Abstract
This paper gives insight into the strategic measures undertaken by Chipotle Mexican Grill in the aftermath of the E. coli outbreak that affected its competitiveness and subsequent performance in the American market. It aims to identify the strategies used by the company after the 2015 disaster and evaluate the effectiveness of those strategies. The paper begins by giving a brief introduction of strategic management concepts appropriate to the case. In the proceeding sections, the essay analyzes Chipotle’s key profitability factors and its customer retention strategy. An analysis of how the company can grow its consumer base will be provided as well. The company’s SWOT analysis and profitability approach, ethical and sustainability issues, and the best practices in the sector will be discussed in the essay. Finally, the paper makes concluding remarks about the discussion made.
Introduction
Organizations in all sectors of the global economy aim for sustainable success. Often, this calls for the formulation of effective strategies in the company or organizational operations. In their famous strategic management book, Thompson, Peteraf, Gamble, and Strickland (2014) define strategy as the measures employed by an organization to tame the competition posed by its rivals while at the same time ensuring it attains optimum profitability. According to Thompson et al. (2014), the strategy adopted by an organization determines both its short- and long-term performance. Towards this end, strategic management can be defined as a wide aspect of organizational leadership that deals with the attraction of customers, positioning in the marketplace, competition, and response to economic and market transformations, among others (Thompson et al., 2014).
The implication suggested is that strategic management encompasses all aspects of a company’s operations from the time it enters a particular market. Therefore, using the economic insights provided by Thompson et al. (2014), it is possible to analyze the performance sustainability of any company in any industry. It can be argued that sustainability goes hand in hand with client/consumer retention. Chipotle has tried to increase its consumer base after the E. coli outbreak using various strategies. One strategy that has worked well for Chipotle is the constant communication of actions they took to avoid such an outbreak in the future. This paper evaluates the management strategies employed by Chipotle Mexican Grill (referred to in the essay as Chipotle) in the aftermath of E. coli outbreak that affected its operations in several states.
Overview of Chipotle Mexican Grill
Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. is an American multinational casual fast-food restaurant headquartered in Newport Beach, California. Other countries of operation include Canada, the United Kingdom, France, and Germany. By 2018, Chipotle had a total of 2,500 outlets located in different countries and annual revenue of $4.8 billion (Appendix A). Additionally, the company operates as CMG in the New York Stock Exchange. Owing to its reputation as a leader in the restaurant sector, Chipotle’s activities are of great interest to the general public and institutions that regulate the food industry ̶̶̶̶̶ such as the FDA. Hence, the outbreak of E. coli bacteria affected the company’s strategic position in the sector. The following sections of this paper draw insights from Thompson et al. (2014) to explain the effectiveness of the company’s strategy after the unfortunate occurrence.
Key Success Factors and Customer Retention Strategy
Chipotle is undoubtedly one of the household names in America’s restaurant sector. It competes with giants like McDonald’s. Moreover, there has been a steady increase in the company’s stock prices – from $42 (in 1993) to around $650 (in 2019) (Chipotle, 2019). This implies that the company is a viable investment opportunity. Therefore, this section examines the success factors that have made Chipotle successful and the strategies it put in place to retain its customer base even after the outbreak of E. coli in its outlets in 11 states.
Corporate Ownership
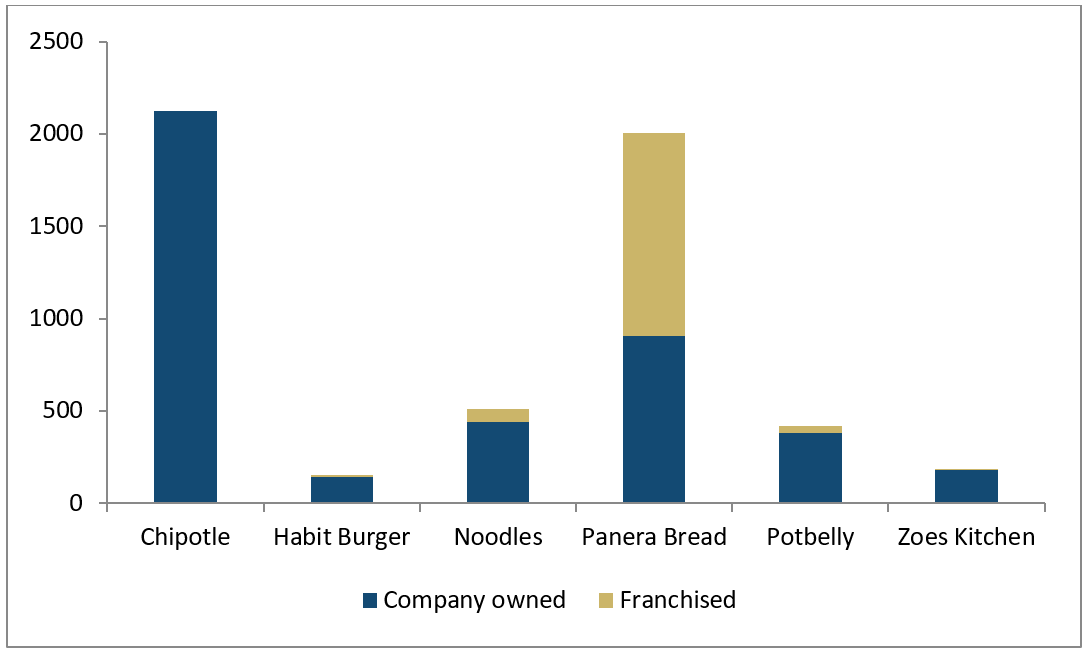
Part of Chipotle Mexican Grill’s success can be attributed to the fact that the company is corporately owned and has no franchises (Appendix C). Corporate ownership is integral to defining an organization’s management strategy. According to Thompson et al. (2014), an organization’s strategy provides a roadmap on what the company should do and not do to leverage competitive advantage. Therefore, at the heart of every strategy are the values held by the company’s owners and the projected vision for its sustainable performance. When Steve Ills started Chipotle in 1993, his goal was to transform the restaurant sector by offering fresh products with fresh ingredients (Chipotle, 2019). Therefore, Chipotle is a corporate-owned company because Ills wanted to retain control over its leadership, supplies, and organizational culture. Strategically, Chipotle owns all its stores in all the countries it operates. This ensures that the company has control over the design and operations of all its outlets.
Chipotle Sells Food with Integrity
Branding is an important marketing strategy as it dictates the perception of the target audience about a given good or service. Customers are often attracted by the company’s slogan, other than the name and logo, as they depict the inherent organizational culture (Chipotle, 2019). Unlike Chipotle’s competitors in the industry, Chipotle ensures that it uses fresh, non-GMO, and organically produced ingredients to make healthy food for its customers (Chipotle, 2019). The assertion is that the company is banking on its market differentiation strategies to leverage competitive advantage in the sector.
As per the mentioned slogan, Chipotle employees are trained to retain the quality of food produced in the company’s restaurants in and outside the United States. Notably, Chipotle is implementing Thompson et al.’s (2014) position that business strategy is all about being different from the rest. The authors contend that organizations that emulate other successful companies are likely to fail due to the lack of a specialist approach that relates and attracts customers. In the contemporary world that is characterized by organizational homogeneity, especially in the production sector, the emergence of specialist organizations is almost inevitable. Hence, Chipotle used the same approach to grow its customer base. Moreover, it is worth noting that a majority of people in the United States are now embracing healthy eating to avoid common lifestyle diseases like high blood pressure. Therefore, Chipotle’s management crafted a strategy that stresses the use of healthy ingredients to promote healthy living.
Going by the above, it is apparent that Chipotle’s success momentum and up-surging financial performance was shaken by the outbreak of E. coli bacteria that sent shockwaves and panic in most parts of the United States. Hence, the strategic measures employed by the company’s leadership were to determine the company’s profitability and competitive positioning in their external market. Although the incident damaged the company’s reputation, Chipotle was relieved when the relevant regulatory institutions assessed the situation and concluded that the company would go on with its operations as usual. According to Thompson et al. (2014), the strategic management choices made at such a point of an organization’s existence determine its future survival.
The Company Has a Small Menu with an Array of Choices
The third success factor for Chipotle is the fact that the company has a small menu that enables it to stock the right ingredients. As a result, the company does not allow spoilt ingredients to be used in the production process. This approach also helps the company avoid the losses caused by wastage. Based on the E. coli incident, one might argue that this strict policy was violated by some of the company’s stores, and this compelled the management to debate on the relevance of a policy change to ensure the company’s profitability after the health care.
Another merit of small menus in restaurant settings is that they are easily distributed through various customer information channels. Indeed, customers are aware of what the company has to offer when they visit as they can easily get their menus on different platforms. As a result, Chipotle does not have to spend a lot of money on the advertisement for new meals as it is known for its classic culinary packages. Although this approach may seem redundant in terms of organizational growth, the company has flourished under this strategy. A diversion in policy is probable in the future, but this will depend on the values of the leaders in charge and the existing organizational culture at the time of change. Nevertheless, the E. coli outbreak could serve as the precedent upon which the right policy is implemented. This suggests that future leaders must prevent a repeat of the incident by all means – even if it means retaining the small menu.
Customer Retention Strategy
Attracting consumers is not as difficult as ensuring customer loyalty. Customer retention is a complex process that requires organizations to develop the right strategies that can be used to convince clients to keep buying their products. According to Thompson et al. (2014), one of the business approaches that define a company’s strategy involves actions that can offer goods and services at the lowest prices and at the lowest possible costs. Chipotle Mexican Grill’s customer retention strategy is to maintain the quality of its products. This is arguably the practice of most companies in the restaurant sector. Thus, although Chipotle might not be able to offer lower prices for its products, the company has succeeded in maintaining a market share consisting of royal customers due to their quality. Again, the incident of food poisoning has negatively affected the company’s future success in the market, as it also affected standards of quality. There are several ways in which such a reputation can be built back. However, it is important to note that the way the company handled the situation ensured that a majority of its loyal customers remained committed to the brand.
Chipotle’s SWOT Analysis and Profitability Strategy
SWOT Analysis of Chipotle Mexican Grill
Customer retention is a strenuous process that requires organizations to develop the right strategies that can be used to convince clients to keep buying their products. According to Thompson et al. (2014), one of the business approaches that define a company’s strategy involves actions that can provide the lowest prices at the lowest possible costs.
Strengths
The first area of strength is the company’s financial standing. Chipotle is debt-free and has a healthy cash flow that could see the business progress well in the coming years. As of 2016, for example, just one decade since its IPO, the company had over $1 billion in cash and investments. Even so, the E. coli outbreak reduced the price of the company’s shares.
Secondly, Chipotle has witnessed accelerated growth since 2006. In 2006, for instance, the company had just above 500 restaurants in the United States. This number has grown five times, and the company now boasts of more than 2,500 outlets around the world. Nevertheless, the company’s performance in the aftermath of the E. coli outbreaks reduced by approximately 36% (Taylor, 2019). Even so, the market returned to normalcy, and customers who had developed some reservations about the company’s products returned. The strategy employed by the company’s leadership at the time stresses the importance of patience in crisis communication as it gave the relevant agencies time to investigate the matter and come up with accurate findings for appropriate action.
Weaknesses
The foremost weakness of Chipotle lies in the sensitive quality of its ingredients. Since the company has differentiated itself in terms of the freshness of its ingredients, hence, products, any hitches can adversely affect its viability in the market. The outbreak of E. coli, for example, resulted in the stalling of the company’s normal operations. It is important to note that Chipotle operates in a sensitive industry that is prone to constant regulation by the relevant authorities. However, the most important thing to the management is to regain the lost reputation and convince customers to continue buying their products. As such, policies must be put in place to ensure that the strategies adopted to curb this weakness close such problems that may occur in the future. Secondly, Chipotle overly relies on the US market. Although it is a multinational company, 99% of the company’s operations are based in the United States (Taylor, 2019). This is a dangerous precedent as the demand for its products depends largely on discretionary spending. With the current uncertain global economy, the vitality of the business in the US could be subject to the country’s macro-economic factors, and the company must implement a strategy to counter this impact.
Opportunities
The restaurant industry is booming in the United States and other parts of the world. This is an opportunity for Chipotle to expand its operations by opening new stores that offer fresh, healthy products to the public. For instance, an international expansion strategy should be embraced by the company to tap into the vast markets in Europe where people have high disposable income that can match the cost of its products.
Moreover, the company’s competitors, such as McDonald’s, have successfully ventured into emerging markets in Asia and Africa. As highlighted earlier, the objective of any organization should not be to emulate rivals and their strategies but to develop differentiation strategies that distinguish them from other players in the industry. Therefore, Chipotle can make use of the unlimited global market while still sticking to its quality and health standards that are necessary for customer retention.
Threats
The casual fast food industry is increasingly becoming competitive in the United States and around the world. There are hundreds of restaurants like Chipotle in the US and abroad that concentrate on healthy foods with low carbohydrate and fat contents. Moreover, other organizations are pursuing the lower-cost strategy that is yet to be considered by Chipotle. This implies that the competitive environment is likely to impact the company’s profitability in the industry as there are already incumbent giants with a high market presence. Secondly, more food safety issues could make the situation worse for Chipotle. Already, the company has suffered from the E. coli outbreak, and should any other case be reported, its reputation and initial customer confidence will be at stake. This compels the company to undertake regular training of its staff in all its stores around the world. Hence, this strategy must be part of the company and implemented by all future managers.
Profitability Strategy
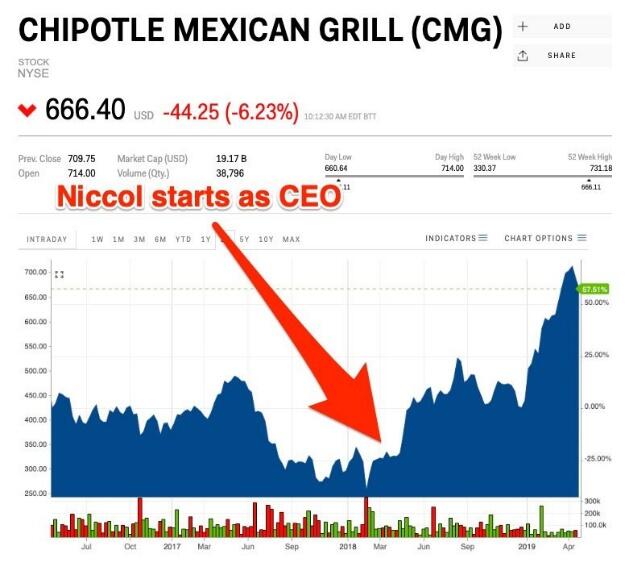
Due to the 2015 E. coli disaster, Chipotle’s performance deteriorated in 2016. Last year, Steve Ills, the founder of the company, appointed Brian Niccol as the new CEO to drive the company’s strategy to the next level. This shift in leadership saw the appointment of Brian Niccol in March last year. In her article published in the business insider, Taylor (2019) attributes Chipotle’s 9.9% growth in sales to the strategies employed by the former Taco Bell CEO. For example, part of Niccol’s reawakening strategies involved the introduction of new menus using similar ingredients; the incorporation of mobile app shopping that is coupled with free delivery; and enhanced marketing campaigns.
This move is in tandem with Thompson et al.’s (2014) argument that sometimes organizations must become aggressive and employ strategies that will enhance their market position. Of the four strategies, the emergence of a mobile app where customers can order their favorite recipes from the restaurant and get free delivery services are the most prominent strategies that have helped the company stabilize since the outbreak. As Taylor (2019) points out, free delivery services enhanced the shopping convenience of customers who got their orders delivered with a mere click of a button. In the modern world that is defined by enhanced digital technology, the majority of people in the United States have access to smartphones. Arguably, Niccol employed this strategy to maximize the unexplored market.
The introduction of new menus is, by all means, an innovation strategy that Niccol integrated into the company’s organizational culture. When Ills was at the helm of the company, the company did not focus on the development of new products as customers knew what they would get from the restaurant. Niccol’s explorative approach was successful because the chain’s loyal customers and new came on board despite the addition of new recipes using the same ingredients Chipotle has used over the decades. As shown in Appendix B, one can conclude that Chipotle’s profitability strategy is embedded in the company’s revamping efforts spearheaded by the company’s current CEO, Brian Niccol.
Chipotle’s Ethical Standards, Social Responsibility, and Sustainability Approach
Apart from making profit and offering value to customers and returns to shareholders, business organizations are also obligated to fair competition, living up to the ethical standards of the societies in which they operate, and giving back part of their resources for the betterment of society (Thompson et al., 2014). This section gives insight into the concepts of business ethics, social responsibility, and sustainability from the perspective of Chipotle Mexican Grill.
Chipotle’s Ethical Standards
Thompson et al. (2014) define business ethics as “the application of ethical principles and standards to the actions and decisions of business organizations and the conduct of their personnel” (p. 255). According to the authors, it is impossible to distinguish ethical issues in business from the conceptions of right and wrong in the wider society. Indeed, an organization must develop an ethical culture that does not deviate from the universal norms held by the societies in which the organization operates. For example, it would be deemed dishonest for Chipotle to use ingredients that have been frozen for weeks and claim to offer fresh, healthy products to its customers.
There are several ethical standards that are currently confronting Chipotle, as identified on the company’s website. The company’s code of conduct comprises of four sections which include a statement of integrity, Anti-Discrimination and sexual harassment policy; it is the law and Chipotle’s confidentiality. Through its integrity statement, Chipotle insists that it is a company based on integrity, honesty, and straightforwardness – committed to always doing the right things. This being the culture of the company, all employees, managers, and board of directors must work as per the set Chipotle standards (2019). For example, employees are prohibited from receiving gifts from competitors, suppliers, or customers. Moreover, staff of the company is allowed to undertake outside business that does not affect the company’s performance. Overall, the entire code of conduct focuses on the aspect of integrity and honesty, virtues that have differentiated the company from its rivals.
The 2015 E. coli outbreak triggered doubts about Chipotle’s commitment to ethical standards. Although the damage has already been done, it is indispensable for Chipotle to employ strategies that can help it regain lost glory. The only way the company can do this is by being consistent in the provision of high-quality products. This approach will not only indicate that the company has moved on, but it will also enhance customer loyalty and the company’s turnover.
Chipotle’s Social Responsibility
The discussed ethical standards can be applied to ensure social responsibility and sustainability. The concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has become an acceptable aspect of the operations of most companies in major industries. It is based on the idea that organizations should take into account the interests of all its stakeholders, including the society in which it operates. Simply stated, an organization must be well-equipped to better the lives of the people living around its factories or facilities. According to Thompson et al. (2014), CSR is defined as “A company’s duty to operate in an honorable manner, provide good working conditions for employees, encourage workforce diversity, be a good steward of the environment, and actively work to better the quality of life of the local communities where it operates and in society at large” (p. 268).
The above definition indicates that a company’s responsibility is not just limited to the immediate stakeholders that affect its operations, but it cuts across all segments of the wider society. Therefore, it is fit to look into the CSR issues related to Chipotle, a casual fast-food restaurant that is committed to the provision of healthy recipes to its customers. When Steve Ills founded the company in 1993, he had a vision of creating a healthy restaurant that is favorable to people’s health. This implies that the company was concerned about society at the time of its launch in 1993.
With the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases increasing in the United States and the continued reference of fast foods with unhealthy eating habits, Ills had to change his strategy to ensure the realization of his vision for Chipotle. Overall, Chipotle has not been proactive in regards to its CSR strategy. In a 2015 article in The Guardian, Marc Gunther argued that Chipotle is accused of constantly refusing to publish its CSR reports like other players in the industry, such as McDonald’s. In a rebuttal, officials from the company contend that it channels most of its resources to sustainability efforts (Gunther, 2015). The implication here is that Chipotle is not concerned about its corporate social responsibility. Arguably, this can affect its future market presence and performance sustainability.
Environmental Sustainability
Like CSR, business sustainability is another pertinent issue affecting many organizations. Before starting a business, it is incumbent of an entrepreneur to analyze its sustainability. Thus, any new business should be able to meet the market’s current needs without impeding on the ability to meet future needs. When looking into the concept of business sustainability, the aspect of environmental sustainability has to be considered. As described by Thompson et al. (2014), an organization’s environmental sustainability strategy “consists of its deliberate actions to protect the environment, provide for the longevity of natural resources, maintain ecological support systems for future generations, and guard against ultimate endangerment of the planet” (p. 275). Since Chipotle’s objective is to remain sustainable for the future, it is critical to note that the company’s sustainability efforts span across the people and the environment in which it operates. With the debate on climate change raging on, Chipotle is committed to being an advocate of environmental sustainability by developing production strategies that preserve the natural environment for the sake of future generations.
Best Practices and Customer Confidence
Thus far, it is apparent that Chipotle Mexican Grill’s reputation and market share were adversely affected by the E. coli outbreak in 2015. The company has been struggling to revamp its operations by implementing strategies geared towards regaining customer confidence. Although one can infer that the progress towards this end is positive, more needs to be done for Chipotle to compete effectively with its competitors. According to Thompson et al. (2014), the process of strategy execution is not a preserve of the management as the input of employees is also important for the process to succeed. This is so because gaining customer confidence after a high-profile disaster that gained a lot of public interest is difficult and calls for a combined effort from all the stakeholders. This section gives insight into the best practices for strategy execution after a crisis that negatively affected the organization’s performance and threatened its sustainability.
First, according to Thompson et al. (2014), the management must create a strategy-supportive organizational structure. This implies that the company has to prepare all its stakeholders for any future changes that can help the company manage the prevailing situation. For example, when Brian Niccol took over from Ills as the CEO of the company, he initiated several changes to the company’s operations that involved all members of the company. For example, he made changes in the menu after close consultation with the relevant stakeholders. This is what best practice requires of any organization that can find itself in Chipotle’s situation.
Secondly, Thompson et al. (2014) contend that adequate resources must be channeled towards the strategy execution process. When an organization is experiencing a downward trend in performance, the common practice provides that the company must adjust its operations by directing more time and resources to the issue at hand. Niccol has succeeded in reawakening Chipotle because he has the necessary resources at his disposal. Besides, changing the perception of customers about the company’s products could not have been easy if the CEO was not given the resources needed to undertake marketing campaigns. The implication here is that strategy execution is a costly affair. From the perspective of Chipotle’s crisis, this paper can conclude that the company, through its founder, availed all the resources needed by the CEO to revamp the company.
Thirdly, strategy execution involves integrating the right policies and procedures that can promote the readjustment process (Thompson et al., 2014). Ultimately, it is worth noting that the decision lies with the management of an organization. The CEO of Chipotle takes credit when the company succeeds. In equal measure, he or she must take the blame when the company’s performance is deteriorating. The E. coli outbreak took place when Ills was the company’s CEO. The company was heading in the wrong direction, and customer confidence was deteriorating. Most importantly, the company experienced a sharp decline in performance. One of the drastic measures the CEO took was to shut down all the company’s stores in the United States and conduct thorough training of its staff on food hygiene. When the FDA finally gave the company the license to reopen, Chipotle had gained some consumer confidence from the actions taken by the CEO. There is no doubt that the situation could have been worse if the management had not implemented some immediate policies to control the situation.
Additionally, managers are expected to exercise the internal leadership needed to effect the strategy implementation process (Thompson et al., 2014). Irrespective of the nature of the industry and the magnitude of the crisis, it imperative for an organization’s CEO to exercise great leadership skills, especially when the company is at the brink of collapse. Hence, best practices compel the managers to be at the forefront of finding a solution to the problem. The implication here is that managers and CEOs of organizations have no option but to step up to the occasion and bring about the needed change. There is no doubt that Chipotle’s leadership acted swiftly to resolve the problem that affected the country. Hence, this prompt action can be used to explain why the company has resurrected after three years of financial underperformance. Going into the future, one can project that the company will continue to experience growth in its financial performance and business portfolio. Most importantly, enhanced internal leadership will also help the company to create an organizational culture where individual and company goals are attained, which may lead to increased employee performance.
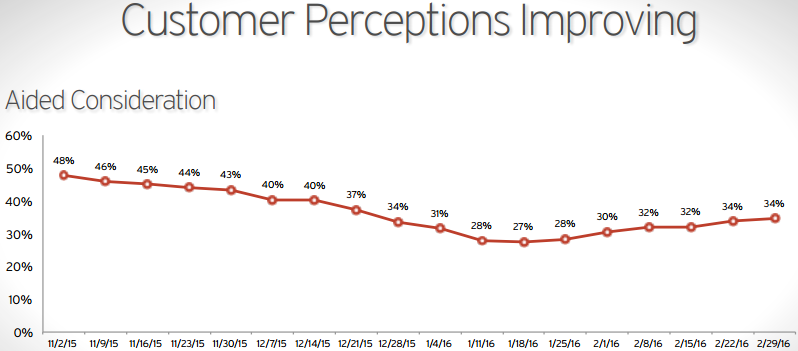
The concept of customer confidence is at the core of every organizational strategy because the perceptions customers have about a given product will determine their purchasing decisions. When considering a fast food store such as Chipotle, customer confidence is built by the pricing and quality strategies employed by the company. Common practice demands that organizations must follow the legal standards set by authorities in the areas in which they operate. Therefore, the outbreak of E. coli at Chipotle negatively affected consumers’ confidence in the company’s products. Even so, customer confidence has been increasing since 2016 (Appendix D). Although one can argue that the 2005 E. coli disaster made the company deviate from its original course, Chipotle’s strategy of offering fresh, fast food products with organically produced ingredients can be thought of as a game-changer in the fast-food industry. This was Ill’s founding vision and one that the company must continue to explore.
Generally, regaining customer confidence entails correcting the problem at hand and changing the way things are done within the organization to avoid the experienced problem in the future. This involves two aspects of strategic management. First, a strategic change of operations at the organization is important to show customers that the organization is working to solve the problem permanently. For example, when Niccol joined Chipotle, he changed a majority of the company’s operations – from production to customer service. His mission was to lead the company to the point of transforming negative customer perceptions into positive ones. Enhancing the reputation of the company will not only help the company achieve the needed development, but it will also help the management strategically adjust the company’s operations.
Secondly, transforming the image of an organization and reawakening its performance means leading from the frontline and ensuring that the company acclimates to the new strategy. For instance, ethical issues were raised after the E. coli outbreak. The company had to address these ethical issues diligently in order to restore favor with the public. One of the actions the company took was to trace the cause of the infection and change the process that led to the contamination.
Conclusion
The E. coli outbreak at some of Chipotle’s stores in the United States called for a strategic adjustment of operations at the company. Founded in 1993 by Steve Ills, Chipotle has emerged as one of the leading casual fast-food restaurants in the US and some parts of Europe. One of the reasons for the company’s rapid success in America’s restaurant industry is the fact that it is corporate-owned, thus, eliminating or reducing franchises. Additionally, the company’s small menu, its robust customer retention approach, and the high quality of food it sells to its customers have increased its consumer base over the years.
Even though Chipotle has enjoyed a favorable market presence in the US, the recent E. coli outbreak that affected outlets in 11 states tainted the company’s reputation. This incident overshadowed the company’s financial strength and position in the market and led to a sharp decline in sales, thus, affecting its profitability and competitiveness. Overall, Chipotle Mexican Grill seems to have survived the near disaster that would have followed the E. coli outbreak by developing effective strategies to regain customer confidence in the products offered by the chain. Like any other company in the same situation would do, Chipotle’s founder brought in a new CEO to spearhead the company’s strategy and availed all the necessary resources needed to return operations to normalcy.
Appendices
Appendix A: Chipotle’s 5-Year Financial Performance
Source: Chipotle (2019).
Appendix B: Brian Niccol’s Performance Record as CEO
Appendix C: Chipotle’s is Entirely Corporate-Owned
Appendix D: Chipotle’s Customer Confidence After the E. Coli Outbreak
References
Chipotle. (2019). Chipotle Mexican grill. Web.
Gunther, M. (2015). Chipotle’s silence on sustainability practices make it a target for CSR advocates.The Guardian. Web.
Taylor, K. (2019). Taco Bell’s ex-CEO used these 6 strategies to spark Chipotle’s incredible turnaround (CMG).Business Insider by Pulse. Web.
Thompson, A., Peteraf, M., Gamble, J., & Strickland III. (2014). Crafting & executing strategy 19/e: The quest for competitive advantage: concepts and cases. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.