Introduction
The purpose of this study will be to explain why competitive markets are usually better for consumers when compared to monopolistic markets. The study will also evaluate the policies that are used to try and achieve competition in Australia. A monopoly or a monopolistic market is defined as a type of market that has only one supplier and many consumers who have no control over what takes place in the market.
This type of market is mostly characterised by high prices of goods and services, excessive barriers to entry in the market and also supply constraints. Because this market is made up of only one supplier, consumers have no choice but to purchase products or services mainly from these firms.
If a monopoly market lacks any government legislation or controls that will limit its powers in the market, then it has the authority to increase the prices of goods or services without in any way affecting the demand for its products or services. A common example of monopolistic markets is the public utility companies that offer services such as water or electricity.
Competitive markets are the complete opposite of monopolistic markets as they have many suppliers and consumers operating in one market. Each of the market’s participants lacks the power to control the price of goods or services offered by the various suppliers in the market which means that they cannot increase prices based on the number of customers who rely on their products.
Some of the characteristics that are used to distinguish competitive markets from other types of markets include the infinite number of buyers and sellers that exist in the market where there are many consumers ready and willing to purchase commodities produced by willing producers, low/zero entries and exit barriers meaning that it is easy for a business to enter and leave the market, existence of perfect information where the prices of products are known by all suppliers, producers and consumers, homogenous products and zero transaction costs.
Competitive markets that are perfect in nature will be productively efficient and they will allocate resources equally amongst the various participants in the markets. These markets however prove to be inefficient in the short long term as outputs will not occur if the marginal cost is equal to the average cost.
Why Competitive Markets are better than Monopolies
The presence of competition in the market will ensure that there is efficiency as competitive markets equate the marginal cost to the average cost of goods that are brought to the market. Competitive firms usually offer consumers with the quantity of goods that are equitable to the price they are willing to spend for the products or services.
The efficiency that exists in competitive markets is also attributed to consumer surplus and also producer surplus which is maximized to ensure that there is no deadweight loss in the market. The average cost of these markets will also be maximised because outputs will always occur when the marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
Marginal cost in this case refers to the change in total cost that arises when the quantity of a produced good changes by a single unit. In the case of monopoly markets, the price of goods and services is usually higher than the marginal cost which means that this type of market will be inefficient in meeting the needs and expectations of consumers who buy products from this market.
For example in the public utility companies, any unit change to the volume of water or electricity supplied to consumers corresponds to an equally higher cost of the total price for these services.
This type of market is also inefficient because the consumer surplus and producer surplus is not properly maximized which results in deadweight loss. This does not however affect the profits that are gained by companies that operate within this industry because of the high barriers to entry that exist in the market.
Another reason why a competitive market is usually better for consumers compared to a monopoly market is that competitive markets provide incentives to producers for production innovations and channels which will facilitate the creation of new products or services.
Competitive markets ensure that innovative efforts have been directed towards meeting the needs and expectations of members within the society. The existence of perfect information within these markets ensures that producers are able to create new products to satisfy the ever changing needs of customers in these markets.
The signals for price changes that exist in these markets also allow producers and consumers to adapt swiftly to any price changes in the market which is not possible with the monopoly markets.
Monopoly markets do not provide any form of incentives to producers or suppliers of raw materials which makes it difficult for them to engage in product design or innovation activities. Because these types of markets sell products that lack any close substitutes, it becomes difficult for producers to engage in new product innovation activities.
The high barriers to entry and exit that exist in these markets also make it difficult for other companies that want to offer new products and service innovations from breaking into the industry.
These markets do not meet the changing needs and expectations of consumers given the existence of imperfect knowledge within these markets. Imperfect knowledge in monopoly markets refers to how the prices and quality of goods/services is assumed to be unknown in these markets.
Competitive markets are usually better for consumers when compared to monopoly markets because the decision making process that exists in competitive markets is conducive since it allows producers and consumers to be able to adapt swiftly to any changes that might occur in the market.
This allows the various competitors in the market to create products and services that will guarantee their survival in the market place. The level of competition that exists in competitive markets ensures that firms operating within these markets are able to adapt to the changing demands of the consumer market.
Companies in these markets therefore engage in decision making processes that are meant to meet the needs and expectations of consumers by constantly engaging in product innovation activities. Monopolistic markets on the other hand fail to take into consideration the needs of customers because the decision making process is mostly limited to the firms operating within this industry.
This means that any changes to price or the quality of goods and services offered by these companies will be limited to the decisions made by the monopoly. The diagrams below depict the demand curves for both monopoly and competitive markets.
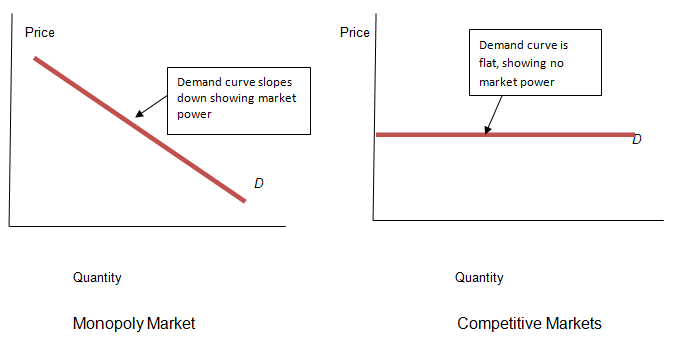
Policies used to Achieve Competition in Australia
Australia has developed a pro-competitive reform policy that will be used to achieve competition in the country. The policy which is known as the National Competition Policy was developed in the 1990s to demonstrate the political backing for market-based approaches in Australia.
The National Competition Policy paved way for the National Reform Agenda that was meant to provide a constitutional framework in enhancing the increase of competition in the various industries and markets that exist in the country.
The enforcement of the competition policy lies in the hands of the Australian Minister for Competition Policy and Consumer Affairs and also the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC). An enforced competition policy is meant to create suitable regulations and infrastructures that will be used by producers and suppliers in maintaining a competitive market.
Another policy that was created to increase the level of competition in the country is the Trade Practices Act which oversees aspects such as competition, fair trading and consumer protection.
The Trade Practices Act ensures that competition within the country has been regulated and that restrictive agreements have been created to govern the practice of competition amongst the various participants of competitive markets.
The Trade Practices Act also ensures that companies in monopoly or monopolistic markets do not abuse their dominance over the market by misusing their market power for their own personal gain. The act ensures that the needs of Australian consumers have been met by protecting consumers from high commodity prices and by also ensuring that the quality of products distributed into the market are of a high quality.
The Trade Practices Act underwent several reforms that would ensure that it had the power to prohibit any predatory pricing by suppliers and producers and that price fixing was restricted on commodities that were not easily available in the Australian market.
The main purpose and goal of both the National Competition Policy and the Trade Practices Act is to correct the relationship that exists between the government of Australia and the business community within the country.
By creating policies and acts that would limit the exemptions placed by the government on the level of competition, the policy makers in the country wanted to rationalise the regulation of infrastructure within the country because the regulations created for the various states were not subject to the competition law developed by the Commonwealth.
The creation of competition policies and reforms were undertaken to review the existing laws and regulations that created impediments to competition in Australia.
Conclusion
The purpose of this assignment has been to determine why competitive markets are more suitable options for consumers instead of monopoly markets. The study has evaluated the various reasons that make competitive markets more preferable to consumers given that they allow the consumer to purchase various products at different prices.
The study has also evaluated the policies that have been developed to achieve competition in Australia as well as the various bodies that are concerned with ensuring competition has been regulated in the country. The policies have ensured that competition is fostered in a positive way to ensure that their no misuse of market power or any price fixing on necessities.
Bibliography
Hubbard, Glen and Anthony O’Brien. Economics. 3rd Edition, New Jersey: Pearson International, 2009.
Brassil, Belinda. Excel HSC legal studies. New South Wales: Pascal Press, 2007