- Infection control is the process through which health care organizations prevent diseases from spreading.
- All health care facilities are required to prevent nosocomial infections.
- This are infections contracted by staff members and patients in the healthcare facility during admission or incubation.
- There are specific procedures and policies used by organizations to control nosocomial infections.
Introduction
Infections obtained in the hospitals is among the major causes of deaths globally. About 2 million preventable infections occur every year, which result to more than 90,000 deaths annually [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 2020]. For this reason, all health care workers should be proactive in disease control in their jobs. This infection control and training program addresses issues related to the spread of nosocomial infections within the settings of health care. Examples of nosocomial infections well known are ventilator-associated pneumonia, Methicillin Staphylococcus aureus, Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, Candida albicans, Clostridium difficile, Acinetobacter baumannii, Tuberculosis, Urinary tract infection, and Legionnaires’ disease. Currently, COVID-19 joins the list of infectious disease that can be obtained in the hospital (World Health Organization (WHO), 2020). Prevention of these infections alludes to the procedures and policies used to minimize the possibility of their spread in hospitals and other health care facilities.

Objectives of this Infection Control and Training Program
- To understand basic concepts used in infection control.
- To know the causes of nosocomial infections.
- To understand the rules, policies, and regulations to be followed in avoiding the spread of COVID-19 virus.
- To comprehend the components of this infection control program and training.
- To know the importance of a committee in control of infections.
The categories of workers eligible for this training program include nurses, doctors, medical laboratory technologist, and the cleaning staffs. Generally, all workers in healthcare facilities should have basic understanding and knowledge of corona virus infection and prevention principles.
The training program will be tailored to the needs of each department.

Importance of Infection and Training Program
The hospital needs this infection and training program because:
- Infections acquired in hospitals are common.
- The training aspect of this program will produce skilled IPC practitioners, whose role is to ensure that infection control is practiced in the healthcare facility.
- Currently, there is covid-19 pandemic, which should be stopped from spreading.
- About 9,000 health care workers in the US have contracted the COVID-19 virus (Center For Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2020).
- Healthcare workers are at the more risk of contracting corona virus in the workplace.
The prevalence of infections acquired in hospitals is 9% globally (World Health Organization, 2020). There is a need for infection control because the cost of healthcare of a patient increases when one contract a disease in the healthcare facility. Nosocomial infections aggravates antimicrobial resistance.
The cost of medication increases in presence of hospital acquired diseases. The government incur a lot of losses in terms of revenue as a result of this infections. The world Bank studies estimated that 50% of health care budgets in two-thirds of developing countries is used in treating hospital acquired infections. Therefore, operative infection and training programs are beneficial because they reduce the rate of nosocomial infection spread as well as mortality, morbidity and health care cost.
The trained workers will co-ordinate develop, audit, revise, and implement policies to be used in control of COVID-19 infections.

COVID-19 Virus
- COVID -19 is a respiratory disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus.
- The virus easily spread from one person to another.
- It is transmitted through droplets, aerosols, and contact with the virus.
- Currently, it is a deadly epidemic in all parts of the world.
Droplet are respiratory secretions released into the air when sneezing and coughing. They land into the eyes, nose, and mouth when causing an infection. Aerosol are liquid droplets or solid particle that are suspended in the air. In regards to contact, one obtains the virus after touching a surface with SARS-2 virus and thereafter touching nose, mouth, or eyes. Corona virus poses a higher risk to people with underlying health conditions such as asthma, heart disease, diabetes, and Suppressed immune systems.
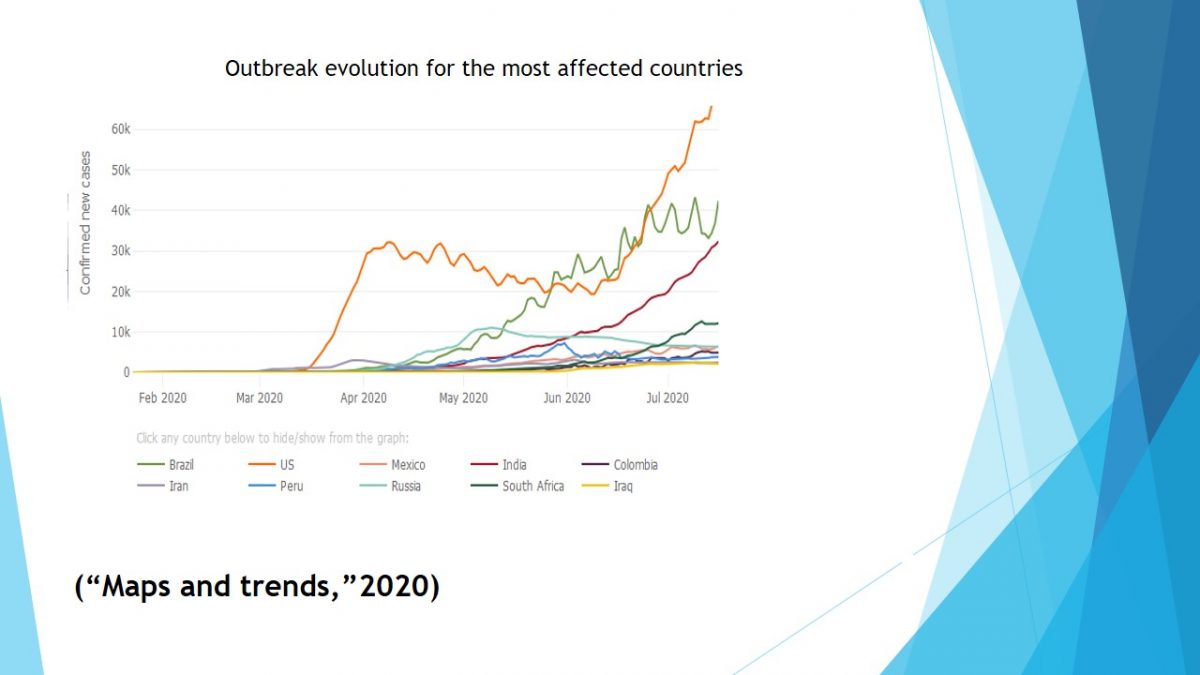
New cases of Corona virus is reported each day. Thus, there is a need for this infection prevention and control program.

Infection Control Committee
- The goal of the infection control committee is to prevent corona virus infection spread in the healthcare facility and community.
- It consist of doctors, Infection control nurses, and representatives from all organization departments.
- The functions of this committee are:
- To receive and manage critical virology data and information concerning COVID-19. This includes surveillance data;
- Address visitation policies, critical patient care practices, disinfection procedures, and workplace safety;
- Develop policies.
The doctors in the committee will include general physician, surgeon, infectious disease specialist, and a virologist. Departments such as housekeeping, laboratory, administration, pharmacy and central supply will have two representatives in the committee.
Functions of the committee
- Investigating and recognizing outbreaks in the hospital and community.
- Educating and training all health care workers about prevention measures.
- Create policies that prevent COVID -19 spread in the health care facility.

Impacts of individuals and their roles
- The individual roles of persons involved in infection control committee include:
- Doctors-recommend and develop polices, and surveillance and identification strategies;
- Nurses-direct intervention when dealing with patient and community outreach, they also implement preparations and precautions in health care settings;
- Departmental representatives educate members of staff in their respective sections.
- The impacts of individuals involved are:
- Doctors are increasing infection control rates in the hospitals and the community by identifying areas that need change;
- Nurses have facilitated reduction of infection in the community, they have lowered the risk of patients contracting the disease in hospitals;
- The departmental staff have created a safe and healthy environment in the sections to avoid spread of COVID-19.
Doctors develop and recommend informed policies and practices pertaining to COVID -19 control to the infection control committee, which are later discussed and implemented.
They also recognize and investigate the COVID -19 outbreak in the community by offering screening services. Nurses intervene directly when dealing with patients to prevent infections, they also teach patients prevention measures through health education promotion. They cover aspects such as a safe environment , canceling group meetings, avoiding touching the eyes, nose, and mouth, early detection of infections, social distancing, and personal hygiene when nursing patients.

Optimum Infection Control Practices in Healthcare Facilities
- Distancing (no hand shaking)/ separation / restriction of movement and of visitors.
- Waste management.
- PPE: gloves, masks, gowns, and eye-protection.
- Hand hygiene.
- Discharge of patients.
- Staff health management.
- Cleaning, disinfection and sterilization.
Control of COVID -19 spread
Transmission of most respiratory disease occurs when sick people are close to each other. Therefore, in hospitals, a distance of about 1 meter should be maintained between patients and all other staffs. In regards to respiratory etiquette, one is required to wear mask when dealing with a sick person. In addition, both the staff and the patient is required to sneeze and cough into a sleeve or a scarf and wash their hands thereafter.
Transmission of COVID-19 increases with direct contact, close contact, touching infected surfaces, and performing aerosol generating procedures such as nasopharyngeal aspiration, endotracheal intubation, and swabbing.
In this COVID -19 pandemic era, all patients reporting to facilities of health care with acute respiratory signs and symptoms such as shortness of breath, fever, and cough should be separated from other patients. This implies that a different waiting area should be created in the health care facility. At hospital entrance, all sick people visiting the hospital must be triaged, before being directed to the appropriate waiting area.

Guidelines for Preventing COVID -19 Spread in Health Care Settings
- High infections rate among healthcare workers has been reported (Ng et al., 2020).
- Therefore, employers should ensure that equipment, training, and procedures undertaken are fully protective.
- The guidelines to be utilized are from the State Health Department and CDC.
- The CDC site contains advice for home care, infection control, clinical care, and evaluating people under investigation.

Policies to Prevent Infection Spread
The policies to be adjusted in this health care organization include:
- Utilizing teleconferences, phones, and emails rather than physical contact when communication with co-workers.
- Conducting meetings using zoom or Skype.
- Encouraging the staff to stay at when unwell.
- No staff should fear loss of benefits or pay and other benefit when ill.
The above policies promote social distancing. It also reduces the contact with corona virus patients and surfaces with SARS-COV –Virus .

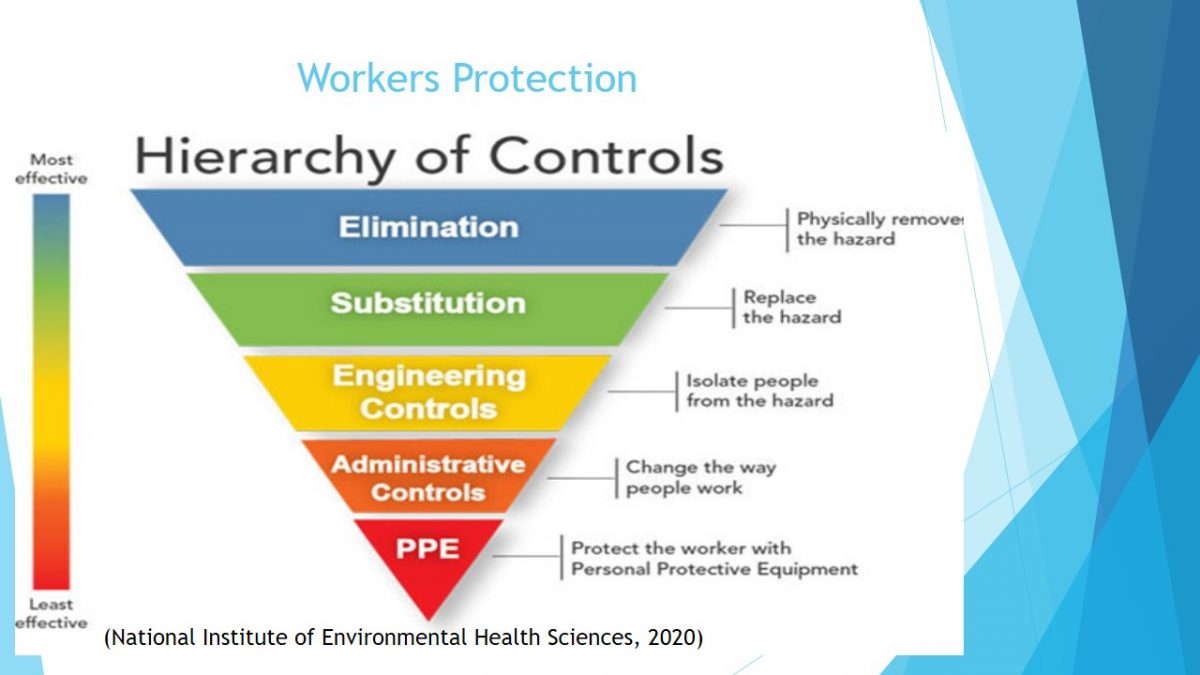
Workers Protection
Workers should be protected by starting with the highest hierarchy in the pyramid. Engineering control requires protection of workers from risks, this is achieved by ensuring that the workplace is well ventilated. Additionally, plastic shield, sneeze guards, biological safety cabinet, and UV irradiation systems are engineering controls needed in the healthcare facility laboratory.
The administrative controls involves alteration of organization policies and the way of carrying out duties. In this case, work from home policies will be established for the staffs not involved in healthcare deliveries such as secretaries. Furthermore, sick employees will be allowed to work at home.
Personal Protective Equipments (PPEs)
- According to OSHA standard, employers are required to: train employees on how to wear and use PPEs effectively.
- Provide appropriate PPEs without deducting from the employees salary.
- Train the staff to store, maintain, and replace PPEs.
- Undertake assessment on the PPEs.
- PPEs include gowns, face mask, gloves, and eye protectors.
In the OSH Act both the employee and the employer have a responsibility to make work environment friendly.
The employers are required to provide a healthy and safe environment. On the other hand, the workers should take part in the creation and implementation of health and safety policies. The involvement of both workers and employers in this act ensures that the law is implemented suitably.

Plan for this Program Implementation In The Healthcare Facilities
- Participation of the employer and employee in leadership.
- Risk identification and management.
- Prevention, communication, and control of risk.
- Evaluation of the System.
Training Technique:
- The training will be hands on;
- Drilling will be conducted;
- Trained observer will be included to reduce accidents;
- Specific processes such as decontamination procedures will be practiced.
Program design:
- The program will be Interactive;
- It is designed for workers;
- It involves approach to all workplace hazards;
- Structured materials from training will be provided.
The success of the program will be monitored by the infection and control committee.
The program will successful if:
- Covid-19 transmission cases among healthcare workers in the hospital is greatly reduced.
- All health care workers apply the hospital infection control policies.
- The staff practices matches the rules, guidelines, and standards set by the government.
This infection control and training program enlightens and protect employees from COVID -19 virus.
The process of this program implementation include: training the employer and the employee, collecting COVID-19 spread data, analyzing and presentation of data result to the formed committee. Lastly, policies and actions plans are formulated according to the data results.
Additional materials to be used in the training include CDC website—protocols, Engender Health training program—web-based, an instructor guide, NIEHS training program, and ICAT tools. In the training a drilling opportunity will enable the trainee to wear the PPEs appropriately.



References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Characteristics of health care personnel with COVID-19. Web.
Maps and trends (2020). New Cases of COVID-19 in World Countries. Web.
National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.(2020). NIEHS COVID-19 response training tool: Protecting yourself from COVID -19 in the workplace. Author.
Ng, K., Poon, B. H., Kiat Puar, T. H., Shan Quah, J. L., Loh, W. J., Wong, Y. J., & Raghuram, J. (2020). COVID-19 and the risk to health care workers: A case report. Annals Of Internal Medicine,172(11), 766-767.
World Health Organization. (2020). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report. Web.