Introduction
Incremental innovation in food production has resulted in different animal products that meet people’s needs. The developments and achievements recorded in this field have transformed people’s consumption and marketing strategies. The link between food innovation and animal welfare is something continues to inform superior ideas for promoting sustainable practices. Governments and societies have managed to implement superior policies and initiatives to protect both wild and domestic animals.
Animal welfare remains an issue that stakeholders, environmentalists, biologists, and researchers continue to take seriously. The purpose of this research paper is to analyze consumer attitudes towards animal welfare from the lens of food innovation. The findings can inform superior policies and programs to maximize sustainability in the manner in which companies and entrepreneurs embrace innovative procedures to process or produce animal-based food materials.
Background Information and Problem Statement
Every culture or group has its unique understanding of the role of animals in the natural environment. The norms, beliefs, and practices specific cultural groups promote tend to dictate the way they consume different products. Different religious teachings have been observed to determine the level at which human beings can interfere with animals (Vetter et al., 2014). Past laws and regulations also create room for people to use animals for their personal benefits or aims.
However, the last century has resulted in a number of laws and policies aimed at protecting different animals from human brutality. Such amendments have continued to reshape most of the ideas, principles, and practices many people consider whenever interacting with animals.
Consumer concern is an issue that has emerged as more people continue to focus on the most appropriate measures to support the welfare of different animals. Emerging challenges experiencing in different parts of the world have managed to transform people’s attitudes and perceptions about domesticated animals and the use of the products they give (Heise and Theuvsen, 2017). However, these expectations have failed to converge due to the absence of streamlined policies that can support the rights of all animals across the globe. Emerging technologies have resulted in genetic modified organisms (GMOs) and the use of medicines to improve animal breeds and their products.
These issues have encouraged different stakeholders to present divergent opinions regarding the attitudes of different animals towards animal welfare. The proposed study will, therefore, offer evidence-based ideas to understand consumer attitudes towards the influence of food innovation on animal production and how stakeholders can strike a balance to promote sustainability.
Literature Review
Human beings have for many centuries viewed animals as essential creatures that support or meet their needs. Vetter et al. (2014) observed that animals were important since they provided manure for agricultural product, meat for consumption, and milk. Wild creatures were also observed as integral parts of the global biodiversity. Such animals play a positive role in maintaining the integrity of the natural environment and making it possible for different plant species and microorganisms to thrive. Similar trends or ideas would eventually be considered to address the issue of animal production for human consumption.
Most of the studies completed in the recent past have presented evidence-based information that can guide more people to understand their relations with animals. For example, Miranda-de la Lama et al. (2018) observed that around 75 percent of global citizens were certain that all animals were important. Another study by Heise and Theuvsen also revealed that many people across the world were concerned about the welfare of different animals domesticated for various economic purses (2017). This was a clear indication that many consumers were becoming more concerned about different animal products.
Several aspects or viewpoints have emerged as different stakeholders focus on the most appropriate approaches to process animal products. For instance, Miranda-de la Lama et al. (2018) observed that many people believed that animals were capable of experiencing different levels of suffering (see Figure 1). Majority of consumers are against the idea that all animals raised for milk or meat production do not require desirable husbandry practices. Only around 17 percent of consumers believed that there was no need for better support systems and habits whenever raising different animals, including pigs, cattle, and poultry (Heise and Theuvsen, 2017). Many people across the globe acknowledged that there was a need to raise animals properly and fulfill their needs. Additionally, all individuals had a duty to protect animals from any form of suffering.
Figure 1: General ethical aspects.
Researchers and animals rights activists have in the past taken the issue of processing animal-based food products seriously. You et al. (2017) acknowledged that animal welfare and agricultural practices could not be separated from each other. In a country like Germany, many citizens managed to stage public protests against inappropriate food factory procedures and practices that affected the welfare of such animals.
Their main concern was that hens raised for egg production were confined in different cages. The ultimate challenge was that such animals were deprived of natural sunlight. Similarly, many people have raised concerns regarding the manner in which different animals are raised. For example, some have indicated that farmers fail to provide adequate food or support to different animals while at the same time expecting to reap numerous economic benefits from them.
Factory farming and food processes practices have forced many consumers or citizens to raise their concerns. The point of contention has been that most of the approaches make it impossible for people to support the rights of the affected animals. Activists in different regions were observed to view such animal practices as a form of slavery (You et al., 2017). This was the case since most of the behaviors and economic activities were unethical, inappropriate, or cruel to the targeted animals.
With the above issues in mind, many people have gone further to change their purchasing behaviors and consumption trends. In a study conducted by de Graaf et al. (2016), it was observed that many people were becoming reluctant to purchase eggs produced throughout the use of modern innovations and technologies. This was also the same case for meat associated with inappropriate animal handling or raising practices. Additionally, people’s beliefs and religious thoughts played a critical role in dictating the purchasing behaviors of different consumers.
Many scholars have identified several consumption aspects in the recent past. For instance, You et al. (2017) observed that issues of quality, trust, attitudes, and product image could be considered to dictate the purchasing behaviors of different people. Individuals who were convinced that specific products were produced using unhealthy procedures found it hard to purchase them. Those who questioned the husbandry practices involved throughout the production process were cynical about the targeted meat, milk, or eggs (de Graaf et al., 2016). This is a clear indication that human beings have over the years been keen to focus on the procedures and practices used to maximize animal production for economic gains.
Findings and Discussions
The consulted studies and research articles have presented evidence-based ideas that address the issue of consumer perceptions on inappropriate food innovation practices that put animals at risk. The outstanding observation from such findings is that many people have become sensitive whenever focusing on the way producers of different animal products raise their domesticated animals (Spain et al., 2018).
Heise and Theuvsen (2017) conducted a study that revealed that over 60 percent of consumers in the United States were becoming concerned and interested in the welfare of different animals. The main focus was on the manner in which emerging technologies was dictating the nature of animal production.
When human beings genetically engineer animals to increase food production, it becomes possible to endanger different species. In the United States, majority of citizens believe that all domesticated livestock should receive humane treatment throughout their lives and should not be use for pursuing innovation (Spain et al., 2018). They should also be slaughtered using the most acceptable or least painful procedures.
Such a practice meets the ethical standards for promoting the most appropriate husbandry practices. Many consumers have indicated that farmers should ensure that their animals are handled effectively, fed properly, and housed in healthy environments. These practices can support the integrity and welfare of different animals. Such practices will ensure that the population of domesticated animals remains sustainable.
Within the past decade, consumers have been keen to promote practices and concepts that resonate with the principles of animal rights and welfare. For instance, many people have been keen to ensure that they purchase eggs produced using care-free or free-range methods (Mikuš et al., 2017). They also avoid genetically-modified animal-based animal products. When human beings take such practices into consideration, it becomes possible for them to protect animals from different forms of abuse.
The use of antibiotics is an issue that continues to raise numerous concerns in different regions across the globe. Most of the consumers of chicken meat have been keen to ensure that the identify chicken that have not been injected with antibiotics. The use of such drugs has become a common practice in an attempt to maximize production. Unfortunately, such antibiotics weaken such birds and affect fertility (Mikuš et al., 2017). Consumers of the marketed meat will also record increased levels of such drugs in their body systems. This means that many people are concerned and worried about emerging food innovation practices whenever focusing on the welfare of animals.
Different consumer groups in America and other countries across the world have engaged in a number of campaigns to ensure that they receive health products from domesticated animals. A report released by the Packaged Facts revealed that more people were willing to purchase eggs and milk that met the credentials for positive husbandry practices (You et al., 2017). Consequently, many companies and farmers were embracing such ideas to introduce superior practices whenever marketing their products to different consumers.
Several trends have been observed whenever analyzing consumer perceptions and attitudes towards animal welfare. Firstly, many people or consumers have become informed about the importance of associating themselves with animals that have been raised in healthier and friendly conditions. Some of the outstanding benefits include improved or better nutrition, food safety, reduced risks for infections, and superior flavors. Activists have been using these aspects to implement different campaigns (Mikuš et al., 2017). Secondly, social media networks and platforms are transforming the way consumers, producers, corporations, and government agencies share information. Today, many people are aware of their unique rights and health demands. Consequently, this knowledge has guided them to support initiatives and actions that will eventually maximize the welfare of all domesticated animals. They also acknowledge that such approaches will empower them to consume healthy animals while at the same time protecting them for posterity purposes.
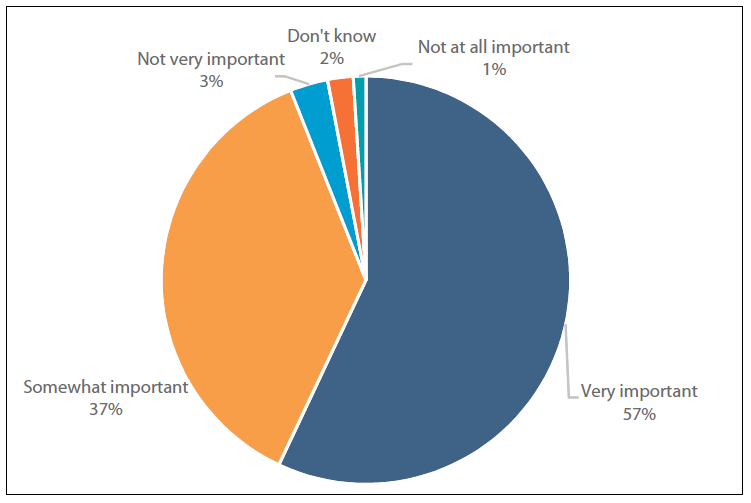
When human beings use innovative procedures to genetically modify animals, chances are high that they will be exposed to numerous dangers, including extinction or mutation (You et al., 2017). This is something that can threaten such animals and make them unsustainable. Those who consume eggs and milk might be exposed to numerous health dangers or problems. Another concern is that the use of inappropriate husbandry practices will result in a situation whereby the sustainability of such animals is no longer taken seriously (see Figure 2). This means that different species will be exposed to the problem of extinction. Poor husbandry practices might also result in different diseases that can affect the targeted domesticated animals and human beings.
Failure to promote desirable practices is something that has been observed to encourage more people to become vegetarians. This is the case since such individuals are convinced that plant-based products are appropriate for consumption and capable of protecting them from a wide range of diseases or infections. Such a development or scenario can affect different sectors of the economy supported by animal-based products, such as manufacturing, food, and tourism (Mikuš et al., 2017). The predicted outcome is that many people will lose their jobs and find it hard to pursue their economic goals.
The use of animals for innovative and scientific purposes is another issue that has raised numerous questions among consumers. For instance, a study conducted by Vetter et al. (2014) revealed that many people were unwilling to associate themselves with cosmetic and pharmaceutical companies that were testing animals to determine the efficacy of their products. Some citizens were also categorical that they would stop to purchase such commodities since they did not support the welfare of animals. Such insights can, therefore, guide stakeholders and corporations to implement superior policies and practices that will eventually promote the rights of all animals, both wild and domesticated.
Conclusion
According to the above discussion, many consumers are curious about the way corporations, individuals and producers are introducing the idea of food innovation in animal production. They have been keen to support stakeholders who embrace desirable practices by purchasing their products. The power of social media has resulted in extensive campaigns aimed at encouraging more people to associate themselves with companies and policies that will eventually maximize the rights and welfare of all animals. Consequently, such measures will protect all domesticated animals and ensure that their numbers remain sustainable.
Works Cited
de Graaf, S., E. J. Van Loo, J. Bijttebier, F. Vanhonacker, L. Lauwers, F. A. Tuyttens, W. Verbeke. 2016. Determinants of consumer intention to purchase animal-friendly milk. Journal of Dair. Sci. 90: 8304-8313.
Heise, H. and L. Theuvsen. 2017. What do consumers think about farm animal welfare in modern agriculture? Attitudes and shopping behaviour. International Food and Agribus. Manag. Rev. 20: 379-399.
Mikuš , T., O. Mikuš, L. Kozačinski, Ž. Mesić. 2017. Croatian meat consumer attitudes towards animal welfare-friendly products and production. MESO. 19: 324-330.
Miranda-de la Lama, G. C., L. X. Estévez-Moreno, M. Villarroel, A. A. Rayas-Amor, G. A. María, W. S. Sepúlveda. 2018. Consumer attitudes toward animal welfare-friendly products and willingness to pay: Exploration of Mexican market segments. Journ. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 22: 13-25.
Spain, C. V., D. Freund, H. Mohan-Gibbons, R. G. Meadow, L. Beecham. 2018. Are they buying it? United States consumers’ changing attitudes toward more humanely raised meat, eggs, and dairy. Animals. 8: 128-141.
Vetter, S., L. Vasa, L. Ózsvári. 2014. Economic aspects of animal welfare. Act. Polytech. Hung. 11: 119-134.
You, X., Y. Li, M. Zhang, H. Yan, R. Zhao. 2014. A survey of Chinese citizens’ perceptions of farm animal welfare. PLoS One. 9: e109177.