
The second issue for change management is to have the support of the top management. In the case of Chainaya Lozhka, the founders and the executive heads of the company were the initiators of the idea of a change process. Therefore, support from the top management of the company was not an issue.
A proper vision for the change management process is necessary. A vision creates the future goal for any process. In case of change processes, it helps in giving an animated shape to an inanimate idea, and therefore gains better acceptance and implementation. In case of Chainaya Lozhka, it is important to build a vision for the change management process. The two founders of the company have an idea, however, to make it a shared visions, for themselves as well as the rest of the company in important. Chainaya Lozhka must have a strategic goal as the expansion plan and the change process are closely intertwined with the company’s vision to become bigger through expansion.
The other issue is related to the culture of the organization, as the change process is set in, a corporate culture too must be changed in order to make the change process more acceptable to the internal stakeholders. These challenges are important for Chainaya Lozhka as the organization was incorporating a predominantly western concept of fast food retail chains. Whereas Chainaya Lozhka was trying to become a fast food restaurant chain with a predominantly Russian cultural traits ingrained in the organization.
Therefore, a change process will require greater control mechanism. Further, the two founding heads of the company, so far, established the corporate culture. However, when the company grows bigger, the corporate culture too becomes wider for acceptance. For instance, high level of integration of Chainaya Lozhka may become a challenge for the company while initiating a change process as the change was inclined toward further expansion of the company. Therefore, the company must strive to develop a sustainable culture for a successful business model.
Further, the other challenges that might be faced by the company are increasing competition from the competitors as more international fast food chains were entering the Russian market, due to its growth prospects. Therefore, high competition may become a deterring factor for change within the organization, as the company may face lower revenues in terms of stiffer competition. Given these challenges that the company might face due to a change initiative, the next section will deal with the strategy that is required in face of change.
Strategies to Manage Change
Peter Drucker states, “One cannot manage change. One can only be ahead of it.” (Drucker 2007, 62) However, in order to move ahead of the wave of change change, Drucker points out that policies and systematic methods to anticipate change in the future must be gathered, in order to introduce change initially and then balance the process and ensure continuity (Drucker 2007, 62). Therefore, the first question that arises in case of Chainaya Lozhka is that if it should undergo a change process.
Chainaya Lozhka should undergo a change process. Change is a necessary element for making the organization move forward and expands (Graetz and Smith 2009, 11). It is an essential part of business continuity. Given the growth potential in the Russian market, it is important to expand, as the market is attractive to new entrants. Strategy is an integral part of any change process (Pettigrew 1992, 5). The strategy process that the company can employ is to introduce franchising of the retail outlets to the suburban regions of St. Petersburg and Moscow. The reasons for these are derived from the external environment analysis of the fast food industry in Russia. The key findings and indicators for the decision are as follows –
- There is greater growth in the suburban market of Russia for fast food chains. The suburban market is also less exploited and unsaturated.
- The income in the suburban areas has been increasing.
- The real estate problem and identification of a good commercial properly in the urban area is a problem, which is not a hindrance in suburban areas.
The above three reasons were the deciding factors for the decision to undergo an expansion process. Apart from this, there has been extensive academic support fro this decision, as researches have shown that in order to grow, expansion, and therefore change is desirable (Lewin and Kim 2004, 325, Floyd 2005, 45). The main competitive strategy that Chainaya Lozhka must employ is differentiation with their Russian culture inclined menu and ambience offering.
The strategy of the organization therefore should be to continue its main menu, which is different from the international fast food chains and holds the Russian national culture close to its restaurant decorations as well as in its food offerings. This must be standardized in all the restaurants across Russia. The emphasis on national culture in the change process is important as change strategy can be helped by using the national culture (Lewin and Kim 2004, 351).
In case of organizational change, Robbins has provided a framework for the establishment of the change process (Robbins 2007, 385). This framework is used in case of Chainaya Lozhka. The change management process can be shown through a flow diagram adopted from Robbins (Robbins 2007, 386). The diagram shows that the identified changes that are required in Chainaya Lozhka are in its structure, culture, and operations. The reason being, Chainaya Lozhka so has been operating solely in St. Petersburg. However, now with plans of expansion, these areas must be changed in order to accommodate greater capacity.
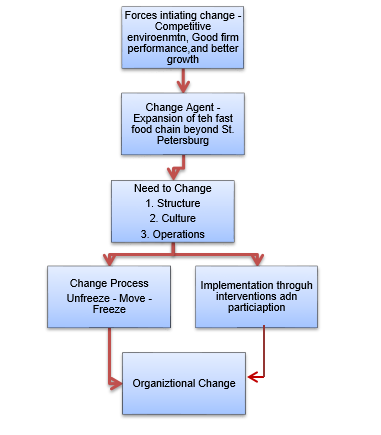
Chainaya Lozhka so has been running in an entrepreneurial model. The company heads took most of the major decisions. The culture of the company and the policies were decided by these two people, and were heavily influenced by their decisions. With expansion, the control of power of the company would shift from the two heads to the smaller franchisee heads of the company. However, on e important aspect that had to be established was acceptance of the corporate culture in totality in all its retail outlets in order to standardize its environments.
The other change component of the organization would be its structure. The need to change the structure is due to the expansion process of the organization (Bobbitt and Ford 1980, 16). So far, the company succeeded in two heads operating as two decision-making divisions working independently. However, as the company grew there would be needed to have greater alignment in all the business processes. Therefore, independent operations would not be possible. Further, the company’s unique structure of two organizational units may become a hindrance to the changed organization. For a smaller company, operating as two different units is possible, as Chainaya Lozhka traditionally did. However, for a bigger company, greater coordination was necessary.
The corporate culture of the company was enforced by the two heads Boris Krupkin and Mikhail Avgustin, through different corporate communication process. Therefore, in order to implement the change process, the company must implement a proper deliverance of the change implementation and the expected short term wins to the company employees in order to increase their preparedness for the change process (Templin 2009, 20). Therefore communicating the change plan to the employees is dubbed to be one of the most important stages of change process (Kotter 1996, 6). Therefore, change management process can be established in the above mentioned strategies.
Future Structure
The future structure of the company that can be employed by Chainaya Lozhka is presented in figure 2. Research has shown that when organizations are small, centralized organizational structure are helpful in controlling cost. However, as the company expands, a more decentralized structure should be appointed (Lewin, Weigelt and Emery 2004, 128). Therefore it is suggested, that as organizations expand, they can employ different structures in different divisions or units of the organization. Therefore, the suggested organizational structure for the organization is in figure 2.
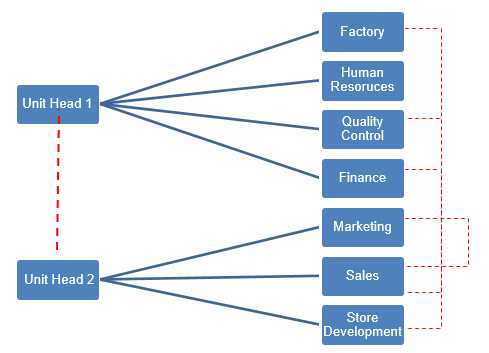
Figure 2 suggests that the sales department should be moved from the unit 1 of the organizational division to the second organizational unit. This is so because there is greater coordination between marketing. Further in order to increase interlinings between the departments in order to increase coordination between the organizational departments. Thus, Chainaya Lozhka must become a more decentralized organization with greater coordination.
Reference List
Aiken, Carolyn, Keller, Scott,. 2009. “The irrational side of change management.” McKinsey Quarterly no.2. Web.
Bobbitt, H. Randolph Jr., and Jeffrey D. Ford. 1980. “Decision-maker choice as a determinant of organizationai structure.” Academy of Management Review vol. 5 no. 1: 13-23.
Coulson-Thomas, Colin. 2009. “Leading and managing change.” Change Management Services: 31-37.
Drucker, Peter Ferdinand. 2007. Management challenges for the 21st century. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Floyd, Steven W. 2005. Innovating strategy process. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Graetz, Fiona, and Aaron C. T. Smith. 2009. “Duality theory and organizing forms in change management.” Journal of Change Management vol. 9 no. 1: 9-25.
Kaufmann, Othmar. 1972. “Strategies of expansion and organizational developments in European and American firms.” Journal of Management Studies vol. 9 no. 1: 82 – 96.
Kotter, John P. 1996. Leading change. Harvard, MA: Harvard Business Press.
Lewin, Arie Y., and Jisung Kim. 2004. “The nation state and culture as influence in organizational change and innovation.” In Handbook Of Organizational Change and Innovation, by Marshall Scott Poole and Andrew H. Van de Ven, 324-353. New York: Oxford University Press.
Lewin, Arie Y., Carmen B. Weigelt, and James D. Emery. 2004. “Adaptation and selection in strategy and change.” In Handbook Of Organizational Change and Innovation, by Marshall Scott Poole and Andrew H. Van de Ven, 110-160. New York: Oxford University Press.
Pettigrew, Andrew M. 1992. “The character and significance of strategy process research.” Strategic Management Journal vol. 13: 5-16.
Robbins, Stephen P. 2007. Organization theory – structure design and application. London: Prentice Hall.
Templin, Paul. 2009. “Preparing people for change.” Industrial Engineer: 20.