Abstract
This paper reviews Cinnabon International Incorporation in an effort to understand the dynamics that the firm encounters in its operations and how it has survived the industry changes. First, the paper assesses the market dynamics with reference the operational structures.
The analysis shows that Cinnabon operates in a monopolistically competitive market, which underscores the need to understand the prevailing market conditions. One of the elements evaluated relates to price and income elasticity.
The competitive nature of the market and its potential growth are assessed by identifying the company’s core competitors and the demand trend. Moreover, the firm’s performance and potential with reference to its profitability growth and strategy are analyzed.
Introduction
Cinnabon International Incorporation is an American firm that was established in 1985 in the US restaurant industry. The firm is a subsidiary of Focus Brands Incorporation. Cinnabon specializes in baked food products and it has established a number of retail outlets across the US.
Despite its specialization in baked goods, the firm has diversified its product portfolio to include coffee, milkshakes, churros, and cinnabon rolls. The firm has strategically located its outlets in train stations, shopping malls, airports, and travel plazas (Fast Food, 2015a).
History
Since its inception, Cinnabon has focused on offering high quality products, hence appealing to the customers’ tastes and preferences. The high quality of its products enabled the firm to attract a substantial number of customers, which stimulated growth during the 1990s.
The firm has adopted the franchising strategy, which has enabled it to establish 1,072 franchise units. Due to its effective business strategy, Cinnabon has managed to position itself as one of the most famous brands in the world. The firm’s growth is enhanced by the adoption of an aggressive expansion strategy.
For example, the firm partnered with Pilot Flying J, which has remarkably stimulated growth by establishing outlets in travel centers and plazas (Fast Food, 2015a). The firm estimates that it will offer fresh-baked Cinnabon products in over 150 Pilot Flying J locations.
Rationale for selecting Cinnabon
Despite its current positive performance, the firm has established its operations in only 40 countries. In the few countries of operations, Cinnabon has established a strong market presence through its aggressive market expansion strategy.
This aspect indicates that the firm has the chance to exploit the growth opportunities available in the global fast food industry. However, the firm must integrate feasible strategic management practices, which is only possible if the top management develops sufficient understanding on the prevailing business environment.
Type of market
Cinnabon operates in a monopolistically competitive market. Ghosh and Choudhury (2008) define a monopolistically competitive market as “a market model that is dominated by a large number of players offering similar, but differentiated products to a large number of buyers” (p. 108).
Furthermore, minimal entry and exit barriers characterize such an industry. Subsequently, the threat of entry is relatively high, thus making the industry highly competitive.
Currently, numerous local and international companies dominate the global restaurant industry and they have diversified their product portfolio, hence maximizing profitability.
Price elasticity of demand
Price comprises one of the fundamental determinants of demand for a particular product. Thus, it is imperative for the firm’s management team to formulate effective pricing strategy. However, effective price formulation is only possible if the firm’s management team develops a comprehensive understanding of price elasticity of demand.
Ghosh and Choudhury (2008) define elasticity of demand as “the sensitivity of quantity demanded of a commodity to a given change in its price” (p. 118). The degree of price elasticity of demand varies across industries. The degrees of elasticity include perfectly inelastic demand, perfectly elastic demand, and unitary elastic demands.
Ghosh and Choudhury (2008) define unitary elastic demand as a situation whereby a shift in a commodity’s price results in a proportionate change in the amount demanded. On the other side, perfectly elastic demand involves a situation whereby a change in price leads to a decline in the quantity demanded to zero.
Conversely, a perfectly elastic demand entails a situation whereby the amount of goods demanded is not affected by changes in a commodity’s price.
Cinnabon International operates in a market characterized by a unit elastic demand. Consumers are price sensitive, and thus a small price increment will scare customers. Thus, a 10% increment in price culminates in a significant decline in the volume demanded, for example, between 6% and 11%.
Therefore, increasing the price point coupled with the resulting decline in the volume demanded means that the sales revenue is affected marginally due to the offsetting effect. McEachern (2012) illustrates this aspect by asserting that if “the price declines from US$ 10 to US$6, the volume demanded increases from 60 units to 100 units” (p. 104).
This aspect shows that the firm deals with products characterized by perfectly inelastic demand.
Income elasticity of demand [Yed]
Forgang and Einolf (2007) define income elasticity of demand [hereby denoted as Yed] as an index used in measuring the consumers’ sensitivity to changes in the level of their income. Forgang and Einolf (2007) affirm that the price of products and household income determine the rate of consumption.
Cinnabon Incorporation specializes in offering diverse baked food products and beverages [normal goods]. Therefore, the firm’s product portfolio is comprised of normal goods. Ghosh and Choudhury (2008) assert that a positive Yed characterizes normal goods.
Thus, an increase in the consumers’ income level leads to a significant increment in the quantity demanded. Subsequently, the demand curve shifts outwards.
Normal goods are categorized into two main categories, which include normal necessities and luxuries. The Yed for normal necessities range between 0 and +1, thus a 10% rise in income level leads to a 4% increase in demand, for normal necessities like soft drinks.
Thus, the Yed in such a situation is estimated to be +0.4, which means that the change in demand is less than the proportionate change in income level. Conversely, a high positive Yed characterizes luxuries. Riley (2010) asserts that luxuries “have an income elasticity demand of >+1” (p. 40).
Therefore, the demand for luxury products rises at a higher rate as compared to a rise in the level of income. For example, if the consumers’ income increases by 7%, the demand for luxury products such as restaurant products can increase by 14%, which indicates that the Yed is +2.0.
This aspect shows that Cinnabon operates in a market characterized by a high degree of sensitivity to income changes. Riley (2010) emphasizes that firms that deal with luxury products characterized by a high Yed experience a high sales volatility during the various business cycles [boom, recession, and recovery].
Closest competitors
The global restaurant industry and specifically the fast food market segment is characterized by a high potential for growth, thus new investors are entering the industry in an effort to exploit the available economic profit. The fast food and restaurant segments are one of the most saturated areas in the US (Fast Food, 2015a).
Despite the firm’s success in establishing a strong brand, Cinnabon experiences intense competition from three main firms, which include Kahala Corporation, International Diary Queens Incorporation, and Mrs. Fields’ Original Cookies Incorporation.
The three competitors have established substantial international market presence due to effective management. Additionally, the firms have developed an extensive product portfolio since their inception.
For example, International Dairy Queens Incorporation was established in 1938 and it has opened over 5,900 quick-service restaurants under the leadership of Warren Buffet’s Berkshire Hathaway. Some of the firm’s products include beverages such as fresh juices, ice cream treats, burgers, cones, snacks, and sundaes (Hoovers, 2015).
Similarly, Kahala Corporation operates as a multi-concept franchisor and it has gained substantial dominance in the global market. The firm operates in over 3,750 locations. Hoovers (2015) posits, “Its flagship brands include 1,500 unit ice cream purveyor Cold Stone Creamery and Blimpie sub sandwiches” (par. 1).
The firm has established outlets in different locations such as airports and mall food courts amongst other high-traffic areas. On the other hand, Mrs. Fields’ Original Cookies Incorporation operates as a snack-food franchisor and it has established outlets in high-traffic areas in the US.
Moreover, the firm has an extensive product portfolio that is characterized by baked goods, cookies, and brownies (Hoovers, 2015).
Closet substitutes or complements
Cinnabon International operates in an industry characterized by a high degree of concentration due to the large number of firms. The industry’s sales revenue increased from US$ 6 billion to US$ 160 billion between 1970 and 2014, which represents an 8.4% annualized growth rate (Franchise Help Holdings, 2015).
The respective industry players have diversified their product portfolio in an effort to meet the customers’ tastes and preferences. Thus, Cinnabon International faces significant challenges due to the large number of substitutes. Customers can easily access substitute products from dine-in restaurants and convenient stores.
Furthermore, the increment in the degree of health consciousness amongst customers has increased the customers’ preference for other substitute food products that are considered as highly attractive and healthier.
In an effort to deal with the intense competition, firms operating in the industry are investing in extensive marketing campaign aimed at creating market awareness of the healthier options of their products.
Change in demand for Cinnabon’s products
The global restaurant industry is expected to undergo significant growth in the future. One of the market segments that will experience growth includes the fast food market segment.
Considering the fact that Cinnabon Incorporation specializes in offering diverse fast food products [baked products] and beverages, the firm will benefit from the growth in demand. Despite the health conscious nature of consumers, the industry is expected to sustain its growth due to the high demand for quick service amongst the youth.
Table 1: Trend in Restaurant Industry Sales. Source: (Maze, 2015).
The restaurant industry has been characterized by considerable growth over the past four decades as illustrated by table 1 and graph 1. Graph 1 shows that the restaurant industry is likely to sustain its remarkable growth into the future.
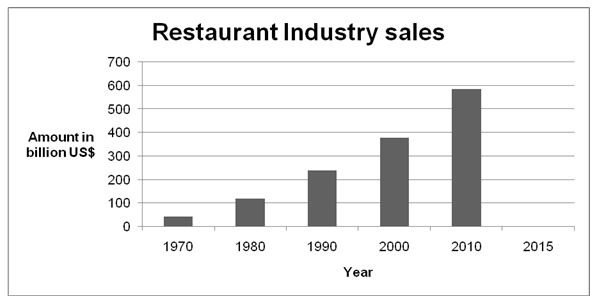
The fast food market segment is projected to generate over $210 billion by 2018. Over 77% of this growth is likely to be generated by fast food companies that have adopted the drive-thru and on-premises format (Statista, 2015).
However, in order to address the change in consumer tastes and preferences, the industry players must be innovative. This approach will ensure that the firm’s products align with the change in consumer tastes and preferences.
The industry’s growth will further be stimulated by the economic improvement, which is currently being experienced. Consequently, a considerably large number of households will experience an increment in purchasing power due to the growth in employment opportunities.
Training of the company’s labor force
The quality of human capital is one of the most essential elements in organizations’ quest to attain and sustain long-term competitive advantage. According to the United States Department of Labor (2015), the baker’s market segment is projected to experience a 6% growth between 2012 and 2022.
However, the survival of the industry will depend on the availability of highly skilled labor force. In order to align with the changing industry trends such as the customers’ tastes and preferences, it is imperative for firms operating in the industry such as Cinnabon International to invest in an extensive employee training.
The training program should be multidimensional. Thus, it should address both the employees’ personal development goals, the customers’ expectations, and the organization’s performance goals.
By investing in employee training, Cinnabon will improve its workforce’s skills and expertise, which will translate into improved effectiveness and efficiency in executing the assigned roles and responsibility. This move will culminate in improvement in the firm’s productivity, hence minimizing the cost of production.
Profitability and sustainability of Cinnabon’s business
An analysis of the demand trend shows that the industry will experience a remarkable increment in demand for fast foods and other restaurant products. Additionally, change in the consumers’ lifestyle coupled with improvement in the US economic performance over the past few years are strong indicators of the industry’s potential.
Therefore, adoption of best practices means that Cinnabon International can sustain growth with reference to its profitability, hence a high probability of attaining financial sustainability.
Strategies to grow Cinnabon’s profit
Cinnabon’s capacity to achieve profit growth will depend on its effectiveness in entrenching best strategic management practices. The firm should incorporate the concept of product innovation.
In its product innovation, Cinnabon should focus on two main dimensions, which include new product development and continuous product improvement. The two dimensions will enable the firm to align with macro-economic dynamics such as change in consumer tastes and preferences.
For example, Cinnabon International will be in a position to address the health-conscious nature of its customers. Thus, the firm will cope with the prevailing competitive pressures.
Company strategy, prices, target customers, production, cost, and advertisement
Cinnabon has mainly targeted its customers based on their demographic characteristics. The firm’s customer base is mainly comprised of the youth, young professionals, and other individuals who have a busy lifestyle. In addition to the above strategies, Cinnabon can maximize its profitability by adopting effective operational strategy.
One of the strategies that the firm’s management team should consider entails improving the quality of its product. Cinnabon’s success over past decades has largely originated from the high quality of its products. Additionally, the firm has diversified its products into baked products and beverages, hence attracting diverse customer groups.
Cinnabon recognizes that consumers are price sensitive in their consumption process. Subsequently, the firm has adopted the penetration pricing strategy by setting the price of its products at a low point. Additionally, the firm has taken into account the customers’ psychological dimension in its price formulation process.
The firm has implemented this strategy by setting the price point using odd-number endings in an effort to influence the consumers’ emotions. In an effort to minimize the cost of operation, the firm undertakes all its production activities in-house.
Additionally, the firm minimizes the cost of production by establishing strong economies of scale. For example, Cinnabon has established a large number of bakeries distributed in different countries. This approach has contributed significantly to cost reduction (Fast Food, 2015b).
However, the firm incurs significant costs in its production cost such as salaries and wages, insurance, supply and logistics and maintenance.
Cinnabon has targeted customers with a busy-lifestyle and the working class who do not carry home-cooked food to their workplace. However, the firm ensures that consumers of different demographic characteristics can consume its products.
In a bid to generate sales revenue, Cinnabon has invested in an extensive Integrated Marketing Communication strategy. The firm creates market awareness using diverse techniques such as advertising and public relations. The firm’s advertising strategy is undertaken through diverse mediums such as print and broadcast media.
The firm’s public relations campaign is undertaken through the DAISY Foundation (Cinnabon, 2015). Moreover, the firm has adopted different social networking mediums.
New markets
In its pursuit for sustainable business excellence, Cinnabon is focused on strengthening its global market presence through internationalization. The firm mainly targets the emerging markets.
Some of the countries in which the firm is focused on developing a strong market presence include Russia, India, Romania, Austria, Cyprus, Greece, and England. One of the approaches that the firm has adopted entails developing new products that are adapted to the demands in the new markets.
Strategies for gaining market share
The firm’s success has been enhanced by the adoption of the franchising strategy. This strategy has enabled the company to sustain and improve the quality of its products due to the product standardization requirement associated with the strategy.
Through this approach, Cinnabon has managed to attain and sustain a strong market share.
The amount of customer purchases and the most successful products
Cinnamon treats some consumer information as confidential. One category of such information relates to a customer’s total purchases. However, Cinnabon generates a substantial amount of revenue from its Classic Rolls.
Other signature products in the firm’s menu include Cinnabon Classic Rolls, Cinnabon Stix, Churro, Cinnabon bites, chocolate milk, soft drinks, and coffee. The comprehensive product portfolio has enabled the firm to maximize its sales revenue, hence the high level of profitability.
Source of revenue
Cinnabon International mainly generates revenue from selling diverse fast food products. The firm has developed an extensive product portfolio in an effort to meet the diverse customers’ tastes and preferences. The firm has achieved these goals by integrating the concepts of product standardization and adaptation in the local and foreign markets.
Other relevant factors
Cinnabon’s management team should be conscious of the prevailing industry dynamics such as change in its target customers’ consumption behavior. This approach will enhance the firm’s capacity to adjust its operational and strategic management practices.
Moreover, it is imperative for the firm’s management team to review periodically the effectiveness of its franchising format in its quest to enhance its growth. The review will enable the firm to determine the necessary changes in its franchising strategy.
For example, the firm might integrate the concept of product standardization in some of its international markets. This approach will enhance its rate of market penetration.
References
Cinnamon: About us. (2015). Web.
Fast Food: Cinnabon’s products continue to capture the taste of the nation. (2015a). Web.
Fast Food: Cinnabon prices. (2015b). Web.
Forgang, W., & Einolf, K. (2007). Management economics. London, UK: M.E Sharpe.
Franchise Help Holding: Fast food industry analysis 2015; cost and trends. (2015). Web.
Ghosh, P., & Choudhury, P. (2008). Managerial economics. New Delhi, India: Tata McGraw-Hill.
Hoovers: Cinnabon Incorporation. (2015). Web.
Maze, J. (2015). NRA; 2015 restaurant sales to grow 3.8%. Web.
McEachern, W. (2012). Economics; a contemporary introduction. Mason, OH: South- Western Cengage.
Riley, G. (2010). AQA AS economics module 1&2 digital textbook. New York, NY: Tutor2u Limited.
Statista: Statistics and facts about the food industry. (2015). Web.
United States Department of Labor: Occupational outlook handbook; bakers. (2015). Web.