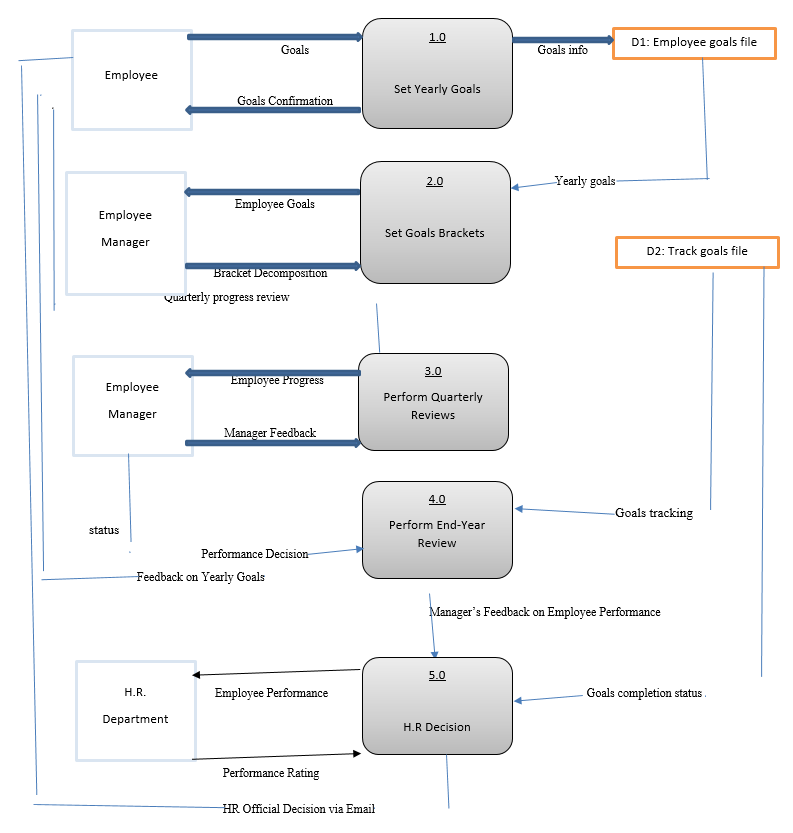
A performance-evaluation data flow diagram (DFD) is a software-based application allowing data access depending on the login side; administrators and employees access evaluation reports on separate platforms. As summarized by Mukunda (2019), the specific software requirements for the data storage process are scripting tools, the operating platform, which can be Windows™ or its equivalent, and the front and back-end programming tools. Johnson et al. (2021) noted that the first step to creating a data flow management system is determining the required technology and supporting hardware for storage purposes.
Moreover, a performance evaluation process is procedural, where the human resource administrator in charge of initiating the review must clarify the criteria and job requirements to be analyzed (Mukunda, 2019). Performance review is so holistic that, apart from evaluating on provided appraisal criteria, the process also entails employee strengths and weaknesses identification for further assistance (Mukunda, 2019). The Mukunda (2019) data flow diagram, albeit designed for a learning institution, has a critical relevance in the universality of performance evaluation in any workplace. Functional requirements that are important for a comprehensive evaluation are the administrators, the staff, and supervisors.
The functional differences are distinct when considering appraisal responsibilities in the two diagrams. Whereas in the first data flow diagram, the admin controls a wide array of data characteristics and entries, the second DFD shows the role of employees and supervisors in making data personal entries and saving/printing reports by administrators. Mukunda (2019) approved the data flow diagram for workplace applications, given that it covers the entire scope of a performance evaluation process, including employee self-reflection and collaborative coordination between top managers and their subordinates. The staff side shows how employees can access their performance data, whereas the self-appraisal function promotes idea exchange between administrators and subordinates.
References
Johnson, R., Carlson, K., & Kavanagh, M. (2021). Human resource information systems. SAGE Publishing.
Mukunda. (2019). Performance appraisal. International Journal of Current Engineering and Scientific Research (IJCESR), 6(4), 63-69.