Introduction
The primary purpose is to understand better how platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections measure against traditional therapies regarding orthopedic injuries. The scholarly question is as follows: How effective are pallet-rich plasma injections, as an alternative treatment, in the management of tendinopathies and articular injuries as compared to traditional therapies? Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) contains high concentrations of growth factors and cytokines and is believed to promote healing and tissue formation and exert anti-inflammatory effects (Cole et al., 2010). Blood is collected from the patient; the plasma is then separated from the blood through centrifugation, producing the PRP.
PRP is then injected, as an autograph, into the area of pathology. PRP injections are used to treat spinal disc injuries, joint degeneration, muscle injuries, and tendinitis, as well as torn tendons (Cole et al., 2010). In this rapid review, we will analyze the current literature to evaluate the effectiveness of PRP therapy in the management of these common orthopedic conditions as compared to standard traditional treatment in the management of these conditions and determine if PRP injections may be safely and effectively incorporated into the treatment to determine if PRP therapy might be offered as an alternative to the conventional treatments.
Literature Review
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Combination Therapy
Theory Description
While considering literature sources, different opinions and theories regarding PRP application were considered. However, particular attention should be paid to the theory of combining PRP and HA methods while treating patients with osteoarthritis (OA) (Belk et al., 2020). This theory assumes the implementation of both approaches to minimize patients’ risks as well as reduce their pain and increase safety. Particular attention this theory pays to the tissue issues while providing injections. For example, the combination of PRP and HAs injections is used to create a synergistic effect on tissue regeneration and healing.
Moreover, the study in which this combined approach was considered has drawn different results. The first was conducted concerning the application of PRP only. The second is regarding a single use of Has. The third one was about their combined implementation in the treatment process. The theory and data assume that the third variant will positively affect patients’ tissue regeneration (Belk et al., 2020). Consequently, compared with other studies and points of view, where only a single approach was considered, this theory is remarkably important for future research and outcomes.
Theory Application
The theory of combined use of PRP and HAs injections is applied to the current project in different ways. First, it allowed one to consider the profound benefits and drawbacks of PRP and HAs injections. While treating the same disease, which is OA, it was easier to identify the advantages of PRP compared to HA methods. Second, the combined use of these injections allowed one to determine new approaches in OA treatments. It means there is still room for thoughts and different ways of finding better and more rational ways to treat OA. In addition, this theory pointed out the necessity of further studies in this sphere.
The methodological strategies were based on finding qualitative data on existing research. A more detailed description of the strategy is provided in the subsequent ‘Methodology’ below.
Literature Gaps
The given rapid review identified two major gaps in the literature: the lack of consensus and limited exploration. The first gap is the lack of consensus and comprehensive understanding regarding the comparative effectiveness of PRP injections versus traditional therapies for managing orthopedic conditions. The second gap identified is the limited exploration of the combined use of PRP and HA injections in treatment protocols.
Exploring Symptoms of Chronic Epicondylitis
The study was conducted by applying a range of sources regarding the chosen topic. Mainly, different scholarly articles were used to identify peculiarities of such aspects as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections and other research objects (Annaniemi et al., 2022). The first source used in the research to profoundly explore the data was connected with symptoms of chronic medial or lateral epicondylitis. The importance of the discussed research in the article was in analyzing 55 patients who had chronic ME and LE (Annaniemi et al., 2022).
Another important aspect was that these patients should have already had some treatment before the study’s intervention. Particular criteria of the study, such as disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) and others, were used to obtain specific data regarding patients’ health state after the treatment (Annaniemi et al., 2022). The authors of the study highlight that because of the PRP injections’ application, the patients’ outcomes were significantly improved compared to the results in the absence of this treatment (Annaniemi et al., 2022). Consequently, the study highlights specifics concerning the benefits of applying PRP injections, which helps form the current research.
Outcomes of Specific Treatments for Knee Osteoarthritis
Considering the issues regarding knee osteoarthritis, it is essential to pay attention to particular studies that discover the outcomes of specific treatments. For example, Belk et al. (2020), in their research, explore two types of treatments. In addition to the PRP mentioned in the previous source, the authors consider hyaluronic acid (HA) treatment, which is also a nonoperative treatment option for OA (Belk et al., 2020).
The importance of this study to the research is in comparison of PRP and HA injections for the treatment of OA. Specific methods were applied to measure the results of the research, such as the McMaster University Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) and visual analog scale (VAS) (Belk et al., 2020). As a result of this study, which was implemented in the current research, one should highlight the particular benefits of the PRP compared to HA treatments (Belk et al., 2020). According to Belk et al. (2020), “mean improvement was significantly higher in the PRP group (44.7%) than the HA group (12.6%) for WOMAC total scores” (p. 1). Therefore, this study gives detailed statistics regarding the peculiarities of the PRP and HA treatments.
Treatment of Patients with Plantar Fasciitis
The following literature source was chosen for the review because of its relation to Plantar Fasciitis (PF). The study by Bezwada et al. (2022) directly connects to exploring the role of PRP in treating patients with PF. In addition, the article discovers and highlights the peculiarities of the Plantar Fasciitis disease itself. For example, it stresses that this condition is encountered by an orthopedic practitioner (Bezwada et al., 2022).
The study has explored 70 patients with PF. These people were treated with a dose of PRP (Bezwada et al., 2022). To conduct a patient’s health state assessment, the researchers used a visual analog scale (VAS) and another tool called the foot and ankle ability measure (FAAM). As the study results and implications for the current research, it is essential to stress the reduction in VAS score after applying PRP (Bezwada et al., 2022). In other words, PRP treatment can be effective also for patients with plantar fasciitis. The importance of this study for the research is in determining the beneficial application of the PRP to a particular disease.
Comparative Analysis of Treatment Methods for Knee Conditions
Another literature source also compares two methods of the patient’s treatment. The study by Hohmann et al., 2020 analyzes the differences between intra-articular knee injection and hyaluronic acid (Hohmann et al., 2020). A particular interest for the current study was in the periods used by researchers to investigate outcomes. The results were measured at six and twelve months after the application of both treatments.
To assess the results, such metrics as WOMAC and IKDC were applied (Hohmann et al., 2020). Consequently, the outcomes have shown, as in other studies, that in these circumstances, the PRP method will be more valuable than HA (Hohmann et al., 2020). However, the exciting result of the study has shown that concerning clinical outcomes, PRP has not shown specific benefits compared to HA.
Potential Treatment Opportunities for Knee Osteoarthritis
Huang et al. (2022) in their article discussing the potential treatment opportunities for patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA). The significance of this study is in the profound analysis of both PRP and HA treatments. However, the critical point of this research is that it tries to assess the effectiveness of the application of PRP in combination with particular HAs (Huang et al., 2022). To do this, the researchers worked with 99 patients with OA (Huang et al., 2022).
The evaluations were conducted four times: before the injection of PRP and HA, after one month of it, after two months of it, and after six months of it. The same WOMAC index was used to assess the results. The study’s results showed that the combination of PRP injection and HYAJOINT Plus could be helpful and effective for the treatment of patients with knee OA.
Treating Recalcitrant Plantar Fasciitis and Achilles Tendonitis
The following study was conducted by Mangone et al., 2022 and is related to treating Recalcitrant Plantar Fasciitis and Achilles tendonitis. This research discovers peculiarities concerning the benefits and outcomes of the PRP injection to treat the abovementioned disease. As for the importance of the current study of this research, one should highlight that its outcomes were assessed in two terms: short-term and long-term results.
As the purpose of the study, the authors name the search for the answer To PRP injection as a helpful and rational alternative to surgery (Mangone et al., 2022). As specific measurements, there were if PRP can decrease patients’ pain (Mangone et al., 2022). The assessment of the outcomes after the injection was conducted during the period from 6-8 weeks until one year (Mangone et al., 2022). As per the study’s results, it is crucial to stress that 88 patients with whom the study was conducted showed an average improvement of 67% for 6-8 weeks via visual analog scale (VAS) (Mangone et al., 2022). Consequently, this study confirmed that PRP can reduce pain in patients while providing an alternative method of treatment to surgery.
PRP and Cartilage Restoration in Osteoarthritic Knees
Further literature describes the research regarding the particular issue of osteoarthritic knees (OK). The study was conducted by Prodromidis et al., 2022 and it explores the points of using PRP and its role in restoring the articular cartilage of OK patients (Prodromidis et al., 2022). The researchers used a systematic literature search to find the data related to this issue. In addition, the Cochrane methodology was applied to search sources in four databases (Prodromidis et al., 2022).
Studies showed that PRP did not show a significant improvement in cartilage thickness (Prodromidis et al., 2022). In addition, the study concluded that according to the studied literature, PRP did not respond to the appropriate measurements and standards in the treatment of knee OA (Prodromidis et al., 2022). Therefore, the research provided data that underlines the nonprofit of PRP, which is the first case compared with the sources mentioned earlier.
General Overview of Plantar Fasciitis Treatment Effects
The study by Sawan et al., 2023 analyzes the general situation with plantar fasciitis treatment and its effects. The authors researched a range of different medical journals. Among them were Google Scholar, Science Direct, and PubMed (Sawan et al., 2023). The data between 2000 and 2013 was determined as the criteria for choosing sources.
In conclusion, the authors list possible ways of treatment. Due to the data in the researched articles, among possible ways are rest, stretching exercises, and analgesics (Sawan et al., 2023). However, the authors highlight that specific methods, such as PRP or corticosteroids, should be applied in case of the absence of improvements while using the abovementioned approaches. Consequently, the source’s relevance to the current study is caused by discovering alternative methods to PRP at the beginning of the treatment.
Types of PRP Injections and Their Role in Lateral Epicondylitis
The following study is crucial for the study because of the presence of a vast quantity of new variables. First, the authors Sağlam & Çetinkaya Alişar (2022) consider two types of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections. There are ultrasound-guided type and palpation-guided types of PRP (Sağlam & Çetinkaya Alişar, 2022). Moreover, the research aims to study the treatment of the new disease, lateral epicondylitis (Sağlam & Çetinkaya Alişar, 2022). In these terms, the research’s data will allow one to implement the latest information in the current study.
The research was conducted between January 2021 and August 2021, and sixty patients participated in it (Sağlam & Çetinkaya Alişar, 2022). To assess the study’s outcomes, the authors used the VAS scale system (Sağlam & Çetinkaya Alişar, 2022). After the injections, according to VAS, a significant improvement in the scores was stated. Therefore, the study showed that both variants of PRP could benefit the patient’s state and improve treatment.
Correlation Between Platelet-Rich Plasma and Steroid Injection
The study by Sarma et al., 2023 explores the correlation between platelet-rich plasma and steroid injection. The study was conducted concerning plantar fasciitis (Sharma et al., 2023). First, the authors define the term plantar fasciitis (PF) and its peculiarities. According to Sharma et al. (2023), “plantar fasciitis (PF) is a common orthopedic problem, with heel pain worsening the quality of life” (p. 1). After this, the particular benefits of PRP injection are determined, such as safety and long-lasting outcomes (Sharma et al., 2023).
The authors used hospital-based and randomized clinical trials to compare the effects of PRP with steroid injection (Sharma et al., 2023). To assess the study’s results, such systems as VAS and the American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) were used (Sharma et al., 2023). Consequently, the results have shown that RPR has a better result compared to steroid injection because the mean VAS points were decreased significantly in the patient’s group to whom PRP was applied.
Assessment of PRP for Cartilage, Tendon, and Muscle Damage
Another research conducted by Tischer et al., 2020 aimed to study how PRP can be used and assessed as a method for such issues as cartilage, tendon, and muscle damage. The authors state that PRP is popularly applied in such spheres as orthopedics. However, they state that there needs to be more consensus regarding this question, and further research should be conducted (Tischer et al., 2020).
The research’s method was to provide people with surveys in two phases. Among the questions and indicators that have been used in the study, one should highlight such aspects as PRP application, three common indicators, and future research areas (Tischer et al., 2020). According to Tischer et al., 2020, “therapeutic PRP application was regarded as useful (89%), possibly even more important in the future (90%)” (p. 2). However, research concludes that further studies are needed because of the lack of considerable information about the application of PRP.
General Observations and Advantages of PRP in Tendon and Ligament Injuries
The article by Xu et al., 2013 was chosen as the concluding source of the literature review. The particular benefit of this source is that it has significant data regarding the general observations, analysis, and advantages of PRP regarding tendon and ligament injuries (Xu et al., 2023). Notably, the research contains and studies sources from the past two decades (Xu et al., 2023).
As for the conclusions of the research, one should highlight that the data confirmed the domination of the USA and China regarding the number of medical publications on the topic of PRP application (Xu et al., 2023). In addition, PRP is commonly used in many countries worldwide and can be beneficial for patients. However, the authors stress that the inconsistency of the preparation of the procedure and other issues have specific adverse effects and should be studied profoundly.
Summary of Sources
Therefore, the complete and integrated critique is that the given compilation of studies comprehensively examines the efficacy and practical application of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) treatments. It showcases its potential in differential medical conditions such as chronic medial or lateral epicondylitis, knee osteoarthritis, plantar fasciitis, and Achilles tendonitis. However, there needs to be more consistency across the studies regarding the assessment methodologies using measurement tools such as DASH, WOMAC, VAS, and IKDC. The latter makes direct comparisons and synthesis of results challenging.
In addition, the majority of studies focus on the comparative effectiveness of PRP versus other treatments, such as hyaluronic acid and steroid injections. In essence, there is limited exploration of the combination of the therapies, which can potentially yield synergistic benefits. While the consensus leans towards PRP’s superiority in a range of contexts, the study by Prodromidis et al. (2022) presents a conflicting perspective by arguing against its efficacy in knee osteoarthritis. There is a pressing need for more standardized protocols for PRP preparation and administration, as highlighted by Xu et al. (2023). It is needed to eliminate the variability and enhance the overall reliability of PRP treatment outcomes.
Methodology
The search for literature for the study was based on finding qualitative data on existing research. Tools such as Google Scholar, EBSCO, ProMed, and others were used. The last date for the search was May 2023. For quality assessment, such tools as the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal were used. In addition, a wide range of metrics used in studied sources, such as AOFAS and VAS, were also applied in the current study. In addition, the AACN Levels of Evidence will be used to make the necessary evaluations and appraisals alongside the JBI. Therefore, they will be cohesively integrated into the evaluation sections of Table 1 of the Appendix, which contains information on the literature review matrix.
Data extraction from the reviewed sources was conducted, considering different sections in each article. Remarkably, each study explored such sections as abstract, methods, results, and conclusions. The process assumed reading each section, defining the most important current research terms and statistical data, and implementing them into the study. The literature review matrix can be accessed in Table 1 of the Appendix below.
The Simmons Library database directory of open-source articles was searched for relevant articles within the last three years (2020 to 2022) with the key search term of PRP injection or plalete-rich plasma injection in the title with the additional search term of osteoarthritis knee or plantar fasciitis or plantar heel pain or plantar fasciopathy or lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow or lateral tendinopathy or lateral epicondylalgia. The search criteria were limited to peer-reviewed, full text in English. This yielded a total of 329 peer-reviewed journal articles. Researchers BB and RD reviewed studies and discussed whether a study would qualify for inclusion in this rapid review. The strong rationale is that the most up-to-date, relevant, and evidence-based sources are only used to arrive at the most factual of conclusions.
A main update was that articles were included if they were written in English and the entire test was available. Different types of studies were included, such as randomized control trials (RCTs), non-randomized trials, qualitative, and cohort studies. Articles were excluded if the study was not limited to the specific topic of knee OA, Lateral epicondylitis, and plantar fasciitis. Considerations during the selection process also included types of interventions used in a study and articles, including background information and expert opinions toward PRP. The essential characteristic is that the abstract of each article was carefully reviewed. After applying the exclusion and inclusion criteria, the final number of articles included in this rapid review was 11. The last date of the search was June 3, 2023. The literature Review Matrix is attached below.
The review’s objective is to explore profoundly the pros and cons of different methods in treating patients with OA. Notably, the benefits of PRP and HA approaches should be studied. The study characteristics are based on the profound literature review of quantitative and qualitative research. This study aims to discover different nuances of PRP injection processes while considering empirical data obtained from past research. The years of considered sources are between 2000 and 2021. Particular studies were conducted short-term, such as from January 2021 to August 2021, and the language of the studies is English. The PRISMA flow diagram can be accessed in Figure 1 below.
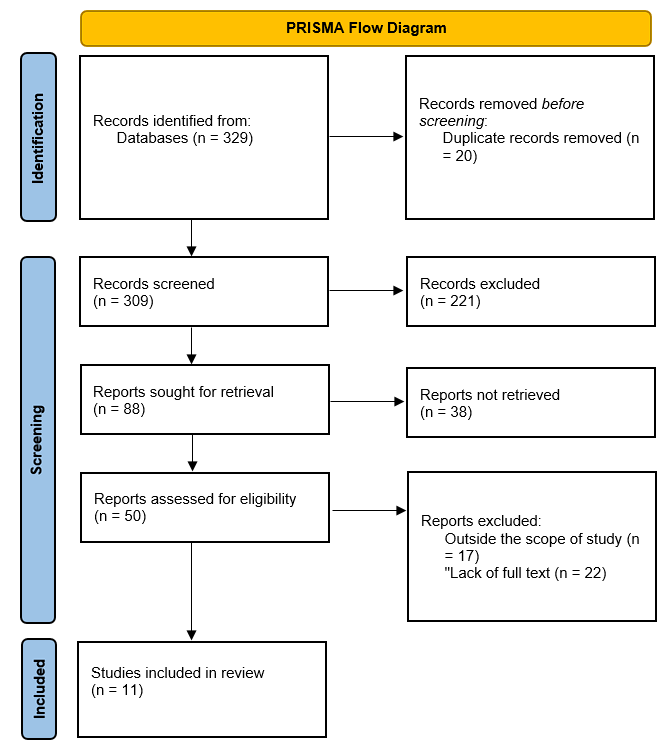
As publications are used for eligibility, one should consider specific studies conducted in the name of organizations and scientific associations that have credibility and confirmations. In addition, particular studies include differential systematic indexes and analyses to investigate the patients’ outcomes after the application of PRP and injections. For the synthesis, the studies were grouped using three parameters. First, the year of study determines its actuality. Second, the studies’ objects, particularly the research of PRP or HA. Third, the type of the study, qualitative or quantitative, and the number of participants that were observed.
Results
As for the studies’ characteristics, it is essential to state that all of them are based on the research of the PRP application for patients’ treatment. A wide range of circumstances are considered in each of them. First, the variable of different diseases to which PRP injections were applied was studied in the sources. Second, the review of various types of PRP and their benefits to the patients is explored. Third, the comparison with other treatment methods, such as HA injection, was discovered in detailed research. Additional characteristics of studies include their data and actuality, which is from 2000 to 2021.
Moreover, all studies used scores to assess the outcomes after the PRP and HA injections. For example, the overwhelming majority of researchers used the VAS metric to obtain the data. Particular studies were based on practical, clinical explorations, while others were focused on the literature review of available sources.
According to the AACN Levels of Evidence, one should state that all chosen studies have evidence-based data and proven statistics. They were conducted using actual samples, which were people of different ages and genders, to obtain the most accurate results regarding the PRP’s effects. The studies’ results were also measured by qualitative, proven metrics, highlighting their credibility and, according to the AACN, can be determined as well-designed RCTs.
In applying the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Tools, it is essential to evaluate the methodology rigor, significance of the findings, and relevance to the practice of these studies. An analysis of the congruity between the research design, methodology, and data analysis, as well as the clarity of reporting the results and conclusions, will further solidify the studies’ validity and reliability. The evaluations of the critical JBI and AACN appraisals are provided in the literature review matrix, which can be accessed in Table 1 of the Appendix below.
The obtained findings showed the significant benefits of the PRP injections compared with traditional surgery and other substitutes such as HA injections. Other findings state that the combined use of the two abovementioned methods can be helpful in patients’ safety and reduce pain. For example, the study by Sawan et al., 2023 considers that at the beginning of the treatment, particular methods such as rest, stretching exercises, and analgesics (Sawan et al., 2023). The study by Huang et al. (2022) found that combining PRP and HA injections can also help improve the treatment’s outcomes (Huang et al. 2022). Therefore, all studies were vital because of the different perceptions of the standard issue. It allowed one to answer the study’s purpose and define why platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are better than traditional medicine.
Discussion
Result Interpretation
As the general interpretation of results, it is essential to state the overall benefit of PRP application for patients’ treatment. The literature review, which formed the basis of this research, has shown specific statistics and data that can be synthesized to create a solid view of the issue regarding PRP injections’ advantages. However, some results have shown considerable drawbacks. Among them is the absence of a consensus on the necessity of PRP application and the need for further research to obtain more qualitative data regarding the peculiarities of this type of substitution to traditional medicine. These outcomes of the study relate to the nursing profession in terms of highlighting the new, alternative, modern methods that could be more effective from the time and source point of view, significantly ease the patients’ struggles, and create safer circumstances.
Literature Review Analysis
About the literature review, the benefits of PRP applications noted in our research echo specific positive findings from other studies, which indicates a consensus on its potential advantages. However, our conclusions about the need for more consensus on the necessity of PRP application are divergent from previous reviews, where PRP application was viewed more favorably.
In comparing our research to the broader body of literature, it is clear that the question of PRP injections as a substitute for traditional medicine is still contentious, reflecting the results from several previous studies. Identifying areas requiring further research is consistent with the literature, which suggests a shared understanding of the limitations in the current evidence base. In addition, our findings on the implications for nursing practice align with other evidence. The latter highlights that the PRP application is a potentially efficient and patient-friendly alternative that can revolutionize different aspects of healthcare delivery.
Research Limitations
As the limitation of the review, one should state the limited quantity of sources that were reviewed. PRP injections have many peculiarities that should be studied; therefore, many more sources should be reviewed. In addition, there is the need for access to specific official governmental data concerning medicine and, particularly, PRP. It should help determine the practical drawbacks and benefits of this approach.
Another limitation is in the scope of people that have been studied in the chosen research. One should state that some studies were qualitative, and the number of people was about 13. To obtain more precise information regarding the benefits of PRP, a significant number of residents should be studied.
Research Implications
As for the implications of this research to the nursing practice, one should highlight the possibility of determining particular benefits of the PRP. Nurses can substitute the traditional methods of treatment with these injections. In addition, because of the specific data obtained in this research, nurses can also use other methods, such as the combined application of PRP and HAs. Overall, it will be helpful to improve the treatment outcomes and increase safety during the process. Considering the policy, the implementation will be crucial to construct future standards and laws concerning the everyday use of PRP and its safety measures. Additionally, future research should be conducted based on this study because it provides a significant number of assessments and statistics obtained during practical examinations.
References
Annaniemi, J. A., Pere, J., & Giordano, S. (2022). Platelet-rich plasma injections decrease the need for any surgical procedure for chronic epicondylitis versus conservative treatment – A comparative study with long-term follow-up. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 102. Web.
Belk, J. W., Kraeutler, M. J., Houck, D. A., Goodrich, J. A., Dragoo, J. L., & McCarty, E. C. (2020). Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 49(1), 249–260. Web.
Bezwada, S., Khare, T., Ramamurthy, B. D., & Devisriprasad, S. (2022). Role of platelet rich plasma in the management of plantar fasciitis: A prospective interventional study. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 16(2), 14-18. Web.
Cole, B. J., Seroyer, S. T., Filardo, G., Bajaj, S., & Fortier, L. A. (2010). Platelet-rich plasma: Where are we now and where are we going?Sports Health: A Multidisciplinary Approach, 2(3), 203–210. Web.
Hohmann, E., Tetsworth, K., & Glatt, V. (2020). Is platelet-rich plasma effective for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review and meta-analysis of level 1 and 2 randomized controlled trials. European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology, 30(6), 955–967. Web.
Huang, H.-Y., Hsu, C.-W., Lin, G.-C., Lin, H.-S., Chou, Y.-J., Liou, I.-H., & Sun, S.-F. (2022). Comparing efficacy of a single intraarticular injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) combined with different hyaluronans for knee osteoarthritis: A randomized-controlled clinical trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 23(1). Web.
Mangone, P. G., Binns, E. L., & Bock, S. (2022). Successful treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis and achilles tendonitis using platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection, short and intermediate results. Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics, 7(4). Web.
Prodromidis, A. D., Charalambous, C. P., Moran, E., Venkatesh, R., & Pandit, H. (2022). The role of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) intraarticular injections in restoring articular cartilage of osteoarthritic knees. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Open, 4(4). Web.
Sawan, Z. H., El-Tohamy, S. A., Hafez, A. S., & Basha, O. H. (2023). General view about plantar fasciitis treatment lines: Review article. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine, 90(2), 2227–2230. Web.
Sağlam, G., & Çetinkaya Alişar, D. (2022). Ultrasound-guided versus palpation-guided platelet-rich plasma injection for the treatment of chronic lateral epicondylitis: A prospective, randomized study. Archives of Rheumatology, 38(1), 67–74. Web.
Sharma, R., Chaudhary, N. K., Karki, M., Sunuwar, D. R., Singh, D. R., Pradhan, P. M., Gyawali, P., Duwal Shrestha, S. K., & Bhandari, K. K. (2023). Effect of platelet-rich plasma versus steroid injection in plantar fasciitis: A randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 24(1), 1-12. Web.
Tischer, T., Bode, G., Buhs, M., Marquass, B., Nehrer, S., Vogt, S., Zinser, W., Angele, P., Spahn, G., Welsch, G. H., Niemeyer, P., & Madry, H. (2020). Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) as therapy for cartilage, tendon and muscle damage – German working group position statement.Journal of Experimental Orthopaedics, 7(1), 1-9. Web.
Xu, J., Du, W., Xue, X., Chen, M., Zhou, W., & Luo, X. (2023). Global research trends on platelet-rich plasma for tendon and ligament injuries from the past two decades: A bibliometric and visualized study. Frontiers in Surgery, 10, 1-20. Web.
Appendix
Table 1. Literature Review Matrix.