Introduction
The purpose of this paper is to create a mini-management plan for Cyber Software Incorporated. The plan is expected to help the CEO of the company to solve organizational problems. The plan will begin with a discussion on the vision and mission statements of the company.
This will be followed by a discussion on the organizational structure that the company should adopt. Moreover, the culture that suits the chosen organizational structure will be discussed. The last part of the plan will focus on how changes in the POLC framework will prevent future mishaps.
Vision and Mission
The vision of the company is to be the leading developer of the most trusted cyber protection products in the US. The CEO envisions a company that is always at the cutting edge of the industry to win the trust of its customers. The vision statement supports this aspiration by motivating employees and the management to develop the best products.
The vision statement is appropriate because it provides a clear basis for goal congruence. Currently, the company lacks goal congruence since its software developers have divergent opinions concerning the most effective course of action or objective to pursue. The vision statement will align everyone’s efforts to the goal of making Cyber Software, the leading company in its industry.
The mission of the company is to use the most advanced technologies to develop better software and cleanup procedures to keep customers’ information safe. The mission statement is appropriate because it clearly indicates the purpose of the company.
It emphasizes the CEO’s belief that the company must always improve its products (software) and establish damage control procedures. Thus, it enables employees to realize that all their decisions and actions must focus on product improvement to ensure customer satisfaction. This will lead to the achievement of the market leadership envisioned by the CEO (Jeffs, 2008).
Organizational Structure
Democratic Hierarchy
Cyber Software should adopt a democratic hierarchical organizational structure. This means that the CEO will be the final authority in the company. However, the CEO and managers at various levels will consult employees before making decisions that affect them. A democratic hierarchy will benefit the company in the following ways. First, it will provide a clear reporting structure (Cameron & Quinn, 2011). The structure will define the scope of employees’ authority and responsibilities at various levels of management.
This will improve efficiency by preventing employees from covering similar ground. Specifically, it will eliminate role duplication (Jeffs, 2008). Second, the structure will facilitate cooperation among the strong personalities that have emerged in various divisions. The structure is characterized by a chain of command that enables employees to know the sources and recipients of instructions. In this respect, the structure will ensure obedience by eliminating the conflicts that are likely to arise as employees struggle to protect their egos.
Third, democracy will allow employees to have adequate authority to manage their work (Cameron & Quinn, 2011). This will promote creativity and innovation to enable the company to improve its competitiveness.
Employees are also likely to develop a strong sense of ownership and job satisfaction if they are in control of their work. Finally, the structure will provide clear lines of communication. Effective communication will enhance the planning and implementation of strategies.
Organizational chart
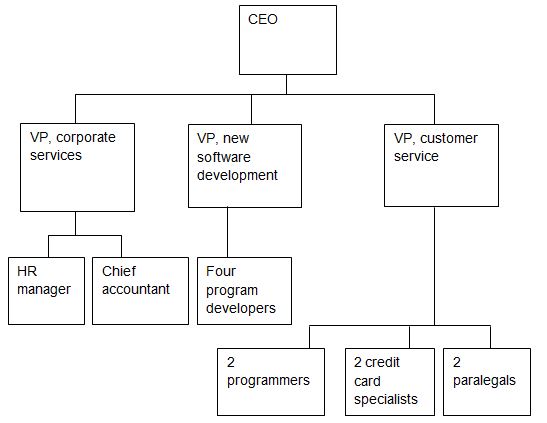
Joseph Jackson is the CEO of the company. Megan Rogers is the vice president (VP) of corporate services, whereas Christine Williams is the VP of new software development. Ken Peterson is the VP of customer service. All the vice presidents will report directly to the CEO. Philip Howard is the human resource manager, whereas Mary Hope is the chief accountant. Howard and Hope will report to the VP of corporate services. The four program developers will report to the VP of new software development.
The programmers include Judy White, Michael Ashok, Richard Robinson, and Andrew Thompson. In the customer service division, the two programmers are James Edgar and Charles Wong. The two paralegals are Erick Gamble and Anne Jones. Credit card specialists include Abraham Cameron and Bob Wolfgang. The paralegals, programmers, and credit card specialists will report to the VP of customer service.
Management Team Profiles
The CEO has worked for 15 years as a software developer in a fortune 500 company. He has also worked for five years as a senior sales executive. This involved selling cybersecurity software. Currently, the CEO oversees the operations of the three divisions of Cyber Software. His duties include new market development, leading the entire company, ensuring profitability, and formulating policies in collaboration with managers. He has a Master of Science in Software Engineering and a Master of Business Administration.
The VP of corporate services has worked for ten years as a finance manager. She also worked for six years as a senior administrator before becoming the deputy CEO of a midsize software company in the UK. Currently, she is responsible for supervising the human resource manager and chief accountant. She also develops finance and human resource policies for the company. Her qualifications include a Master of Science in Finance and a Bachelor of Business Administration.
The VP of new software development has over 20 years of experience in developing cybersecurity software. She is responsible for new product development, research, and establishing software security procedures. She has a Master of Science in Software Engineering.
The VP of customer service has worked for seven years as a customer representative and ten years as a customer relationship manager. His current duties include handling customer complaints, marketing, and establishing procedures for providing customer support. The VP has a Bachelor of Science in Information Technology and a Master of Business Administration.
Organizational Culture
The new organizational structure calls for the adoption of a hierarchy culture. This means that the company will abandon its free work environment and adopt a bureaucracy to ensure stability and control.
The new organizational culture will ensure control by providing a framework for distributing authority and participation in decision-making processes (Cameron & Quinn, 2011). It will help the company to improve its efficiency by encouraging specialization among employees and standardization of procedures. As a result, the company will produce reliable software within short turnaround time.
The culture change should be implemented in the following ways. To begin with, the CEO will be required to create new values to guide the behaviors of employees (Jeffs, 2008). Respect, accountability, and meritocracy are key values that will be adopted to achieve stability, efficiency, and predictability. Respect must be enhanced to ensure effective collaboration between employees and their supervisors. This will eliminate the conflicts that are likely to arise if employees undermine each other.
Accountability will promote high performance and reduce mismanagement of the resources of the company (Cameron & Quinn, 2011). By internalizing accountability as a value, employees will focus on pursuing the vision of the company by consistently achieving their targets. Meritocracy is an important value because it will promote fairness and excellent performance.
Only qualified individuals will be selected to hold various leadership positions. The profit and cost performance of the company will improve significantly if employees are assigned duties based on their merit or competence.
The CEO must also collaborate with his managers to develop new rules or policies to govern the company. Control, stability, and efficiency can only be achieved if there are rules that facilitate effective management of employees, products, funds, and company assets (Cameron & Quinn, 2011).
For instance, clear product development policies will ensure that the software developed by the programmers meet customer expectations in terms of security and usability. Similarly, clear reporting policies are likely to avert conflicts between employees who are competing for power.
Implementing the new culture will also require the CEO to hire effective leaders. The leaders must embrace a functional hierarchical leadership style in order to succeed (Cameron & Quinn, 2011). In this respect, all members of the management team should be able to organize, coordinate, and oversee processes and employees.
This will ensure effective management, efficiency, and achievement of long-term objectives. The leadership ability of managers should be assessed during recruitment to ensure that only the right individuals are hired to lead various divisions in the company.
POLC Framework and Future Mishaps
The key elements of the framework are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Changing these elements will prevent future mishaps in the following ways. At the planning stage, the company will adopt new vision and mission statements. The new statements will prevent strategic drift by ensuring that the company sticks to its long-term goal of being the best (Jeffs, 2008). The company will have to respond rapidly to changes in its external business environment to remain at the cutting edge of the industry. This will prevent failure.
Organizational change will involve creating a new structure and culture. The new organizational structure will prevent failures that are likely to arise due to poor lines of communication and reporting. Specifically, it will eliminate too much freedom among employees, which is likely to cause wastage and unnecessary disagreements in the process of making decisions (Jeffs, 2008). This will be reinforced by the hierarchy of culture that will promote accountability and high performance.
The hierarchical leadership style will provide employees with the opportunity to grow or develop their careers through promotions (Cameron & Quinn, 2011). This incentive will boost productivity. By limiting employees’ authority, the management will prevent costly failures such as ineffective products that are likely to arise if employees have the freedom to control all aspects of their work. Similarly, controlling employees through rules or policies will prevent the failures associated with misunderstandings.
Conclusion
Cyber Software should adopt a democratic hierarchical organizational structure to address its challenges. The structure will provide a clear reporting system, thereby preventing conflicts and inefficiency in the company. A hierarchy culture will ensure a seamless transition from the flat to the hierarchical organizational structure. The CEO should adopt values, leadership styles, and rules that support the hierarchy culture to avoid failure in the future.
References
Cameron, S., & Quinn, R. (2011). Diagnosing and changing organizational culture. London, England: Palgrave.
Jeffs, C. (2008). Strategic management. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons.