Executive Summary
In order to establish a successful business, it is important to develop a comprehensive strategic plan, which is the basic blueprint for the actualization of a business plan. Reflectively, the strategic plan is inclusive of the business environment, penetration strategies, and success measurement parameters at the micro and macro business environment. This strategic plan is for the Early Learning Center, located in the UAE, within the region of Abu Dhabi. The mission of the business is to provide the most cost-effective and reliable nursery services within the targeted region and beyond. The business will serve customers from high and low economic ends since daycare services are used across all classes. At present, the nursery service industry within the targeted region is relatively non competitive since there are few centers offering these services. Thus, the Early Learning Center is projected to penetrate this market within very minimal resistance.
External Environmental Analysis
Demographic Environment
The population in the United Arab Emirates is one of the fastest-growing in the world. The population increased from 1.0 million in 1980 to 8.4 million in 2010 (Dagnino & Rocco, 2013). Projections made by the United Nations show that the population will increase further to reach 15.5 million by the year 2050. Therefore, the demand for the ECLC product exists and is sustainable in the UAE market since every household is a potential client as long as they have children. This population increase will create demand for the nursery services offered by the ECLC.
Economic Environment
The UAE is amongst the leading oil producers in the world. The recent rise in oil prices has increased government spending. By combining the increase in government expenditure with vibrant tourism, transport, and trade, the outcome is a favorable environment to conduct digital marketing. For 12 months to May 2013, inflation rose by an average of 0.7% (Cheverton, 2012). An increase in government expenditure implies that there is more money in circulation and people can afford to pay for nursery services for their children.
Cultural Environment
Heritage and culture are valued by the targeted market. The United Arab Emirates is a diverse, multi-ethnic, and multicultural society, which makes it a perfect destination for the highly stratified ECLC nursery services (Blythe, 2011). High rates of literacy in the UAE mean that demand for nursery services is on the rise. Besides, Urdu, Arabic, English, and Hindi languages are spoken in the UAE. This makes it easier to tailor a marketing language. Considering that Islam is the main religion in the UAE, the cultural-based ECLC nursery will register a success.
Political Environment
In the UAE, the government’s regulations, taxation strategies, directives, norms of leadership, and employment regulations are highly flexible for business. The UAE is one of the most promising business places with remarkable expansion in the corporate world. The nursery service sector has taken advantage of the favorable political conditions to expand their market niche. The stable political environment in the UAE is a pull factor rather than a push factor for the revolutionary ECLC nursery service approach.
Technological Environment
Social media such as Twitter and Facebook are currently the most utilized platforms and can be exploited positively to reach more customers in the UAE. This will not only control loses, but also give an accurate record of sales and projections if the ECLC adopts different social media platforms (Dagnino & Rocco, 2013). The advent of computer scanners at retail checkout counters means that the supply of different nursery services should be accompanied by barcodes. This will ensure strategic product positioning.
Natural Environment
Although most companies have been operational within sustainable environmental practices, there have been incidences of conflict between these companies and the conservationists. For instance, most nurseries have been accused of negligence, especially in hygiene and waste disposal. Therefore, ECLC should package its products to include the aspect of environment friendliness to appeal to potential clients.
Product and Branding Strategy
Product Objectives
The ECLC has several products that are able to benefit from quality, feature, and style improvement since the business already operates in a market that is sensitive to preference changes. Therefore, the objective of the ECLC products is to create an environment of its own competition through the creation of multiple products to suit the needs of different customers. Besides, the products will be packaged as ideal, price friendly, and of high quality to meet the needs of the potential clients.
Product Mix
The Early Learning Centre (ECLC) offers different products that are tailored on the basis of scope, pricing, and duration to meet the demand of different categories of clients. The center is staffed with skilled or, in fact, teachers with specialization in Early Childhood Care and Education (English and Arabic teachers). The center has 13 teachers, 9 with both bachelor’s and postgraduate professional requirements in early childhood care and education, and the rest 4 teachers have diploma level experiences in Montessori or specifically in the early years. The products appeal to children from the age of six months to four years. The center has very flexible service hours from 7:30 am to 4.30pm, five days a week with pick-up times at 12:30pm, 2.30pm, and 4.30pm.
As part of the depth and product life cycle, the Early Learning Centre (ECLC) has continued to use innovation and expertise capabilities in the development of different products through multiple branding to appeal to a myriad of customers across Abu Dhabi and beyond. Most of the nursery care services are positioned as the first of their kind besides existing in the form of multiple brands. The average price for a semester of care is between 13,000 AED to 15,000 AED. The low prices for high-quality services have endured customers to the Early Learning Centre since they are able to enjoy good service at a reasonable price. As a result, the center has been successfully packaged as a center for satisfaction, fulfilling customer desires, and expansion into new territories.
As part of the strategies meant to increase the visibility of the Early Learning Centre products, the business has adopted focused differentiation as part of business and product management. For instance, the company has adopted different lines of products since the Early Learning Centre has resounding information about customer trends across the UAE. In addition, the Early Learning Centre has endeavored to create a permanent bond with the customers through sponsorship events as part of the corporate social responsibility. Through these differentiation mixes, the Early Learning Centre has become one of the most visible and affordable daycare centers in Abu Dhabi. For instance, the loyalty cards and private membership services have created a cult-like following for the Early Learning Centre, especially among the working-class families.
Pricing Strategy
Pricing Objectives
Pricing of products and services is of fundamental importance in the four elements of the marketing mix that generates profit for business enterprises. The factors that influence the price of commodities and services can be categorized as external and internal (Dagnino & Rocco, 2013). Pricing thus, is more than just simple calculations of the cost of production and setting up a mark-up. Consequently, pricing policy becomes a major component of enterprise marketing plan, which is part of the whole business plan. The pricing objective adopted by the Early Learning Centre is quantity maximization since the centre’s main mission is to become a leader in terms of market share amongst other day care centers and nurseries in the UAE. Consequently, the pricing objective of the Early Learning Centre seeks to maximize the number of the products and services that clients have subscribed.
Demand and Price Sensitivity
Since the products offered by the Early Learning Centre fall in the basic needs category, their price elasticity of demand lies between zero and one (0 < PED < 1). This implies that demand by the low-end and high-end of clients is inelastic. However, the two groups of users have different degree of inelasticity. The price elasticity of demand of the Early Learning Centre services for low-end consumers is -0.65 and -0.45 for high-end consumers. This implies that the demand for the nursery services by the high-end consumers is less elastic than demand by the low-end consumers because a change in the price of electricity by one unit results to change in quantity demanded by lesser units (0.45) than that of low-end consumers (0.65). Graph 1.0 shows the demand curve for the two groups of users and the effect of price increases in the quantity demanded.
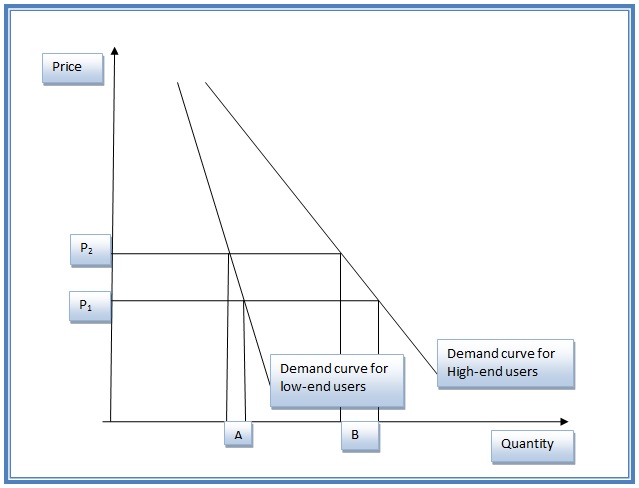
From the graph, assume that the price charged for nursery services at the Early Learning Centre increases from P1 to P2, the quantity demanded by low-end clients will decrease by area B while for high-end clients will decrease by area A. Area B is greater than area A because demand for nursery service by high-end clients is more elastic than the demand by low-end clients.
New Product Pricing Strategies
Owing to the pricing objective of the Early Learning Centre; quantity maximization, the business’ marketing strategies include multiple pricing, ‘good, better, best’ pricing, loss leader pricing, and product bundle pricing. Multiple pricing aims at luring customers to make large purchases by offering slight discounts to customers who subscribe to many services. The prices of single services are slightly higher to those that purchased in bulk. For example, subscribing to two services at once will cost the customer approximately 2,000 AED less than subscribing to a single service. Besides, the prices are offered in a series of three formats with the price of each series rising above the price of the previous series.
The products are also bundled together and the customer who subscribes to a single service can get complimentary service for less. Product bundling has helped the Early Learning Centre to achieve its objective by making it possible to sell items that might have not been sold. In calculating the unit cost of the services retailed by the Early Learning Centre, it applies the Conjoint Analysis, which is a marketing research tool that is used to determine attributes of each product and how the features affect the prices. The choice to use conjoint analysis is supported by the fact that it is flexible and less expensive to carry out than concept testing (Dagnino & Rocco, 2013).
Product Mix Pricing
The extent to which the prices set are sound on cost, demand, and competitive criteria are within the scope of product affordability, product differentiation, and product usability at the Early Learning Centre. For instance, due to multitude and complexity of factors involved in determining the price of products, the Early Learning Centre has been proactive in assembling relevant information on the market conditions, which determine the long term price changes. However, the short term price policies are tactical in nature as they Endeavour to realize short term business objectives, and are employed by the Early Learning Centre in relation to the goal they are intended to achieve for each pricing strategy (Blythe, 2011).
Price-Adjustment Strategies
The past literature in price formatting suggests that price formats are chosen by companies to attract particular customers and position such a product in the market. For instance, prices that end in 9 (odd pricing) such as 400.99 AED or 400.59 AED have the potential of creating a price image in the minds of customers. The price image is that the product or service in cheaper. This center may use this strategy to fulfill the promotional and everyday low price (EDLP) formats (Dagnino & Rocco, 2013). On the other hand, use of even pricing may be advantageous or disadvantageous, depending on the targeted customer. For instance, the high economic-end customer would not consider price image as the determinant factor in purchasing. Rather, the higher the price of a product, the higher the chances of product intake since the mind of such a customer will create a perception of quality. However, even pricing may not auger well with the low economic-end customer since the perceived price image would be the expensive tag. The Early Learning Centre will have to use proactive price-adjustment strategy to make the services appeal cheaper to the low-end clients.
Marketing Communications Strategy
Marketing Communication Objectives
Advertisements are very manipulative and use tactics that directly and involuntarily appeal to the mind of the target person. Usually, advertisements appeal to memory or emotional response. Reflectively, the success of the Early Learning Centre products promotion messages will be deeply entrenched in the principle of keeping reliable and professional reputation in exchanging ideas and convincing customers. The advertisement message will be presented in two channels, that is, below-the-line and above-the-line. Under the below-the-line approach, the products will be marketed directly through the print and visual press. On the other hand, under the above-the-line approach, the advertising message will be presented via the social media to appeal to the low-end and high-end customer segments. The use of social media to advertise the Early Learning Centre products was informed by the need to;
Attract
The main objective of this marketing plan is to attract the young family customers market through the Early Learning Centre website and a twitter fun page in order to sell the products to customers.
Customer retention and loyalty building
Properly modified Early Learning Centre website and the twitter fun page will reassure the customers on quality. Through massive recruitment of Early Learning Centre products funs in the twitter page, the business will not only benefit from an increased traffic of online compliments, but also record high rates of customer loyalty as most customers are influenced by reactions from other clients. Customer retention strategy is meant to position the company as a market leader in terms of customer satisfaction tracking and response (Dagnino & Rocco, 2013). This will be achieved through optimization of the Early Learning Centre website’s search engine.
Promotion Mix and Six-Step Communication Effectiveness
As Early Learning Centre’s business is based on B2B model, the company’s promotion and advertising activities should include usage of all marketing tools of B2B Marketing Mix in order to promote their services. With its decided joint partner(s), the business will recruit a marketing company that will have the responsibility of marketing its services across the regions of the UAE (Blythe, 2011). This strategy is likely to be successful since the contracted company will have better knowledge of the industry, requirements, and approach to minimize conflict as a result of different perceptions (Cheverton, 2012). Also, placement of publications in industry and trade media would maximize the increase in awareness about the Early Learning Centre. In the initial stages, public conferences, seminars and workshops need to be organized for potential customers where individuals from organizations can express concerns, voice feedback, and get acquainted with the Early Learning Centre’s services. A minimum of 4 seminars in 3 locations within the target market over 3 months are required.
The Early Learning Centre’s key aspect is to build loyalty and trust towards the brand. The center’s superiority in comparison to its competitors must be clearly established. Social media will be used as a promotional tool to place brand in the digital sphere. Presence in professional social media websites such as LinkedIn can be used to advertise the Early Learning Centre’s Abu Dhabi presence and expected establishment in Dubai.
In terms of personal selling, the Early Learning Centre can appoint trained sales executives to attend seminars and expos in order to approach target customers and generate business. The main message of the Early Learning Centre in its advertising campaigns will revolve around the creation of increased value with the adoption of center’s high-end quality services. With regards of the estimated costs involved in marketing and promotional activities, the Early Learning Centre’s initial promotion budget should range between 5,020 AED and 12,000 AED roughly amounting to 7% or 8% of the business’ expected revenues.
Distribution Strategy
Distribution Objectives
Marketing strategy distribution channels are essential before actualizing projections of a blueprint. The Early Learning Centre’s distribution objectives and strategies are to meet the demand of customers across the UAE and ensuring efficiency in the supply chain management. As a strategy for further penetration of the Abu Dhabi market, the Early Learning Centre has improved on its distribution network by adding a fleet of automobile product display shops. These automobiles are fitted with visible posters of the center’s products. The automobiles are allocated to different regions across the Abu Dhabi where the availability and visibility of the company’s products are minimal.
Through timely appeal to emotions and self prejudice, the Early Learning Centre products are packaged to engage the ‘perceived goodness’ and need to identify with ‘the ideal’ in the functionality and deployment within different television, social, and print media advertisements (Blythe, 2011). These attractive values are clearly painted as perfect in the various advertisements about the products through use of bright and powerful communication themes. In order to make this strategy successful, the advertisement messages are modeled on the platform of consistency and direct appeal to the target market.
References
Blythe, J. (2011). Essentials of marketing communications. New York, NY: FT/Prentice Hall.
Cheverton, P. (2012). Key marketing skills: strategies, tools, and techniques for marketing success, Sterling. London, UK: Kogan Page.
Dagnino, G., & Rocco, E. (2013). Competition strategy: theory, experiments and cases. New York, NY: Rutledge.