Company Background
- Emirates Airline is a Dubai-based airline company founded in 1985 (McKechnie et al., 2008).
- Its is the largest airline in Middle East operating more than 3,500 flights a week.
- It has a growth rate of more than 20% p. a, with more than 10% increase in the number of passengers annually.
- The company is owned by the government but operates as a separate entity.
- The company aims to increase its market share by 15% in the next five years.

Company Profile
- Name: Emirates Airlines.
- Founder: UAE government, 1985.
- Goal: “To reach on top by excelling in what we do.”
- Mission Statement: “We exist to deliver the world’s best inflight experience.”
- Vision Statement: “Ro make civil aviation safe, leading and sustainable.”
- Company Slogan: “Fly Emirates, fly better.”
- HeadOffice: Town Center, UAE.

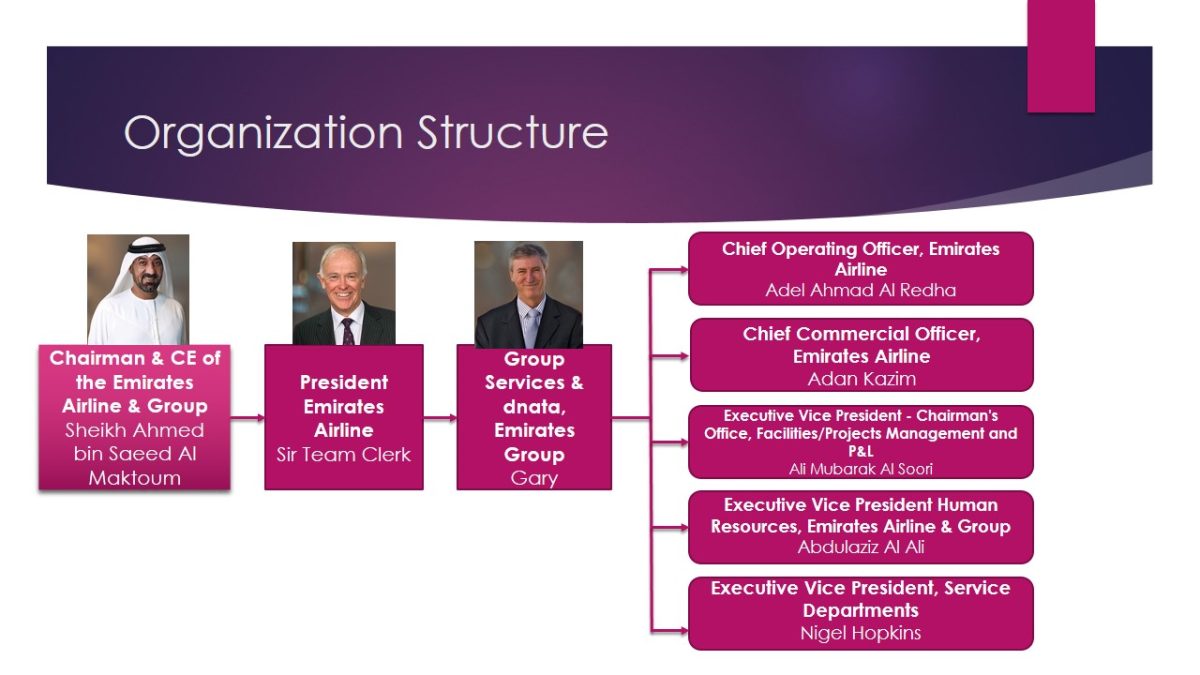
Organization Structure
- Chairman & CE of the Emirates Airline & Group Sheikh Ahmed bin Saeed Al Maktoum;
- President Emirates Airline Sir Team Clerk;
- Group Services & dnata, Emirates Group Gary:
- Chief Operating Officer, Emirates Airline Adel Ahmad Al Redha;
- Chief Commercial Officer, Emirates Airline Adan Kazim;
- Executive Vice President – Chairman’s Office, Facilities/Projects Management and P&L Ali Mubarak Al Soori;
- Executive Vice President Human Resources, Emirates Airline & Group Abdulaziz Al Ali;
- Executive Vice President, Service Departments Nigel Hopkins.
- Group Services & dnata, Emirates Group Gary:
- President Emirates Airline Sir Team Clerk;
Emirates Airlines has a hierarchical organizational structure, starting from the chairman to the operational management. Although the chairman of the Emirates Group, Sheikh Ahmed bin Saeed Al Maktoum is also the Chairman of Fly Dubai, the two companies operate independently with totally different management structure.
Emirates Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy
- Emirates launched a competitive marketing campaign that is customer-driven.
- The strategy also involves the use of superior products to gain competitive advantage.
- The strategies involve:
- Reduced prices:
- Emirate aims to offer clients competitive prices.
- The labor cost at Emirates is almost half of that of American and United Airlines.
- Low prices give the airline a competitive edge over its rivals.
- Superior services:
- Emirate has more than 10,000 cabin crew consisting of more than 120 nationalities and speaking a total of 55 languages.
- The airline provides luxurious travel experience with entertainment and leisure.
- First class passengers get to enjoy regionally inspired dishes and inflight lounge 9for A380 fleet.
- Customers also have access to fast internet and live matches at the comfort of their seats.
- Reduced prices:


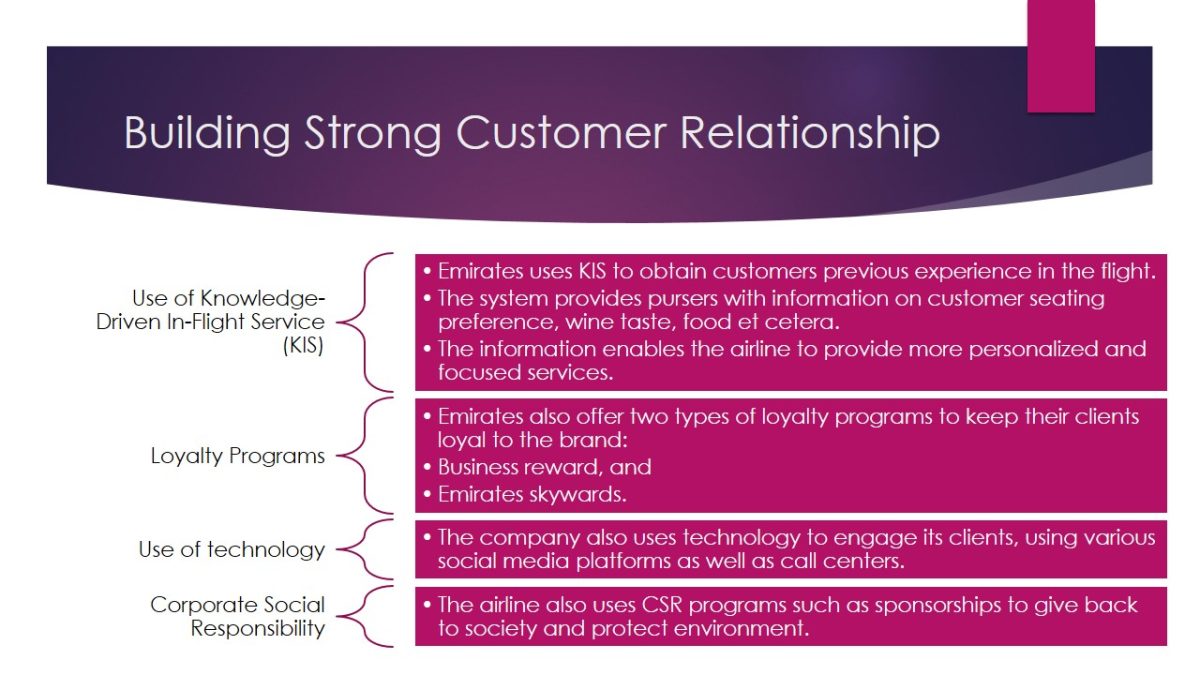
Building Strong Customer Relationship
- Use of Knowledge-Driven In-Flight Service (KIS):
- Emirates uses KIS to obtain customers previous experience in the flight.
- The system provides pursers with information on customer seating preference, wine taste, food et cetera.
- The information enables the airline to provide more personalized and focused services.
- Loyalty Programs:
- Emirates also offer two types of loyalty programs to keep their clients loyal to the brand:
- Business reward, and
- Emirates skywards.
- Use of technology:
- The company also uses technology to engage its clients, using various social media platforms as well as call centers.
- Corporate Social Responsibility:
- The airline also uses CSR programs such as sponsorships to give back to society and protect environment.
SWOT Analysis
- Strengths:
- Strategically positioned hub in Dubai.
- Strong labor force of more than 40000 employees.
- Strong corporate culture.
- Environmental friendly.
- Strong band
- Entry into air cargo
- Weaknesses:
- Relatively low salaries and wages.
- Few landing zones in the US.
- Opportunities:
- Agreement with the Australian Tourism Board on joint marketing strategy
- Signed deal between Emirates and Mauritius government.
- Threats:
- Economic impact of Corona virus
- Travel bans by most countries
- Increase in competition in the Middle East.

Marketing Mix
- Price:
- Emirates offers high quality services and therefore charges premium prices as opposed to other airlines.
- Product:
- Emirates flies in more than 6 continents coveting about 60 countries and over 100 destinations.
- That airline purchases new fleets very year, and, therefore, has one of the youngest fleet in the industry.
- Place:
- Emirates’ main hub is in Dubai, which is strategically located in an area that receives millions of tourists every year. The airliner also enjoys abundance of oil reserves in Dubai.
- Furthermore, Emirates has more than 120 travel shops around the world and 12 in Dubai.
- Promotion:
- The company used both traditional and modern marketing methods, Emirates markets its product on social media, print media and billboards.
- People:
- Emirates does not only care about customer satisfaction but also its employees and shareholders. When the company makes a significant amount of profits, it increases share prices to shareholders and provide bonuses to employees.
- Processes:
- Using KIS, websites and social media platforms, the company uses technology to automate most of its services and to increase customer interactions.
- Physical Evidence:
- Although most of the services offered are intangible, Emirates acknowledges the importance of physical evidence, and therefore, provides the highest quality in the market.


B2B & B2C Selling Strategy
- B2B Strategy:
- Strong Brand:
- Emirates continuously build its brand through quality services delivery, customer satisfaction, marketing and differentiation to attract other businesses.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
- The company uses CSR programs such as sponsorships and donations to partner with other businesses.
- Strong Brand:
- B2C Strategy:
- Segmentation:
- Emirates segments its products into two: profitable and non profitable.
- Targeting:
- The company targets high ranking individuals and businesses who are looking for luxury.
- Positioning:
- The firm’s positions itself as a brand that offer high quality products using innovation and technology.
- Segmentation:

Marketing Relations with other department
Marketing departments should have cordial relationship with other departments.
The three departments that interact mostly with the marketing department are:
- Product development:
- They develop products that are pushed to the market by marketing department.
- All the information regarding the products must be relayed to the marketing departments.
- Finance department:
- Prepares and allocates funds for marketing.
- Proper planning should be encouraged to avoid conflict.
- Operations department:
- Ensures that the items meets the quality standards of the organization.
- The two departments should work closely to ensure that demand volume is met.

Measuring & Managing Return on Marketing
Two common methods to measure and manage return on marketing are:
- Single attribution:
- Value are assigned either to the first or last program to complete the deal.
- The method is easy and relatively cheaper to implement.
- However, it does not take into account the influence of other touches.
- Full marketing mix model:
- Involves the use of statistical techniques such as regression analysis to determine how various independent marketing touches affects sales.
- The method is accurate but requires sufficient data.

Reference
McKechnie, D. S., Grant, J., & Katsioloudes, M. (2008). Positions and positioning: strategy simply stated. Business Strategy Series.