Introduction
This paper presents a detailed discussion on the effects of increase in the prices of oil both in the short run and long run period of time. The risk to growth following a progressive increase in the price of oil will be conclusively discussed both in the short run and long run period. As a response measure to the increase in the price of oil, monetary policy formulated by the Federal Reserve Bank is worth investigating and making inferences.
The threat to growth following rising price of oil
In the early 70s, decrease in the output and rising inflation rates lead to sharp rise in the price of oil. Even In the year 2007, much more rise in the price of oil was associated with fluctuation in the outputs and inflation rates.
During the same year, the alterations in the price of oil were activated by a change in the supply of the same commodity in the market place. War between the Arab and Israel prompted the formulation of an oil embargo consequently reducing the supply of oil in the market place in 1973. Another factor sourced from the supply side was the consequences of the Iranian revolution in the year 1979.
On the other hand emerging economies of china and Japan are the recent cause of the rise in the price of oil. Rapid economic growth and development taking place in these nations creates demand for oil to be used in various sectors of the economy. In recognition of the fact that developing nations are considering trading with up coming economies, expenditures on the products from the United States reduce to a greater extent.
Use of AD-AS model
This is a model relating the price with the level of production in an economy with reference to employment rates, gross domestic produce policies to stabilize inflation rates, an ultimately macroeconomic observable fact. The AS-AD model takes into custody the interface between the Aggregate Demand (buyer) and the Aggregate Supply who in this case are the sellers both analyzed in the long and short run period of time. In a macroeconomic context, aggregate demand is specified by a sum total of C+I+ G+ (X-M) in an open economy.
Effect of a rise in oil price on inflation and output
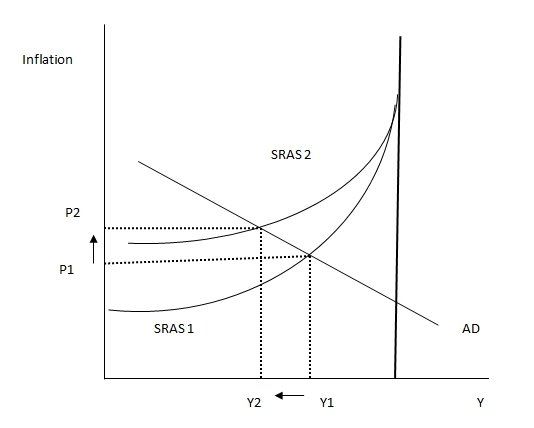
The graph below shows the effect of a rise in oil price on inflation and output. An inward shift in SRAS following a rise in the price of crude oil imparts on the price level causing a contraction of the AD signified by a movement from Y1 to Y2. Y f c represents full employment of factors of production in the long run. It is now evident that continuous increase in the price of oil reduces output level and raise inflation from P1 to P2.
Effect of the response of Reserve Bank to the oil price increase
The reserve bank can manipulate the interest rates to stimulate growth by creating demand in the economy. Low interest rates attract people to borrow from financial institution consequently raising their purchasing power. Recessions are related with the surging prices of oil and the increase in the rates of funds from the Federal Reserve Bank. It is important to focus on some economic effect of the prices of oil and the federal funds rate.
An empirical approach tries to analyze the decline in output from an increase in the price of oil. In an investigation by economic researchers, the findings were that an increase in the prices of oil and a subsequent increase in the funds rate by the Federal Reserve Bank would have a cumulative effect of lowering the gross domestic product. In the year 2004, there was a 30% increase in the price of oil from $33 to $ 45 per barrel.
The immediate reaction was maintaining the funds rates at a constant value which ultimately reduced the growth rate by only 1.2%. If the funds rates had been increased (in the form of tightening the lending rates), then prediction shows that development would have declined by 2.1%. The investigation shows a clear difference in the effect of an increase in the funds rates and when the rate is maintained at a constant value.
Federal Reserve Bank is usually responsible for the changes in the interest rates which affect the supply of money in the market. A higher interest rate acts as a disincentive to borrowing money from the bank. The succeeding consequence is little money chasing the same product. On the other hand, a decrease in the interest rates motivates people to borrow more funds from the bank therefore increasing the supply of money in the market.
This means that more money chasing the same product. Because of the competition for the same product, it is possible that growth in national income will be registered but at a higher cost of inflation as indicated in the graphical diagram above. The use of monetary instrument to influence growth in an economy by a decrease or increase in the interest rates is strictly under the control of Federal Reserve Bank.
Conclusion
This essay is explicit on the effect of high prices of oil on output and inflation rates. Exogenous variables are responsible for the shift in the AD or AS curve in the short run. The long run graphical illustration of a supply curve is a straight vertical curve.
This shows that in the long run, the supply curve is not affected by exogenous variable in the industry. To regulate the supply of money in the market, monetary policy is employed by the Federal Reserve Bank. For a progressive increase in the price of oil, the model clearly substantiates the value attached to maintaining the interest rates at a constant rate.
Reference List
Bernanke, S, M Gertler & M Watson, “Oil Shocks and Aggregate Macroeconomic Behavior: The Role of Monetary Policy: A Reply,” Journal of Money, Credit, and Banking, vol. 36, no. 2, 2004, 287-91.
Olekalns, N, et al, Principles of Macroeconomics, 8th edition, McGraw-Hill, North Ryde, N.S.W, 2008.