Introduction: The Need for Economic Growth and the Obstacles in the Way
The economic growth rates have been rather shaky in Russia over the past few decades (see Fig. 1). The observed phenomenon can be attributed to the fact that the state has been recovering from the effects of the USSR collapse for quite long and trying to identify a unique path that would define its further strategy in the global market. Because of the current political issues that clearly aggravate the situation, the economy of Russia clearly needs a rapid and powerful impetus so that it may revive. The focus on private entrepreneurship and, therefore, substantial investments in the private sector, along with the endeavors to build stronger ties with the global economic community, can be viewed as the possible recommendation from the further strategy of the state authorities.
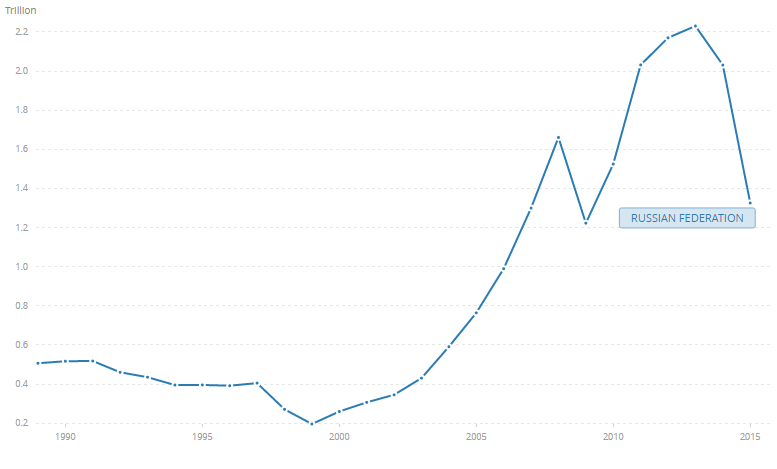
Russia has recently had a conflict in the economic domain, mostly due to the political issues that the sanctions imposed on it by the EU members. However, due to the efficacy of the oil and gas industry, the country’s GDP has been bearable over the past few years. Furthermore, a recent report points to the fact that the corruption rates are rather high in the Russian economy domain. Therefore, the chances for a rapid improvement and the promotion of active economic growth are rather low in the designated environment.
According to the 2016 data, the GDP rates have been dropping significantly since 2011, reaching their top in 2013 ($2.31 trillion) and plummeting to $1.326 trillion in 2015. Therefore, it is imperative to introduce the measures that will help prevent further reduction in the economic growth rates. A combination of political, financial, and economic innovations is required for these purposes.
Current State of the Labor Market in the Country: Essential Data and Its Analysis
When considering the specifics of the labor market in Russia, one must mention that the state government has been developing a unique labor market model. The framework designed by the state authorities is quite different from the Western counterpart because it is supposed to represent the needs of the Russian people and be applicable to the environment of the target market. The model has been in development since the 1990s and is currently being tested in the context of the Russian market. The principles of hidden unemployment, which currently appear to dominate the Russian market, can be viewed as an obvious factor shaping the strategy in question. Being the primary reason for concern, the unemployment rates define the choices made by the managers of Russian companies. For instance, dismissing the staff members is not considered a common practice in the labor market environment; instead, the hidden unemployment strategies, such as a shortened working week, unpaid leave, etc., are deployed in the system. The employees, in their turn, appear to be satisfied with the approach used by managers because the fear of being fired and, therefore, being unable to gain the resources necessary to sustain the basic living standards is diminished.
Food Security Situation: Evaluating the Current Sustainability Situation
The situation related to food availability in Russia has changed drastically since the collapse of the Soviet Union and the emergence of separate republics. Particularly, the range of food available to an average citizen has increased dramatically. The specified change can be explained by an admittedly positive change in the average household income level and the reduction in poverty rates. With the increase in the average income, the purchasing power of the Russian people has risen significantly, which has led to a massive increase in product consumption rates, as well as the variety of food purchased by the citizens.
Moreover, the very process of consumption appears to have changed as well. Although there is a tendency for the population to shift from consuming fats to buying starch-based food, obesity rates still remain a problem. Therefore, there is an obvious issue as far as the dietary choices of the target population are concerned.
Major Sectors of Economy and Their Market Structures: Assessment
As stressed above, oil and gas can be deemed as the industry of the highest priority in Russia. However, the precious metals and minerals industry also plays an important role in the Russian economy. As far as the market structure of the identified areas of the Russian economy is concerned, one must keep in mind that the current state of the target market is comparatively new, and that the past tendencies still affect the Russian economy to a considerable extent. Because of the significant power that the state authorities used to have over the large industries, including oil and gas, the present-day regulation processes carried out by independent owners can be deemed as lacking certainty.
As far as the market structure is concerned, there are several large corporations that determine the changes in the target market and can be viewed as the companies that determine the development of the oil and gas market. Although Gazprom is typically viewed as an independent organization that carries out essential transactions in the identified environment, it is the affiliate of the Rosneft and Gazprom Group, which, in fact, can be considered the largest company in the oil and gas industry at present. Apart from the specified corporation, the firms such as Bashneft, Russneft, LUKOIL, Surgutneftegaz, and several others need to be mentioned as the corporations that govern the identified domain.
A closer look at the market will show that it, in fact, is very powerful. It is clearly in the stage of its maturity, yet its resources have not yet been drained, and it is certain to remain profitable for an impressive amount of time. Furthermore, the bargaining power of buyers is comparatively low in the identified realm because the customers cannot affect the prices of the product. The bargaining power of suppliers, on the other hand, is very high because of the lack of substitutes in the oil and gas market. The threat of new substitutes is, therefore, very low, and so is the threat of new entries. Indeed, in light of the fact that the industry dominated heavily by the corporations that have been operating in it for decades and, therefore, have gained the reputation and the power required to stay there long, it is unlikely that new entries will affect the oil and gas domain significantly. Consequently, the competition rates are very high in the identified realm.
Major Sectors of Economy and Their Ownership Status: Assessment
At present, Gazprom, which is the greatest Russian gas company, is private. As explained above, the transition from being a state-owned enterprise to becoming a private corporation implied that the company should suffer an impressive shock. Nevertheless, Gazprom managed to recover from the change and adapt toward the environment of the global economy comparatively fast. Particularly, most organizations in the target area can be defined as joint-stock ones at present.
State Trade Policies and Essential Trade Partners in the Global Market
Crude petroleum, refined petroleum, and petroleum gas are the primary exports of Russia. When carrying out the necessary transactions, the companies that are currently under the jurisdiction of Russia follow the principles set by WTO. It should be noted, though, that the compliance with the standards set by WTO is a rather challenging task for the Russian companies because they also have to exist in the environment of the Russian market, with its unique characteristics and requirements.
The fact that the current RF regulations do not allow gaining immediate independence from the foreign investments also has had its mark on the Russian economy. As a result, the process of struggling against the binding requirements of the WTO exhausts the Russian companies operating in the oil and gas market and drains them, triggering a drop in sustainability. Therefore, the transfer to the WTO-based principles is a necessary step that, nonetheless, requires the restructuring of the Russian market, as well as its economic relationships, in general.
Trade Pacts of Which Russia Is a Member or a Potential Member
China, Germany, Ukraine, and the United States are currently among Russia’s major trade partners. However, because of the conflict in the eastern regions of Ukraine, the trading process between the states has become significantly slower. The free trade agreement that Russia has with Ukraine has been suspended due to the military conflict mentioned above. Nevertheless, RF remains a part of the CISFTA agreement, which includes Ukraine as well and, therefore, implies that the essential economic transactions should be carried out among its members.
Furthermore, Russia has extensive trade relationships with Belarus under the aegis of the Union State agreement. The Eurasian Economic Union, in its turn, regulates the trade-related operations among Armenia, Kazakhstan, Belarus, Mongolia, and Russia. The latter is also a part of the CSTO agreement, which allows the state to perform essential trade-related processes with Bulgaria. Finally, the Commonwealth of the Independent States opens a plethora of opportunities for RF to maintain economic relationships with the remainder of the former members of the USSR.
Immigration and Emigration Rates and Their Impact on Russia
In 2016, approximately 17 migrants per 1,000 people have been registered. There is no need to stress the fact that migration as a phenomenon has its advantages and disadvantages relative to the state economy. The increase in the number of immigrants from neighboring states poses an economic threat to the state because it produces higher unemployment rates among the target population.
Role of Foreign Direct Investment into and from Russia
Foreign investments allow the Russian private entrepreneurship to flourish. Because most of the companies that determine the economic growth of the state are private, there is an urge to convince investors to view them as the target for their financial support. However, because of the military issues mentioned above, investors are reluctant to consider Russia as their target. Their doubts are quite understandable; with the lack of political stability in the state, there is a high risk of losing the money. Thus, restoring the sense of safety and economic security that the Russian market used to have is essential to the well-being of the Russian economy.
Character of State and Government and the Effectiveness of the Public Policy
The issues related to the social conflict inform the choice of the state policies but do not define them. The public policies, in their turn, create the environment in which private entrepreneurship is encouraged. At present, public policy in Russia is shaped by the system of laws based on the principles of democracy.
Conclusion: Trends, Opportunities, Threats, and Recommendations
Despite the profound economic philosophy and the well-developed strategies, Russia may face a serious threat to its well-being because of the recent political conflict. Before the military confrontation erupted, RF was clearly attempting to create prerequisites for entering the environment of the global economy, the endeavors to align the state policies with the international policies, as well as the enhancement of the private sector pointed clearly to the recognition of the need to become a member of the global market. Unfortunately, the recent conflict distracted the state authorities from promoting the economic change. As a result, private entrepreneurs have fewer opportunities for excelling in their performance. More importantly, the government is currently unable to invest in the development of the essential industries because a range of financial resources is used to address the current economic constraints, including the sanctions imposed on Russia by the EU. Therefore, it is imperative to create the environment in which a faster resolution of the issue becomes a possibility. As soon as the military confrontation is over, Russia will be able to become a full-fledged member of the global economy realm.
Bibliography
“GPD (Current USD).”World Bank. 2016. Web.
Lunze, Karsten, Elena Yurasova, Bulat Idrisov, Natalia Gnatienko, and Luigi Migliorini. “Food Security and Nutrition in the Russian Federation – a Health Policy Analysis.” Global Health Action 8, no. 1 (2015): 1-10.
“Russia.” The Central Intelligence Agency. 2016. Web.
“Russia.”The Economist. 2016. Web.
“Russia.”The Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 2016. Web.
“Russia – Labor.” Export.gov. 2016. Web.