Introduction
Effective leadership plays a vital role to develop the company; therefore, business organizations have leaders to protect the organizational culture and concentrate on the mission of the companies. However, the leadership problem arises in the family business in most of the cases, for instance, unresolved conflict, mismanagement, and different views are the key problems in this field.
Business owners can deal with these issues successfully when good relationship among the members create and ensure flexible and secure business environment.
However, family business environment can change at any time for different reasons, such as, divorce, financial crises, health issues, obscure leadership approach and clear strategies, succession, ineffective remuneration policy, favouritism, no unified objective, unskilled human resource, and so on (“EMyth: The Challenges of a Family Business” par.2).
Research Aims and Questions
- How non-family member leaders can contribute for the development of family business and national economy;
- The extent to which family members accept the decisions of the leaders of non-family members;
- Assess the impact of non-family member leaders on the stakeholders;
Contributions of research to business organizations
The proposed research will enhance and broaden present theoretical perceptions on the effectiveness of non-family member leaders in family business; in addition, it will encourage other researchers to use the result of proposed research for the future research.
In addition, the proposed dissertation will assist the family members of the family business in the UK and other nations in order to identify the loopholes of the business and restructure organizations considering the outcome of this result regarding the effectiveness of non-family member leaders.
Reason for Study
Cable (6) reported that there were more than 3 million family businesses in the United Kingdom, and these firms provided about 9.2 million jobs (40% of total private sector employment), and generated revenues of £1.1 trillion in 2010 (35% of private sector turnover).
Moreover, Cable (6) further addressed that family businesses have significant role to shape the national economy (in 2010, it contributed £81.7bn in tax receipts or 14% of total government revenues) for which it is essential to manage such business by improving leadership quality and increasing labour productivity; as a result, this is one of the most important area of research.
Literature Review
Klein (1) explored that it is very important to investigate the function of non-family leaders in the family business; however, it is also essential to compare their role with the leaders appear from the family orientation; such comparison would provide a greater understanding to develop a business model that ultimately resolve the theoretic debate regarding the role of non-family leaders.
In order to conduct literature search, this study would consider three areas, which raised by the research questions; on the other hand, it would look for the shared deliberation of the family owner and non-family leader to come into a close relationship, associated recruitment process of the non-family leader and his behaviour all through the employment.
The European Commission (4) mentioned that due to the economic contribution of family business and its long-term substantiality during the financial crisis and recessionary economy, continuous efforts to the local community development and their ethical standard turned them essential for the national development; moreover, the states needed to provide special concern for them.
The corporate data illustrated that 60% of the European firms are under family business category and they are working in different sectors with successful record of accomplishment; most of the SMEs are under this category.
The most acceptable and agreed definition provided by the EC is that a firm would be considered a family business if the founder or owner or ‘majority of decision-making rights’ or acquired share capital are concentrated within the family members such as spouses, children, parents, or direct heirs and at least a single delegate of them who officially represent them.
For listed companies, the company has considered a family business if 25% of share capital of decision-making rights concentrate to any founder or owner of his family members; furthermore, the EC has just guided the definitions and urged to implement them in the individual national context of the member states with improved choice.
The Ernst & Young (1-36) conducted a landmark study with 280 family businesses with joint efforts of the FBNI, and Credit Suisse in order to identify the greater insight with the procedure of conducting such business; furthermore, its core competences, strategies, and professionalism to sustain under the hard economic condition.
Among them, ten business leaders were executives (family members) among more than 1000 executives, who became most prominent and gained awards from the academia for their contribution to the family business arena within the surveyed respondents; however, the performance of the family executives were more exciting and remarkable than the non-family business leaders.
Under the present economic reality, the findings of the research identifies that although there are some disadvantageous attributes of family business, the performance of family business leaders even new family members are superior than the non-family leaders while 30% new family members are coming into the business with business degrees and perfect skills.
On the other hand, Birchall & Ketilson (15) advocated with the non-family leadership arguing that the family leadership in the family business could be aligned with nepotistic; they could develop widespread paternalistic exercise that a non-family leader would never put into practice where family members would not be privileged to influence unethically.
Moreover, enterprises single ownership and self-employed people could consider, as the family business in many countries where unattractive representation of labour markets looks very worse in such small companies; moreover, the most common dilemmas of them is lower wages with less career opportunities that could not attract potential non-family leaders.
As the non-family leader are standing apart and composed with business skills and committed to the family, they could provide exceptional control over the business that lets the non-family leader to strongly handle emotional and soft issues rise from family leadership.
At the same time, the non-family leaders have to face tremendous threats from the family members who are most likely habituated to integrate emotional blackmailing in the business.
This proposed literature review would search the most neglected research direction aligned with gaps with existing direction of non-family leaders with the aim to identify function of business leaders to strengthen the prospective of modern family business pointing to the success and failure of them.
Thesis Statement
Amanna and Jacques (204) pointed out that the academic literature of family business has evidenced with better performance than non-family business during the global financial meltdown although the conventional wisdom regarding contribution of non-family leaders prolong confusing idea and required to have further research to identifying the actual truth.
Under the present global financial crisis and its long-term recessionary impact, the rate of recovery in the family business is greater than the non-family business, but this data does not evidenced to any positive role or optimistic contribution from the non-family executives.
Thus, the role of non-family executives in the family business remain unclean and grounded with huge conceptual gap; so, this literature has aimed to look for most resent studies based on the concurrent recessionary economy in order to enrich the area with better understanding and to provide direction for further research non-family leaders.
Research Methodology and Methods
Research philosophy
Williams (1) stated that research philosophy is a significant aspect of research methodology to collect data in useful and correct way considering time limitation and budget constraints; however, three philosophies include positivism (highly structured methodology to quantify and assess the outcome), interpretive (applicable when business is too complex) and realism philosophy (interdependency of human values and beliefs).
However, Williams (1) argued that researcher could collect all the data when it considers positivism, interpretive philosophy based on the critical thinking about positivism philosophy and realism philosophy depend on the fact that human are not the objects for research; therefore, proposed research will consider positivism and interpretive philosophy to discuss the effectiveness of non-family member leaders in family business.
The strategy (induction/deduction)
Burney (5) stated that Induction method (also known as “bottom up” approach) is more widely used in the scientific research field to formulate some tentative hypotheses to explore and to develop the theory and measurement.
On the other hand, Burney (4) argued that deduction methods commonly used in the social research and it starts with theory; however, the next graph demonstrates the distinction between the deductive and inductive method –
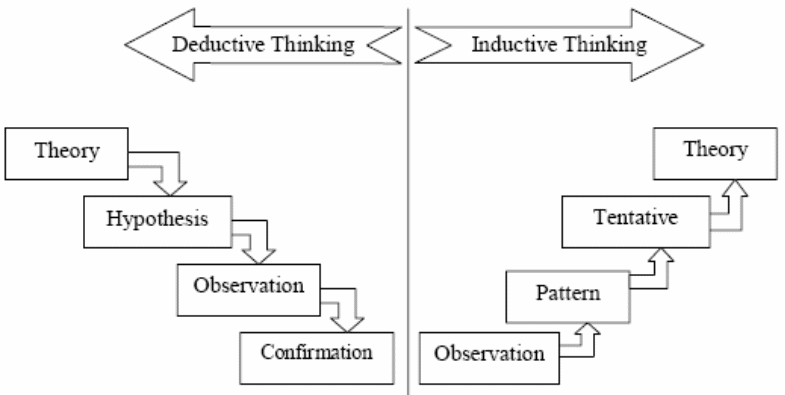
However, the proposed research will consider deductive approach because this is appropriate with the research field “Effectiveness of non-family member leaders in family business” while it is beyond the knowledge of the researcher to introduce a theory from observation.
Research Design
The proposed research will consider both qualitative and quantitative approaches to analyze the importance of non-family member leaders in family business, for instance, qualitative research will play vital role to gather border opinion of the family business owners and quantitative research approach will help the researcher to identify the behavioural attributes with statistical representation.
However, the proposed research will contain six major steps or chapters considering both primary and secondary research, for instance –
- Problem statement: This chapter will to identify core principles of leadership styles in family business, objectives of different stockholders, and different perspectives regarding organizational challenges;
- Development of a research approach to the problem;
- Research design formulation: the proposed research will provide methodological framework to illustrate the effectiveness of non-family member leaders in family business and it will contain overall process to organise the paper;
- Fieldwork or Data Collection: Semi structured questionnaire will be prepared for the data collection from the owners and members of family business; Data preparation and analysis: Effective measurement tools will be used;
- Report preparation and presentation;
Sample Size
The researcher of the proposed study will conduct face-to-face interview as the owners and employees of family business are too cooperative to participate in the interview; therefore, researcher will prepare a questionnaire to interview on specific factors to reach conclusion in this regard. At least, 200 respondents will participate in the interview process; however, the following table gives more information about interviewees –
Table 1: Profiles of family business members and owners. Source: Self generated.
Data Collection Strategy
The strategies for the data collection programmes will be based on the traditional process along with questionnaire, such as, the researcher will apply personal or face-to-face interview, telephone interview, and web survey through semi-structured questionnaire to analyse the effectiveness of the leaders of non-family member in the family business.
However, the rationale for considering traditional approach for data collection is to have sufficient time and budget to conduct field survey using questionnaire, the family business stakeholders, and owners are responsive to share their views to contribute to conduct research on leadership approach in family business.
Data Analysis Process
The qualitative data regarding the effectiveness of non-family member leaders on family business will be analysed in descriptive manner, for instance, the research will carefully read the text or lessen the tape records in order to shape the quality data; after filtering process, the data will be presented in the main text.
The descriptive and interpretive analysis of qualitative research approach will focus mainly on the difference between leaders of family business and leaders of corporate company leaders in decision-making process to solve conflicts and dilemmas since the human resource are not skilled enough in case of family business.
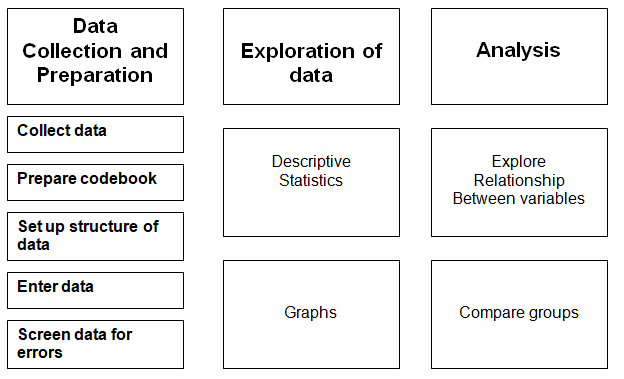
On the other hand, quantitative data regarding leadership style in the family business will be graphically presented using statistical software, such as, Microsoft excel, Matlab or others; however, selection of software will be based on the questionnaire (number of variables) of the proposed research. However, the next figure shows data analysis process –
Potential threats to validity and reliability
The researcher can be biased at the time of questionnaire design and data analysis process; as a result, the researcher of the proposed study will check the instrument considering both external and internal validity to make the data reliable to all range of business employees and owners of family business.
Ethical issues
As the research involved human participation, the proposed will collect data after getting consent from the business owners and members of the family business; in addition, the proposed study will treat personal information of family business holders as confidential data (respect for anonymity and privacy) following Data Protection Act 1998 in the perspective of the UK.
Participant Information Sheet
Table 2: Participant Information Sheet. Source: Self generated.
Resources
It should require a laptop, statistical software, tape recorder, mobile phone and some other tools; on the other hand, it needs at least $2500 to conduct research on the effectiveness of non-family member leaders in family business; however, this cost associated with transportation costs for field survey, preparation of documents, collect secondary data sources (purchase books), and additional overhead costs.
Timetable.
Table 3: Research schedule. Source: Self generated.
Conclusion
The proposed research with non-family members in the family businesses and its direction to the literature review has aimed to support the relevant research questions for this study while main objective of this paper is to generate literature adequately demonstrates the significance of non-family leaders in family businesses.
The outcomes of the research would enhance the family business with new findings and show the future direction for further research with non-family business leaders comparing with the family leaders in context of their origin, performance, and professionalism.
The potential strengths of the proposed research include available secondary data sources along with primary data to shape literature review and develop a strategic framework to develop leadership approach in the family business with non-family member CEO to cover in detail all areas related to this field.
At the same time, key strengths will be the outcomes of survey report to analyse qualitative and quantitative data, the result of the overall research on problematic dynamic particularly in the family firm, comparison with non-family businesses and family businesses, importance of the family attachment and emotions, evaluate the advantage and disadvantage of non-family leadership, and the market advantage.
The proposed study will not contain major weaknesses, as the research will take appropriate measure on time; however, some possible weaknesses include time and budget constraints since it will consider large participants for field survey.
Works Cited
Amanna, Bruno. & Jacques Jaussaudb. “Family and non-family business resilience in an economic downturn”. Asia Pacific Business Review. 18.2 (2012): 203-223. Web.
Birchall, Johnston. & Ketilson, Lou Hammond. Resilience of the Cooperative Business Model in Times of Crisis. 2009. Web.
Burney, Aqil 2008, Inductive & Deductive Research Approach. Web.
Cable, Vince 2011, The UK Family Business Sector: Working to grow the UK economy. Web.
EMyth: The Challenges of a Family Business 2010. Web.
Ernst & Young 2012, Built to last Family businesses lead the way to sustainable growth. 2012. Web.
Klein, Sabine. “Non-Family Executives In Family Businesses – A Literature Review.” Electronic Journal of Family Business Studies (EJFBS). 1.1 (2007): 1-2. Web.
The European Commission 2007, Final Report of the Expert Group: Overview of Family–Business–Relevant Issues: Research, Networks, Policy Measures and Existing Studies. Web.
Williams, Jennifer. Research Paradigm and Philosophy. 2011. Web.
List of Abbreviations
FBNI = Family Business Network International.
SMEs = Small and Medium Enterprises.