- Corporate-business-functional strategy
- Strategy effectiveness in achieving strategic and operational goals
- Strategy change expectations in the future
- Competitive factors that affected the timing and outcome of decisions
- Financial factors that affected the timing and outcome of decisions
- Total liabilities, equity, and cash comparison
- Work Cited
Corporate-business-functional strategy
It is sad that many organisations fail to make strategies until an emergency strikes, which is met with much opposition. As a result, Chester settled on corporate-business-functional strategy that included three levels of management.
To start with, corporate strategic level defines the market situation of the products. Much survey was done in order to come up with diversity of goods especially new good which were distributed to different geographical markets. Business strategic level sought to navigate the market situation in terms of competition.
In fact, this strategy made changes that made the company to have more competitive benefits over the other products and in the market. Lastly, functional strategic level did support the activities carried out by corporate and business strategies. This strategic level employed the contributions of information systems, labour as well as production processes to fulfill the activities of business and corporate strategies (Thomas 1).
Strategy effectiveness in achieving strategic and operational goals
Initially, the goods met a lot of competition but Chester decided to maintain its traditional segment as it was providing the greatest amount of positive cash flow, until funds were available to expand market share within the industry. To penetrate into the market with all the products offered by Chester, the supply was monitored so as not to exceed demands while still offering a competitive price.
The modern nature of Chester aimed to produce and sell goods that fulfilled customers demand on technology based products. With improved technology, the company through internet services such as emailing and social sites received orders online. This allowed the company to make more sales to customers online which excluded the middlemen hence minimizing costs.
Strategy change expectations in the future
This strategy helped in determination of the long-term changes of the organisation under the corporate level. At this level, organisational planning, diversification and specialisation of the company occurred. “Chester developed policies aimed at becoming and maintaining the lowest cost distributor in the industry under strategies based on Cost-leadership” (Thomas 1). Since this company was venturing into market, it enjoyed advantage of selling unbranded products as a start.
Differentiation is yet another strategy that reduced firm’s products susceptibility to cost forces impacted by competitors. The uniqueness to customers attracted their attention and willingness to pay extra to have the product that met their demands. Focus plan assured the organisation victory over certain customers through basing their production on particular system in a given geographical area. The company was strict on the channels of distribution and each stage of production process.
Under functional level we efficiently incorporated experts who improved the organisation through advertisement, promotion, and marketing research. This was carried out in marketing, inventory control, and shipping production activities. This allowed functional strategies interconnect with other levels and to sum up, this level purposed to increase sales and to make the company outdo the other companies (Thomas 1).
Competitive factors that affected the timing and outcome of decisions
Competitors dominated a segment of these sales. The company must have lost battle to their competitors since the inventory records exceeded the minimum requirement of $2 million. It was unfortunate that the situation was not adjustable at the time when this simulation was done.
In conjunction, there was imbalance that posed risk of losing customers to our competitors since stock outs against the expenditure of carrying additional inventory could not meet demand expectations. Given the employed information systems, the company was able to reach more customers who increased our sales. In addition, this must have motivated us to produce more since there was ready market. Some competitors who kept their traditional means of production might have faced a low production (Thomas 1).
However, this overwhelming production might have exceeded the inventories. This in response discouraged some customers who opt to buy from other organisations. The stock price complicates future profitability of the organisation. For instance, liquidation of plant might have brought in cash though shareholders who may wonder about the long term competitive consequences.
Financial factors that affected the timing and outcome of decisions
It is evident that if inventory exceeds more than a sixth, there is a possibility of expending more cash that would have declined the performance since the organisation had to obtain emergency loans. These loans are known to have reduced the profit margin.
The company optimistic nature led to surplus in market segment. Had our company exceeded the average product, our sales would have increased. Average product is a key factor on demand level since the demand average requirement should range from 50% to 150%.
From the cash flow statement it was evident that the company had many liabilities that reduced the cash flow. These liabilities almost summed to same ratio to assets in all rounds. Had this ratio been less in favour of liabilities to assets we would have expected a higher ranking.
It was observed that the ranking would have been better since in this duration, the stock prices raised by $9.38, which might have been attributed to performance, asset base, debts among others. Quest to expand and automating the organisation might have increased difficulties in debt piling to shareholders. Excess stock price more than $15.00 signifies danger of high debts, loss of market share due to price adjustment and loss of 1 year of production of a new product.
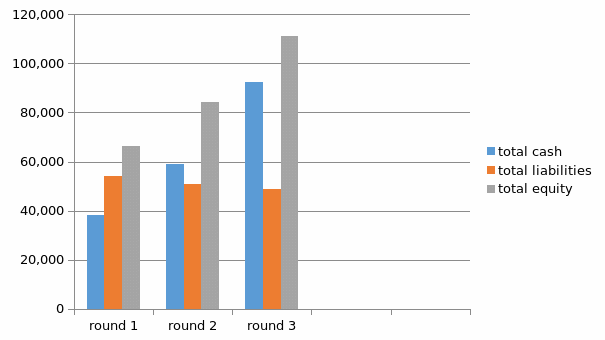
Total liabilities, equity, and cash comparison
Work Cited
Thomas, Joe. “strategy levels.” Encyclopaedia of business, 2nd ed. Referenceforbusiness. n.d. Web. <www.referenceforbusiness.com/index.html>