Introduction
Total personal incomes continue to vary in United States workforce. The professional and business world leads in the income category (Morrison, unpaged). The professional world includes bankers, engineers, and other technocrats who have gone to school and have attained a degree or two in order to earn such high incomes. On the other hand, uneducated workers still earn meager incomes in comparison.
In this regard, what effect does the level of education have on total personal incomes? This paper will discuss this aspect by looking at the data available. Additionally, the research will focus on whether private and public schools have an effect towards income levels.
To achieve this end, the paper will look at months of school attendance and the highest attainable level of education as the main variables that have an effect on total personal incomes. This will assist educational public policy formulators in coming up with essential policies that are reminiscent of what the field requires (Morrison, unpaged).
Methodology
According to the National Bureau of Labor Statistics, there is a strong correlation between income levels and the level of education. Professional Degree Holders earn more than High School Diploma Holders (Bureau of Labor Statistics, unpaged).
According to the Bureau, it follows that a higher education means more earnings. According to IPIUMs data, at least 33% of the population have at least attained 12th grade level of education. In light of the above, the researcher will analyze the verifiability of this statistical observation.
First, the researcher will determine the percentage level of school attendance across the country. Secondly, I will relate this with the official numbers at the National Bureau of Labor Statistics (Bureau of Labor Statistics, unpaged).
The researcher will try to ascertain the fact that those with a low level of education have higher unemployment rates. This way, the researcher will compare the unemployment rates and the percentage of population that has a lower education level compared to the entire population.
The other aspect this paper will focus on will be the school enrolments. The paper will compare school enrolments in public and private schools. This comparison will inform the reader about the changing nature of school enrolments.
The focus will be on the people between a certain age bracket (6 years to 18 years) that should be in school but is not in school. Perhaps this number is contributing to the unemployment levels in America, which will be the focus of this paper.
To do this, the researcher will use comparison tables and bar graphs. Additionally, the researcher will use other visual objects such as pie charts and percentages. For further analysis and explanation in order to understand the numbers, the researcher will compare means and use inferential calculations.
This includes a t-test to ascertain the verifiability of the official percentage of the unemployment level and the percentage of people with a perceivably low education and income. Additionally, the researcher will employ the use of regression analysis to determine the relationship between total personal incomes and time.
Data Analysis
School Attendance Levels
A cursory look at the data on the highest grade of schooling from IPIUMs reveals that majority of the people, which is over 30%, go up to 12th grade. The rest on both sides are below 8%. According to Bureau of Labor Statistics, there is a 6.5% unemployment rate in the country (USA).
While this represents a huge number of people, it significantly stands out that majority of these people do not have a college degree. The following table indicates the enrolment levels in schools in United States. As the graphical representation below indicates (Table 1), there are currently less than 1% people between the ages of 6 years and 21 years that have not enrolled in at least a certain level of school.
Table 1: Enrolment Levels
Source: IPUMS 2011. Web.
Although this may not be statistical, the concept that only people who did not attain some level of education do not get jobs is disputable from this data. We can say that virtually everyone has an education but the rigors of getting a job are hard (IPUMS, unpaged).
Public vs. Private Schools
On the issue of public and private school enrolment, it is important to understand that public schools lead the pack. Figure 1 below indicates this. This data captures the age of between 6 years and 18 years. Additionally, it reflects the enrolments between 2001 and 2011 (IPUMS, unpaged).
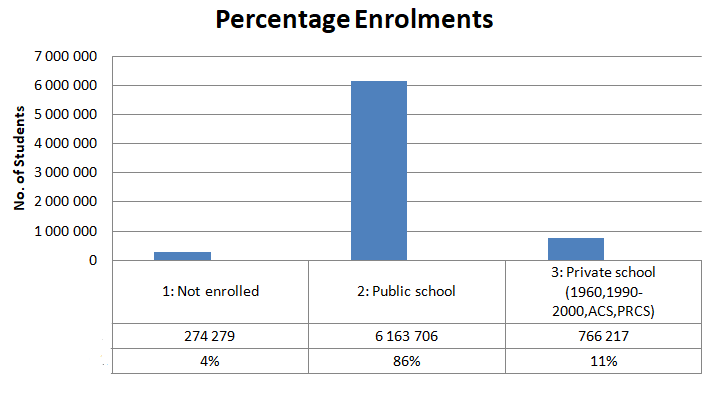
This may indicate that since 2000, there has been less and less people not enrolled in school that fall between the ages of 6 and 18 years. This is indicative of the government’s effort to cut illiteracy levels.
In Table 1 above, the recorded number of people recorded to be out of school was 21.83%. However, this figure captures a wider range of population of ages 6 and 21 respectively. Additionally, there is the general inclusion of the data from 1850 to 2011 (IPUMS, unpaged).
Could the above government effort be the reason why total personal incomes have increased over the last eight years? The conclusion by the Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates as such lends its credibility from the conclusion of this research that, truly, there is a connection.
While the people out of school averages that include the 1850 up to 2010 were 21.83%, the average that included 2000 up to 2010 was 4%. This shows that the years preceding the year 2000 had so many people out of school and hence illiterate (IPUMS, unpaged).
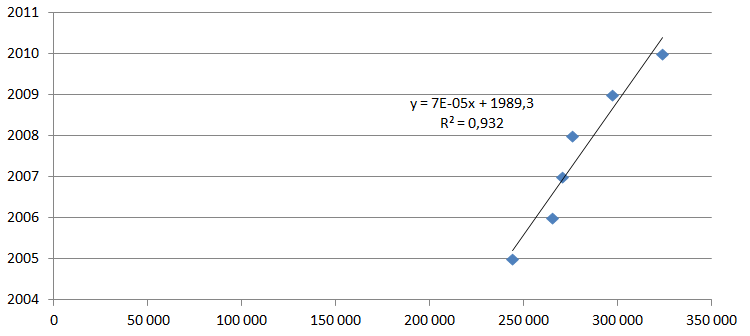
A regression analysis shows that this is likely to improve in the next few years. Below is a historical regression analysis of the incomes in the last 6 years since 2005 up to 2010.
Regression Chart
The regression chart (in the appendices section) informs the manner in which the future total personal incomes will pan out. All indications are that this is likely to increase in the next few years (IPUMS, unpaged). The equation that predicts this trend is y = 7E-05x + 1989.
Y represents the income level and X indicates the preceding year. For example, the prediction for the 9th year (2014) will be as follows according to the regression equation: Y=7E-05*9+1989. This is equal to 358,032.9.
Discussion
The data analysis brings a sharp consensus regarding the effect of learning on total incomes. The Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that people with higher education have a higher income. This factor is likely to be the influence of the increase in total personal income levels over the last few years as the level of illiteracy reduced drastically.
This has increased the economic situation of the citizens and bolstered their income levels. It is also crucial to note that people with a lower educational level form a huge number of the unemployed cluster of 6.5% (Bureau of Labor Statistics, unpaged).
It is no secret that the USA administration has been pushing for more people into college to ensure majority of Americans realize these economic fortunes.
From the analysis, it is evident that public schools are hugely preferred against private schools. A staggering 86% of Americans enter into public schools and this indicates that to have an influence, the government should inject more funding to these institutions.
Conclusion
The analysis, discussion, and data available have shown that there is a direct relationship between the highest level of educational attainment and the Total Personal Income levels of Americans. Americans with a lower education level earn significantly lower. The same case applies when it comes to unemployment. The discussion also revealed that Americans prefer public schooling as opposed to private schooling.
This may be by design or by circumstances. While the Bureau of Labor Statistics says that unemployment level stands at close to 7%, the data above reveals that the number of people aged between 6 and 21 that were reportedly not enrolled in school between the year 2000 and 2010 was 4% (IPUMS, unpaged).
This indicates that extrapolation of the data backward may increase this percentage. Hence, the level of unemployment is astonishingly close to the percentage of people not enrolled in school at the time in which that particular group was in school.
Hence, the researcher concludes that it is possible to eliminate unemployment by eliminating the percentage of people that are not in school at a particular time. It is possible that this group’s mind opens up on attending school, which enables it to find ways to create employment outside the realms of professional employment or gain employment in professional areas.
Works Cited
Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2012. Employment Projections. Web.
Ipums, 2011. IPIUMs USA. 2013. Web.
Ipums, 2011. IPIUMs USA. 2013. Web.
Ipums, 2011. IPIUMs USA. Web.
Morrison, Richard. 2012. Chart of the Day: Income Levels vs. Education Levels. Web.