Introduction
Business excellence entails more than putting in place an evidence proven quality system. Therefore, the topic of business excellence models coupled with how they apply to the UAE organizations like Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation (ENOC) is paramount. The models help in establishing what an organization does or should do right from leadership, operations, strategies, managing customer relationships, information processing, reinventing process, and addressing the people’s issues. The topic is important since these issues determine the competitive advantage for any organization. Indeed, ENOC requires strong management systems to enhance its present and long-term competitive advantage. This move is necessary to ensure long-term performance so that stakeholders can generate value from their investments.
Research questions, objectives, and aims
The research question for this paper is how can BEMs help ENOC to achieve its strategic performance goals to deliver optimal value to the stakeholders? Responding to this question, this paper’s objective is to discuss how ENOC has used one of the BEMs (4P model) to achieve both short-term and long-term success. The paper seeks to provide a potential benchmark that other organizations in the UAE can use to enhance their success by deploying effective BEM(s).
Literature review
The 4P model integrates different aspects of an organization. Mohammad et al. (2011, p.1221) note that these include ‘soft (intangible) and hard (tangible) aspects, subjective and objective aspects, rational and irrational aspects, individual/personal and collective/organizational aspects’. It offers a recommended structure for enhancing sustainability in realizing organizational excellence (Dahlgaard & Dahlgaard-Park 2004). The model aims at integrating and ensuring harmony amongst people, work teams, or partnerships, organizational processes, and organizational products or services as a precondition for achieving business excellence.
The model is enabler-result oriented having 5 criteria as shown in figure 1. Dahlgaard, Pettersen, and Dahlgaard-Park (2011) note the first 4 criteria constitute the enablers also called critical factors for success while helping in realizing results or success of service and products within an organization. The first 3 are enablers of the system of management while the fourth component is process-oriented, which helps in the development, production, and delivery of services coupled with products of an organization to the market as formulated in the organizational plans and strategies.
The implementation of the model requires the development of an appropriate organizational culture, innovativeness, customer orientation, and deploying effective techniques coupled with tools for management like lean techniques.
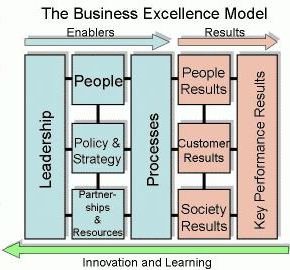
The 4P model shown in figure 1 was first developed and implemented in the Danish context specifically in the manufacturing organizations. Its primary aim was to assess the organizations’ technological status in terms of developing new products and innovation coupled with processes (Mann 2011). It was later adapted in Danish hospitals (Dahlgaard, Pettersen, & Dahlgaard-Park 2011). The model is highly flexible as it can be used to fit in a given organizational context. Even though ENOC does not state that it uses the model, the organization’s policy towards people, products, services, leadership, and growth and operational strategies provide sufficient evidence for the use of a model similar to the 4P BEM.
Methodology
The paper first discusses the 4P BEM. To do this, search for various scholarly articles on the models is done through the web and academic libraries. Different universities have databases where they maintain different academic materials including books and journal articles. Such databases include EBSCOhost, EMERALD, and PROQUEST. Using the terms “business excellence models”, a search is conducted in these databases. Since the searches yield a large number of results, only articles discussing the 4P BEM are selected. Research is also conducted online to access the ENOC website to identify the various strategies used by the organization reflecting the practical application of the model. Comparison is then made between how the organization implements the model and literature on the model. This aspect helps in identifying the gaps between practice and theory.
Brief profile of ENOC
The Emirates National Oil Company (ENOC) is a large energy group in Dubai that was established in 1993. Based in the UAE, ENOC is owned by the UAE government. Most of its operations are in Dubai and Northern Emirates in the UAE. The ‘ENOC Processing Company (EPCL) is one of the ENOC’s subsidiaries and it runs the Jebel Ali refinery whose operations are mainly in Dubai’ (ENOC 2012, par.1). As stated in the organization’s vision, the main interest of ENOC is in gas and oil. ENOC has more than 20 subsidiaries, which are owned both directly and indirectly.
Data analysis
The ENOC’s operational strategies, vision, mission, leadership approaches, policy towards people and the environment reflect the applicability of the 4P BEM model in the organization. Since the establishment of the organization, it has made enormous progress towards meeting its objectives and achieving its mission and vision. The ENOC’s vision is ‘to be a leading regional integrated oil and gas group which is highly profitable and socially responsible towards employees, community, and environment’ (ENOC 2012, par.1). Similar to the concerns of the 4P model, this statement establishes a clear focus on harmony between people (employees and community) and product (oil and gas) as the foundation of building a highly profitable organization,
ENOC states that its mission is to gain development, which is sustainable in the quest to maximize the profitability, meet the energy growing needs of the people of Dubai, and have up-to-date technologies for use in the implementation of the organization’s practices. This move helps in achieving excellent performance, and it gives customers the best service by exceeding their expectations in terms of quality and service (ENOC 2012).
Indeed, the company’s mission is a statement of the 5 criteria of success forming the basic tenets of the 4P BEM. ENOC seeks to gain and maintain industry standards in environment, health, and safety coupled with bringing, making and retaining employees with top talent. This aspect constitutes the definition of the leadership focus of the company to help achieve the enablers of organizational success in its products and services as discussed in the 4P model.
The 4P BEM requires a definition of organizational tools and techniques of management. In the case of ENOC, due to operational challenges, the company has considered various mechanisms of inducing organizational change to gain a competitive advantage in its operational industry. Spector (2007) argues that an organizational framework for change is the review of the structures, which encompass the relationships between positions in the organization. The review seeks to improve organizational needs.
ENOC has been encountering various organizational challenges, which prompted the initiation of various organizational changes to enhance the performance of the organization. This aspect means that the management deploys the tool and technique of organizational change to ensure that it responds ardently to emerging challenges to ensure the sustainability of its business profitability. Considering the organization’s competitiveness in the oil and gas industry in the UAE, its model of operation can be benchmarked by other organizations in the same industry to ensure high performance in the future.
Discussion and Conclusion
Through the group project’s findings, I have learned that the utilization of the BEMs in an organization is necessary to provide a clear definition of organizational direction, construct organizational alignment, and ensure the achievement of pre-descried sustainable goals. A model like the 4P BEM is important in enabling organizations to understand customers, present and future anticipations, and markets. This understanding helps in the construction of strategy and improving the utility of products and services. Such undertakings improve the system coupled with ensuring agility and responsiveness to changes in the external and internal business environment.
At ENOC, the business excellence model aids in improving its people, tapping their top talent to achieve organizational success, and ensuring resourcefulness coupled with developing creativity, which is necessary for organizational improvement. Through the model, the organization spells out its environmental, social, and ethical principles for sustainable outcomes in the future. The findings correspond to anticipated course learning outcomes.
Recommendations
Organizations should ensure effectiveness and efficiency in their operations to ensure high performance. For ENOC to achieve this goal, it should incorporate tools for performance management in its techniques. Such a tool should incorporate strategies for remunerating top talent in the organization as the basis of its retention and optimal utilization to develop organizational innovativeness. This aspect will ensure the effective and efficient utilization of organizational resources including the human resource to ensure the sustainability of business operations.
Reference List
Dahlgaard, J & Dahlgaard-Park, S 2004, ‘The 4P quality strategy for breakthrough and sustainable development’, European Quality, vol.10, no.4, pp. 6-19. Web.
Dahlgaard, J, Pettersen, J & Dahlgaard-Park, S 2011, ‘Quality and lean healthcare: A system for assessing and improving the health of healthcare organizations’, Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, vol.22, no.5, pp. 671-689. Web.
ENOC: Vision and Mission Statement 2012. Web.
Lu, D, Betts, A & Croom S 2011, ‘Re-investigating business excellence: Values, measures and a framework’, Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, vol.22, no.12, pp. 1263-1276. Web.
Mann, R 2011, ‘Awareness and impact of business excellence in Asia,’ Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, vol. 22, no. 12, pp. 1237-1258. Web.
Mohammad, M, Mann R, Grigg, N & Wagner, P 2011, ‘Business Excellence Models: An overarching framework for managing and aligning multiple organizational improvement initiatives’, Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 1213-1236. Web.
Spector, B 2007, Implementing Organizational Change: Theory and Practice, Prentice-Hall, Harlow. Web.