Executive Summary
Many organizations are currently facing the problem of employees deciding to leave the company. There are numerous factors contributing to this phenomenon that require study and analysis. Central to this research paper was the examination of the case of Credit Acceptance Corporation (CAC), which specializes in low-credit automobile financing. Despite the company’s potentially successful activity in the market, one of its main problems was the high level of employee turnover. The issue of high turnover rates became the focus of this research work.
To gain the most valuable and useful knowledge, this work employed various ways to study the available data. First, the company’s background and the definition of the main research components, including audience, scope, and delimitations, were provided. A literature review was then conducted, which helped identify the main factors affecting the company’s dismissals. The main aspects were personal and work-related, which can be both voluntary and involuntary. The literature review showed effectiveness, as it provided knowledge and awareness of the direction in which the company should act to resolve issues. The next step was to use a descriptive research approach and conduct surveys via social media on the Facebook platform.
The collected information and data served as the basis for the formulation of recommendations for the CAC. The first piece of advice that can be useful for the organization is prioritizing the attraction and retention of highly qualified personnel. This can be achieved through compensation and benefits, which are at a level higher than those of the competitors’ market. Another recommendation is to offer staff flexible work schedules. This will help to establish a balance between the working and personal lives of individuals. The last recommendation was to hold periodic skip-level meetings to address underlying issues with management.
Introduction
Background
Credit Acceptance Corporation is a low-credit automobile finance company that works with high-risk customers, providing them with another opportunity to obtain a car and rebuild their credit. It was founded in 1972 and has since grown into a prestigious organization with dealerships offering the corporation’s product throughout America. “The company is known for the financing programs offered through a nationwide network of automobile dealers” (Credit Acceptance, 2020).
In 2001, CAC decided to establish clear organizational goals to become a great place to work for its employees. The former CEO recognized that people are what make an organization, and that keeping employees happy helps achieve its goals. That same year, the company defined three clear organizational goals; one of those three goals is to be placed on Fortune Magazine’s “Top 10 Great Places to Work” list (Credit Acceptance, 2012). Over the past seven years, CAC has appeared on Fortune’s list, but not in the top 10. In 2021, it did not appear on the Fortune list. Although it made it to the list for the last five years, the ranking declined more and more each year. Turnover and attrition are significant issues the organization is facing.
Research Problem
Between 2019 and 2021, CAC experienced significant turnover within the Customer Service Department. The high turnover rate has had several negative impacts on the business. These include team members feeling overworked due to increased work and responsibilities, a lack of trained team members, low productivity, and low employee morale. The main question of this study is: What factors contribute to turnover in organizations?
Since the objective above is rather broad, it is essential to develop a few more specific issues to analyze. To examine this question, the research addresses the following subtopics:
- What issues make people leave or stay in organizations?
- How does turnover affect an organization’s productivity?
- What impact does leadership have on an organization’s turnover?
Each of the subtopics above will include specific questions that will collect the data needed to identify the required information. Analyzing the responses to these questions will provide insights into how both current and former team members might be feeling and what they are saying about the concepts under analysis. A content analysis will be conducted to better understand the impact of turnover on businesses. The research also identifies the factors that have the most significant impact on businesses, as well as those that have a lesser impact, with the aim of then developing a solution to the problem.
The research will enable organizations to identify areas of opportunity. The research will also provide insights into strategies for boosting morale and retaining top talent. Being part of the Fortune list is one of CAC’s company goals, and this research will help develop a plan of action to meet that goal. That is why the selected organization is expected to draw adequate attention to employee turnover and retention to succeed in the market.
Research Audience and Rationale
The source of the research subject pool will be via social media, Facebook. SurveyMonkey will be used to collect responses to questions from all who participate. The survey responses will be anonymous. The results of this research will be presented to CAC’s senior leadership team, the Human Resources (HR) team, and the company’s internal Great Place to Work Committee as a reference tool on what’s happening in other organizations. The research will include information and a plan to keep team members motivated about coming to work every day, thereby reducing attrition.
Research Study Scope/Delimitations
The research focuses on turnover in the selected organization, CAC. According to Macrotrends (2022), the organization currently has more than 2,000 employees. Although the organization experienced a slight increase in employee growth rates during 2020-2022, CAC still struggles with high turnover rates. The organization’s headquarters is in Southfield, Michigan, but the business provides its services across the entire United States. This statement indicates that the selected organization employs staff members from diverse regions of the country. Consequently, the research will provide valuable evidence for various companies operating across the US. Thus, the recommendations provided to CAC to address their turnover can be equally effective for other businesses.
Literature Review
Employee turnover has been an issue in many organizations today. This is because the efficiency and productivity of the company directly depend on the staff, their quality of work, and their interaction. However, HR professionals and company executives have struggled to forecast and control the future. Therefore, they cannot determine in advance how long employees will occupy their workplace. At the same time, they can identify factors that positively or negatively affect an individual’s desire to hold a position in the company. The main negative consequence, in addition to the decrease in efficiency that an organization can experience with a high degree of turnover, is the need for constant search for new employees. Additionally, the company’s financial and operational resources require training new team members.
Furthermore, employee turnover can be either voluntary or involuntary, which also needs to be taken into consideration. Several factors contribute to higher-than-acceptable employee turnover rates. Conducting a study of these sources of motivation for employee dismissal requires a detailed examination to raise awareness and identify ways to retain employees. Research stated that “it results in a series of negative impacts on the organizations, such as reduced organizational performance, disrupted outcomes, lowered product/service quality, and loss of organizational knowledge” (Zhang et al., 2022).
This chapter examines the following factors for this study: work factors, working conditions, leadership, compensation and benefits, and competitive job opportunities, along with the actions that can be taken to reduce turnover and increase retention in CAC and other organizations. Within the framework of this literature review, sources will be utilized that are grounded in evidence-based data and knowledge, providing valuable insights into the problem under study.
Personal Factors and Employee Turnover
The first factor that directly affects the rate of employee dismissal is personal. They are becoming one of the most critical and require special attention from HR managers. Employee performance is influenced by personal characteristics, which, in turn, indirectly affect the long-term productivity of the CAC. According to Soomro et al. (2018), employee performance in the workplace is impacted by changes in family circumstances, age, illness, and social status.
Each of these factors requires special attention, as they present an opportunity to assess their impact and explore ways to support employees in challenging situations. Therefore, family issues can significantly impact the psychological well-being of employees. They can range from conflicts and quarrels to divorce or the loss of a loved one. These events affect the performance of personnel, as in such situations, the primary concern for an individual is to resolve personal issues rather than complete tasks assigned at the workplace.
A factor such as age is gaining more and more recognition, especially in companies where young workers prevail. Of particular importance is the phenomenon of ageism, which is characterized as “a combination of mostly negative – age–based stereotypes, attitudes and behaviors” (Lagacé et al., 2020, p. 42). The prevalence of this aspect is because there is currently a larger population of seniors in the world than young people (Lagacé et al., 2020).
Although many organizations are attempting to rejuvenate their staff by hiring young professionals, older workers are valuable due to their more extensive experience within the company. Thus, in some cases, when generations collide, conflict situations occur due to misunderstandings. This is the result of individuals’ decisions to leave the workplace, prioritizing a more comfortable and calmer life.
The disease becomes a factor beyond a person’s control and can be considered involuntary by the employee. This is because when serious welfare problems arise, individuals may be restricted from performing certain functions in the workplace or generally restricted from attending work (“2020 Employee care report,” n.d.). Last but not least, social status is reflected in the team’s bias. This may be due to the phenomenon where representatives of the same social status are grouped; thereby, employees of a lower status are, as it were, excluded from everyone. This is the result of a feeling of loneliness and isolation, which affects the desire to leave the workplace.
In addition to these phenomena, other factors may also influence the increase in employee turnover. Hence, workplace rudeness, absenteeism, stealing, on-the-job drug and alcohol addiction, and destruction of the employer’s infrastructure are some of the qualities that predict job performance and unproductive behaviors from employees (Viegas & Henriques, 2021). All of them affect the condition of workers and people around them to varying degrees. Therefore, these characteristics can be quantified and utilized in employment assessments to identify individuals who are less likely to leave within a given timeframe.
Unreasonable expectations, personal objectives, and a lack of understanding about the position often lead to job seekers having a negative impact on their performance, both directly and indirectly. When these excessive demands are not met within a reasonable timeframe, the employee becomes dissatisfied and ultimately leaves the corporation.
At CAC, employee turnover is linked to the demographic and cultural features of individuals in specific conditions. Personnel and objectives of the organization may vary from one organization to the next, leading to increased turnover rates because of the organization’s excessive expectations in terms of remuneration and benefits (Soomro et al., 2018). That is why there is no doubt that employees’ personal characteristics and conditions can contribute to employee turnover.
Work Factors and Employee Turnover
Other factors that have an equally strong influence on employee satisfaction with the workplace and the desire to leave it are work-related factors. These indicators include supervision, communication, stress, the nature of the work duties and responsibilities, and employee morale. Unlike personal factors, these factors are directly dependent on the activities and decisions that are made by managers and other representatives of the company’s administrators. Thus, these individuals are responsible for ensuring proper working conditions and compliance with work factors in the organization.
An individual’s or a team’s work plays a vital part in the number of turnovers. It is described as the tasks and duties allocated to, required of, or expected of them. According to Hofmann and Strobel (2020), the level of transparency and complexity of the work function is in a direct connection with turnover. First, these aspects should be discussed even before the company hires individuals.
Every future employee should have a clear idea of what the company expects and what tasks the specialist will face. This aspect also concerns providing an understanding of possible processing requirements for staff, information about weekends and vacations, and the conditions for obtaining them. Employee turnover is lower in corporations with well-defined work roles because employees understand what is required of them in terms of work outputs.
Conversely, employee turnover is high when job duties are ambiguous, as workers believe they are being taken advantage of by their bosses, and there are multiple overlapping roles and reporting lines. This is due to the individual characteristics of people, which affect the ability to endure stress when performing complex tasks (Lovering, 2020). Many individuals lack the ability or psychological readiness to undertake actions that require a higher level of responsibility.
An excellent illustration is when department personnel at CAC are based at the branch level but report to the department supervisor about issues and to the manager about other concerns. In this instance, the specialist clearly performs work that is not implied by the professional requirements of the position. As a result, an individual may experience stress, which can directly impact job performance and the company’s effectiveness.
It can be stated that at CAC, a high turnover rate is influenced by employee stress. Employee unhappiness has resulted from unclear responsibilities, leading to poor performance and stagnation. Workplace environment, job duties, and organizational structures all factor in employee stress at work (Kurniawaty et al., 2019). The job environment alone can be extremely stressful for many employees, and they often leave their jobs to prioritize their well-being.
Some people may not continue working in a place where they are constantly stressed simply because they are overwhelmed. Additionally, persistent discomfort can significantly impact an individual’s psychological well-being. Thus, it can develop into a constant feeling of anxiety. The most adverse consequences for employees may be depression and other mental illnesses that may require specialized treatment, and the need to leave the company.
Work-family conflict is typically the result of inter-role rivalry, in which role expectations from the work and family domains are, to some extent, contradictory, making involvement in one role more challenging as a result of engaging in the other. Work-life and family stress are also linked to decreased job satisfaction among employees and a higher likelihood of individuals leaving organizations. Due to the lack of workplace participation, as well as prolonged shift patterns, work elements such as work engagement, work hours, and job flexibility influence the quantity of work (Sabuhari et al., 2020). Many employees have reported having family issues as the reason for their poor performance.
Moreover, since the work at the organization is so involving, employees tend to spend more hours at work than at home. Such delays in the workplace make it difficult for employees to spend time with those who are close to them. Sometimes, families require one to be present for the children’s special days, such as school events or taking them to after-school activities. When this time is denied, employees get frustrated, and some choose family over work (Soomro et al., 2018).
Workplace culture, respect, accountability, and engagement all play a significant part in keeping employees motivated to work well. Employee turnover is modest at CAC when there are clear tasks, work design, and enhancements for current employees. Individual personnel can set their own goals and work successfully to attain the business goals with little supervision.
Employee turnover is a clear indication of weak management and leadership in many businesses operating in today’s market. Therefore, it can be said that how managers manage the company’s activities and the leadership skills they possess depend on how productive their employees are. Successful management skills and staff motivation are essential criteria that all managers should possess.
Moreover, if we consider a large team, then it necessarily requires the organization to achieve its goals and gain a highly competitive position in the company. Corporations construct jobs in a dynamic business environment to attract, maintain, and develop employees (Saeed et al., 2019). To encourage employees and reduce turnover, the HRM team may consider coordinating a system and establishing clear structures that outline individual employee responsibilities without ambiguity.
Furthermore, a key factor in employee retention, such as the reboot of employees, becomes one of the decisive factors in deciding to leave the organization. According to Sadiq (2022), workers are more likely to be unsatisfied when the workload is too great to handle. This is a direct result of stress and doubts about the suitability of a specialist to perform the tasks and responsibilities assigned to them. The consequence of this fact is that employees develop attitudes as a result of not having enough time after work to attend to their personal lives.
One of the variables that contributes to employee turnover at CAC is the huge workload for employees. The excessive requirements have been linked to job dissatisfaction. An increasing number of specialists openly express their negative attitude towards work, refuse to perform their duties, and withdraw from the company’s daily operations, establishing relationships with the organization’s staff. Constant growing tension and excessive job expectations have led to “work pressure,” which has cost the corporation money in the form of high absenteeism or staff turnover.
Effective communication is a key strategy for organizations. This aspect concerns not only the building of relationships between specialists employed in the organization, but also managers, especially those who occupy higher positions. Good communication among company personnel fosters cohesion and a sense of belonging among employees. Leaders who foster a positive communication culture within their organizations are thus the secret weapon in retaining competent and high-performing staff for longer periods.
In today’s business world, effective communication is recognized as a core management skill and a crucial component of effective management practices (Rajhans, 2018). This is because when building this aspect, managers gain insight into employees’ opinions about the company and can more effectively develop policies and approaches to increase employee satisfaction.
Employee retention is increased when employees and supervisors have a positive relationship. Ineffective leadership is clearly linked to poor work performance, excessive stress, decreased work commitment, job dissatisfaction, and a higher likelihood of turnover (Milosevic et al., 2020). Within the modern framework of performance management, responsible leadership has a positive impact on organizational performance and employee retention. Employee unhappiness is exacerbated by leadership style, as well as a lack of employee participation in decision-making and inadequate communication, which can lead to high turnover rates. Organizations should recognize this and reorganize their leadership to ensure that they prioritize the welfare of their employees.
Compensation and Benefits
Regarding the financial component of employee satisfaction, compensation and benefits become critical aspects. The reason for this circumstance is that monetary motivation is one of the most effective for many specialists. On the other hand, this type of job promotion may have a relatively low success rate, as staff may have a growing need for constant increases. Le Breton et al. (2018) pointed out that “high monetary incentives in financial or managerial domains may create or exaggerate overconfidence, leading to overly risky and suboptimal decisions” (p. 9). This confirms the view that financial incentives for employees’ activities can have a negative impact on staff productivity. Therefore, companies should exercise particular caution when employing this approach to address high turnover rates.
The most typical reason for such a high employee turnover rate is compensation. To tackle this problem, the corporation may make an effort to offer competitive salaries that can attract and retain well-qualified and talented employees. This can be achieved by conducting a benchmark analysis of competitors and examining the salaries of employees in other organizations (Bhattacharya et al., 2020). Thus, the company’s managers will have the opportunity to gain an understanding of what kind of remuneration will have the greatest efficiency and contribute to the growth of employee motivation and desire to stay in the workplace.
Another explanation for why many mid-level executives quit CAC is the lack of opportunities for advancement or promotion (Zimmerman et al., 2019). Individuals often choose to work for organizations that can offer them more advanced positions and better compensation packages. This aspect is the most valuable for specialists when they choose a workplace.
It is worth noting that organizations should be the most transparent when providing information about career growth for employees. A prolonged period of stagnation in professional activity can lead to a high level of dissatisfaction, stress, and a reluctance to perform official duties. For individuals, constant growth and development are essential; therefore, if a company limits these aspects, people prefer to go to those companies where they can achieve their goals. In these cases, one-time monetary incentives cannot play a significant role.
Employees place a greater emphasis on the compensation and perks offered since they devote their time, energy, and skills, and expect a higher return in terms of compensation and benefits. Employee compensation and perks are analogous to the exchange relationship between the company and its employees. Employers provide compensation packages, including medical insurance, social care services, pension benefits, and other benefits, to safeguard their employees against current and future risks.
Employees give their time and energy to recognize the company’s wage and benefits package. Employees, therefore, demand a generous compensation package to meet their personal expectations. However, if employees believe they are not being properly compensated, they will eventually leave the organization (Dousin et al., 2021). As a result, CAC should have a thorough understanding of compensation and benefits, as it will help them keep their staff.
Location and Availability of Other Competitive Job Opportunities
Increased competition, which influences the industry’s overall dynamics, is a major component of the evolving business environment. New businesses are springing up that offer comparable items but different services, and the customer experience they provide becomes the deciding factor. In the twenty-first century, high competitiveness and career-orientedness have caused a situation in which firms regularly lose essential human capital (Indeed Editorial Team, 2021).
In other words, this factor is in some proximity to the factor of career growth of specialists. Competition is an excellent motivator for many individuals; it contributes to the formation of the desire to benefit not only in personal terms but also to provide the competitiveness of the organization.
HR professionals at the corporation have now been paying attention to the opportunities they are creating in their personnel via skills training, as well as tracking their high-potential employees, ranging from top management to customer service representatives and customer support managers. This initiative may have increased effectiveness, as education is one of the valuable aspects of improving the efficiency of personnel.
Al Karim (2019) stated that “the importance of training and development programs can only be appreciated with a clear understanding of its direct impact on employee performance” (p. 8). Thus, company managers should have an awareness of how this aspect will affect people in the organization to build training and courses within the company.
The retention of talented personnel is a challenge that CAC faces in a highly competitive business climate among rapidly emerging countries. Achieving these objectives can be challenging. This is because new opportunities are constantly emerging on the market for employees, allowing them to more effectively realize their potential and showcase their skills.
At the same time, they have the opportunity not to exceed the required work or to perform actions that exceed their professional competence. The corporation continues to struggle with recruiting and retaining essential employees (“Credit acceptance: Number of employees 2010-2022,” n.d.). To address this issue, the company must implement measures to more effectively assess its employees’ talents and skills. Further, managers need to conduct various analyses and implement analytical tools to understand the shortcomings that employees can identify regarding workplace satisfaction.
Employee satisfaction is one of the most significant indicators of retention and willingness to stay. Assessment, as one option for investigating retention tactics, includes employee involvement. When job satisfaction is already poor, loyalty is a successful retention strategy. According to Arifin et al. (2019), work satisfaction enhances employee effectiveness, while both job satisfaction and organizational commitment diminishes turnover intentions and increases employee retention.
Summary
Conducting a study of literature sources is valuable, as it enables a detailed analysis of the factors reflected in the increased level of layoffs in the company. Among the primary factors influencing employees’ desire to leave the workplace are personal factors, including family issues, age, health concerns, or social status (Soomro et al., 2018). On the other hand, no less important are the working factors that directly depend on the decisions made by the organization’s leaders. These include the supervision of managers, the level of communication at all levels of the company, work duties, responsibilities, and employee morale. They can have a particularly serious impact on employees’ desire to perform their official duties.
Furthermore, according to the literature review, other factors of influence include compensation and benefits. They are closely related to financial incentives, but they do not always imply a wage increase. Thus, benefits can be provided to employees through education and professional development training. However, material motivation has faster and more effective results (Le Breton et al., 2018). It is especially relevant in cases when the employer needs to complete a task or solve a problem promptly.
This literature review provided key insights into potential factors that may contribute to the high turnover rate at CAC. Evidence from timely and credible sources has demonstrated that various factors and conditions can influence whether people leave or stay in organizations. According to Holliday (2022), the average turnover rate for an American organization is 18%, whereas CAC has experienced a 35% turnover rate over the past two years. That is why it is significant to understand the specific phenomena that make employees leave their employment places more frequently.
Personal factors that could affect turnover rate, the literature revealed varied personal circumstances that may cause one to leave one job for another or for all. Specifically, Žnidaršič and Bernik (2021) highlighted that changes in family circumstances impact employee performance in the workplace. Other aspects, such as willingness to take on new challenges, age, illness, and social status, are also critical. The problem also lies in the fact that indicators such as age and illness are the reasons for the unavoidable leaving of the workplace, which is always taken into account by the company when managing personnel. Among other factors, there is also a lack of understanding and personal objectives.
Additionally, several work-related factors were identified as contributing to employee turnover. The degree of transparency and difficulty of work functions has a direct relationship with turnover (Schaerer et al., 2018). When employees lack well-defined roles, they tend to feel disconnected. Working environment, job roles, and bad organizational structures are all factors that lead to employee stress at work. When the load is too heavy, workers are more likely to be unsatisfied.
Providing transparency in understanding employees’ job responsibilities becomes central to solving these kinds of problems. Moreover, it is valuable to establish communication in the workplace in a way that ensures managers have constant access to information about employee satisfaction levels and statistics on overwork.
Compensation and benefits studies suggested that they are a motivating factor for employees. They could be in terms of promotions and better pay packages (Le Breton et al., 2018). Pay is primarily obtained in cash and indirectly through bonuses, which assist in managing career and life obligations, and are included in employee compensation. Studies also suggest that if employees are not well compensated, they will move to other places with better compensation packages.
Finally, the availability of competitive jobs at various locations also contributes to employee turnover. People prefer to work either remotely or at places conveniently located near them, as well as at places that are easily accessible. A literature review also showed that a high degree of competitiveness and career-oriented professionals have created a situation in which firms regularly lose vital human capital in the twenty-first century.
Moreover, work satisfaction enhanced employee effectiveness, while both job pleasure and organizational commitment reduced turnover intentions and improved employee retention (Soomro et al., 2018). Retaining employees requires organizations to thoroughly consider the factors discussed in this literature review.
Research Methodology
Research Approach
This chapter outlines the research strategy that will be employed during data collection, as well as the sampling procedures and strategies to be used. This study also discusses the equipment, target population, procedures, and analytic and reporting tools.
Data Collection Approach and Procedures
This study employed a descriptive research approach to collect both quantitative and qualitative data, describing the nature and scope of the effects of employee turnover in organizations. According to Sekeran (2003), a descriptive research design is used to gather information about the current state of a phenomenon, characterizing “what exists” in terms of variables or circumstances within a scenario.
According to Mugenda & Mugenda (2003), descriptive research involves questionnaires and fact-finding inquiries, with the primary goal of characterizing the current state of affairs. This approach will be deemed appropriate by the study because it will facilitate the collection of accurate data, indicating the genuine aspects of the effects of staff turnover on the corporation’s performance.
Procedures
For the study, surveys will be collected via social media on the Facebook platform. The survey will consist of 9 multiple-choice questions for data collection.
Target Population
According to Frederic (2010), a target population is a comprehensive collection of all participants of an actual or hypothetical group of individuals, activities, or items to which a researcher desires to extrapolate the conclusion. The study’s target audience will be random individuals on social media. The target population will consist of 30 or more individuals solicited via social media, specifically the Facebook platform.
Sampling Size and Technique
According to Mugenda & Mugenda (2003), for descriptive investigations, a sample size of at least 10-20% of the overall population is sufficient. A sample size of 30 or more people will be chosen for this research using a stratified random sampling procedure. It is effective because it offers all participants an equal probability of being chosen as a survey responder, eliminating distortion and facilitating extrapolation of the clear approach (Peil, 2005). Participants will be solicited via social media, specifically through the Facebook platform. All responses will be provided anonymously.
Sampling Frame
A sampling frame, according to Mugenda & Mugenda (2003), is a thorough list of all testing units from which a population can be divided. The survey respondents will be anonymous and used as the sampling frame for the analysis in this research.
Instrumentation
The research will gather data from various sources and employ specific methods. Data collection sources and methods will be collected via social media, which will be available in a survey link using the SurveyMonkey tool. Questionnaires are favored since, according to Kothari (2003), they are appropriate data collection tools that enable individuals to answer a large portion of their thoughts about the study issue. According to Kothari (2003), the data acquired via questionnaires is devoid of investigator bias and pressure, which implies that accurate and reliable data is collected.
The current study asked the respondents to answer nine particular questions.
- What factors do you think are causing people to leave organizations? flexibility/compensation and/or benefits/lack of training/leadership/nature of work, and/or responsibilities/employee morale
- What factors influence people to stay? (comfort/leadership/nature of work and/or responsibilities/employee morale)
- Is it true that working conditions have an impact on employee turnover? (Likert scale)
- How much influence do working conditions have on employee turnover? Large Extent/Moderate/Low/No extent
- When staff turnover is high, how would you rank the organization’s productivity? Low/Moderate/Average/High
- Does staff turnover affect an organization’s performance? (Likert scale)
- Do you think leadership is addressing the concerns about turnover? (Likert scale)
- Should leadership conduct skip-level meetings to address any existing concerns to retain employees? (Likert scale)
- Does your organization address diversity and inclusion to ensure employees have a voice? (Likert scale)
Survey Study
The goal of the survey study is to assess the reliability of the questionnaire. A survey is needed to verify the validity of the data collection techniques. According to Kothari (2003), research reliability is determined by analyzing whether the investigation genuinely measures what it was supposed to measure or how accurate the study findings were. Survey research will be conducted to identify design flaws and provide insight into data for selecting respondents.
This study will consist of anonymous participants recruited through social media to validate the dependability of the research method. The clarification of the survey instrument for participants will be developed to improve the instrument’s reliability and validity (Kothari, 2003). The survey study enables the researcher to become familiar with the investigation and its guidelines and procedures, as well as identify items that require modification. The findings will assist the researcher in identifying and correcting inefficiencies that may arise from the equipment, ensuring that they capture what is expected.
Data Analysis and Synthesis Approach
This research is expected to yield both quantitative and qualitative data. To analyze statistical data collected through multiple-choice questions, a descriptive statistics analysis process will be employed. Regarding analysis, the SurveyMonkey survey tool will be utilized to build data arrays, which will be used for later data analysis. The descriptive analysis capabilities in SPSS Version 17 aid in variable response comparability and provide a clear picture of response rates.
The dataset will be analyzed, encoded, and classified according to each of the dependent variables before being evaluated using descriptive statistics, such as percentages, means, and standard deviations. The Pearson correlation test will be used to determine the significance of the research parameters. Tables will be used to illustrate the findings because they are user-friendly and display both response frequency and the percentage of responders’ perspectives. A qualitative data analysis approach will be employed to examine the data collected through multiple-choice questions.
Methodological Limitations
Quantitative research employs a standardized questionnaire with multiple-choice questions, resulting in findings that are constrained by the research proposal. As a result, the outcomes may not always accurately reflect the real occurrence in a generalized manner. Additionally, the respondents’ response alternatives are constrained by the study’s selection.
- Qualitative research results are often difficult to validate. Respondents have more discretion over the content of the data obtained in qualitative research, as it is typically open-ended.
- It is a time-consuming method. Analyzing, recoding, and other analysis processes are required in both quantitative and qualitative research.
- Causation is difficult to investigate. Qualitative research requires careful planning to ensure that the results obtained are accurate.
Methodological Assumptions
The current methodology implies that several assumptions underlie the study. Firstly, it is assumed that all the participants know how to read and can precisely understand the meaning of the questions. This condition indicates that the respondents will have no difficulty understanding and responding to the survey. Secondly, the research assumes that all participants provided honest answers to the questions. This suggestion demonstrates that the study will produce valid and trustworthy results.
Ethical Considerations
Since the research implies working with human subjects, specific attention should be devoted to ethical aspects. Firstly, all participants were informed that they could participate in the survey voluntarily. This step is necessary to ensure that no individual is forced to engage in the project against their will. Secondly, potential benefits and risks are addressed, which highlights the need to ensure confidentiality. The respondents were not asked to provide any personal information, which allowed them to answer the questions without any fear.
Data Analysis
Surveys are helpful and informative instruments that allow researchers to collect primary data and identify leading trends. The Turnover in Your Organization questionnaire was distributed via social media (Facebook). A total of 35 participants were involved. These participants had extensive work experience and answered all nine provided questions. Although these individuals completed the survey on various days, this temporary distribution did not make any difference. Instead, the obtained percentages are rather informative because they reveal specific trends regarding turnover in the organization, and these findings are typically aligned with research evidence.
What Makes People Leave the Workplace
Question 1 focuses on what factors influence people to leave their organizations. According to the responses, compensation and benefits (48.57%) represent the most influential feature, followed by flexibility (22.86%) and leadership (17.14%). Nature of work and/or responsibilities (5.71%) and employee morale (5.71%) were acknowledged by the smallest percentage of respondents. It is worth noting that none of the participants attributed a lack of training as the reason why individuals left organizations.
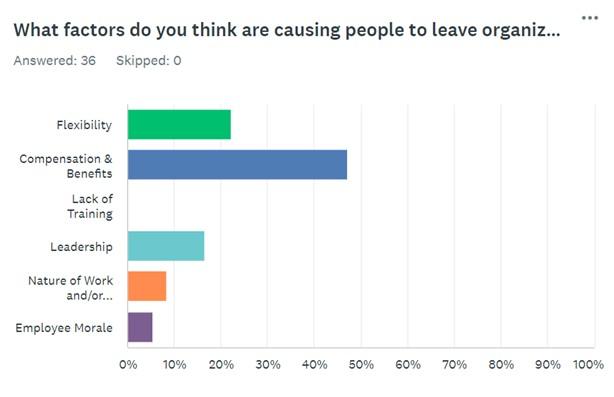
These results are generally consistent with an article by Belete (2018), which examines factors influencing organizational turnover. Although the researcher did not specify which conditions are more influential, we rely on scholarly evidence to support their effect. According to Belete (2018), people often decide to leave their employment places due to insufficient pay, poor leadership, job dissatisfaction, and other factors. Additionally, organizations typically invest in training to reduce their turnover rates and increase employee retention (Belete, 2018). Thus, the information demonstrates that the survey responses are aligned with the answers.
Question 2 draws attention to the opposite feature and determines why people decide to stay in an organization. The leading factor is comfort, and 68.57% acknowledged its significance. Simultaneously, 14.29% highlighted leadership, while the nature of work and/or responsibilities and employee morale each accounted for 8.57%. Employee comfort is a general term that encompasses several specific features.

Figure 3 presents Question 3, which can be considered a summary of the two previous questions, because it identifies the respondents’ views on whether working conditions can impact employee turnover. It is not surprising that 66.71% strongly agreed, while 22.86% agreed with the statement above. Simultaneously, 11.43% neither agreed nor disagreed, and there were no individuals who disagreed or strongly disagreed.
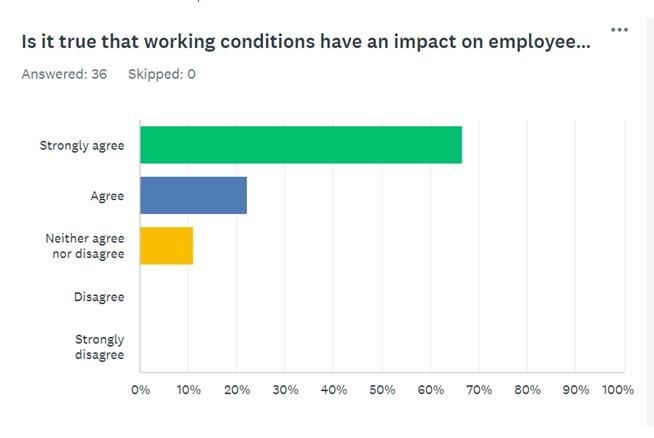
These results are perfectly aligned with the discussion above, as the answers to the previous questions and scientific evidence demonstrate the impact of working conditions. The rationale behind this suggestion is that a broad category of comfort is a leading factor that makes people stay, while flexibility and compensation force employees to look for new jobs. Thus, people analyze their working conditions and make decisions regarding the future of their employment.
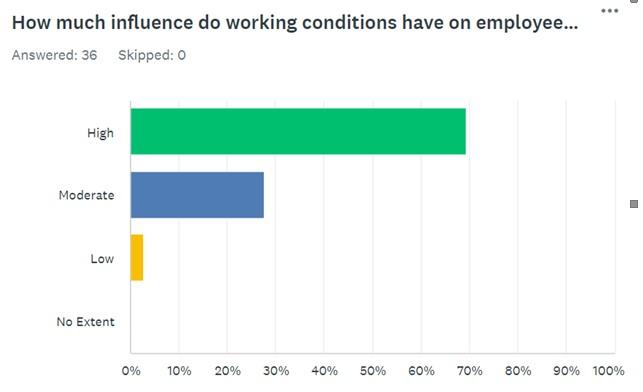
Question 4 is a continuation of the previous one, as this time respondents are asked to rate the influence of working conditions on employee turnover. It was expected that a small percentage would rank it as low (2.86%) and a moderate percentage would rank it as moderate (28.57%). The highest portion of the participants stipulated that the concept under investigation had a high (68.57%) impact on employee turnover, and none of the respondents stated that no extent existed. This percentage distribution is aligned with the discussion and findings above because versatile working conditions, including compensation, managers’ leadership, flexibility, and other factors, can significantly contribute to employee turnover and retention. That is why it is not surprising that most respondents highly assessed the impact of working conditions.
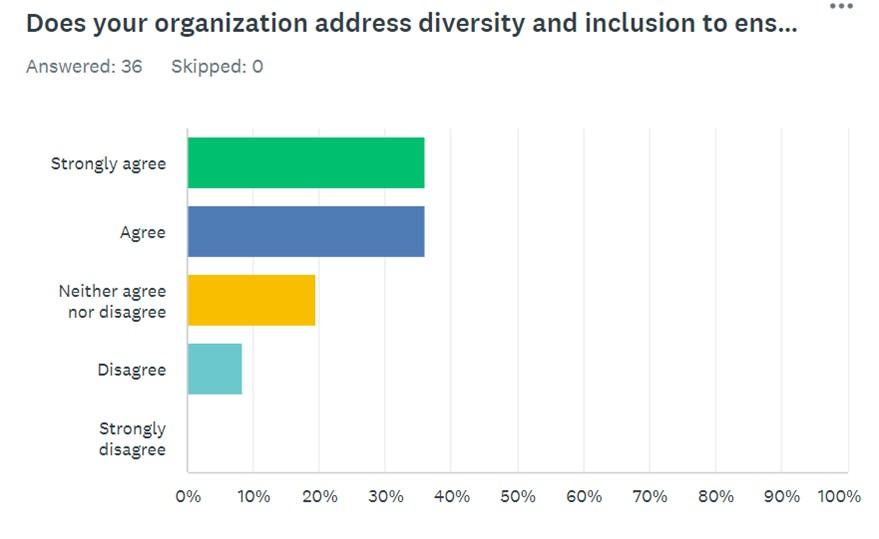
Finally, Question 9 asked the respondents to explain if their organization addressed diversity and inclusion. The distribution of answers follows the following pattern: 37.14% strongly agreed, 37.14% agreed, 17.14% neither agreed nor disagreed, 8.57% disagreed, and 0% strongly disagreed. On the one hand, this information implies positive consequences because a majority of respondents are provided with diversity and inclusion in the workplace. On the other hand, it is not reasonable to ignore almost 25% of the participants who did not distinguish positive outcomes regarding the issues under analysis. These findings suggest that organizations should invest more effort in ensuring that employees have a voice in the workplace.
The findings in this subtopic clearly demonstrate that working conditions can make people leave or stay in an organization. Individuals often consider salary, comfort, flexibility, and opportunities for promotion when choosing their employment positions. Thus, organizations should highlight these aspects if they want to reduce employee turnover. As for CAC, this organization now has a straightforward course of action to retain more workers.
Turnover Effect on Organizational Productivity
Question 5 asked respondents to evaluate the organization’s productivity when dealing with high staff turnover. A significant portion of the participants assessed it as low (51.43%) and moderate (25.71%). Simultaneously, it was unexpected that a relatively large number of respondents stated that productivity was average (11.43%) or even high (11.43%). The latter results are surprising because they contradict the literature findings.
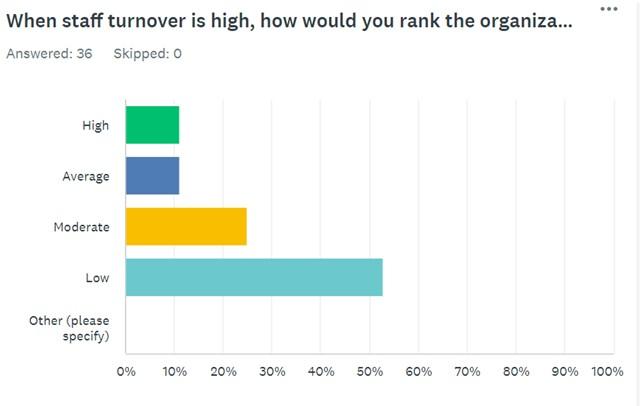
In particular, De Winne et al. (2019) employed a non-linear approach to demonstrate that labor productivity increases when low turnover rates are observed. Moreover, organizations typically struggle to cope with frequent changes in the workforce, as this state of affairs necessitates spending additional time and effort on training new employees (De Winne et al., 2019). That is why it is not clear why a substantial part of the respondents understated the negative effect of increased employee turnover on the organization’s productivity.
As for question 6, it is closely connected to the previous one because in this case, respondents are asked whether staff turnover affects the organization’s performance. The majority of the participants (68.57%) strongly agreed, while 25.71% agreed with the statement. The remaining respondents (5.71%) disagreed with this fact, which indicates that no one chose either the “neither agree nor disagree” or the “strongly disagree” options. The article by De Winne et al. (2019) explains why a significant portion of the participants assessed a positive correlation between employee turnover and the organization’s performance. These scholars stipulate that companies can reckon on improved outcomes if they manage to achieve low turnover rates (De Winne et al., 2019). However, a small portion disagreed with the statement, and it could be useful to discover why they submitted this answer.

This subtopic is important because it highlights why businesses should draw attention to their turnover. According to the responses, the majority of answers note the strong connection between high turnover and decreased productivity. There is strong logic behind this idea because the absence of experienced employees hinders the company’s ability to succeed in the market. That is why CAC and other organizations should strive to reduce turnover rates.
Leadership and Turnover
Question 7 moves further and focuses on what the respondents think about whether leadership addresses turnover issues. The answers are as follows: 2.86% strongly agreed, 20% agreed, 25.71% neither agreed nor disagreed, 45.71% disagreed, and 5.71% strongly disagreed. This information reveals that many individuals did not witness a positive impact of leadership on turnover concerns.
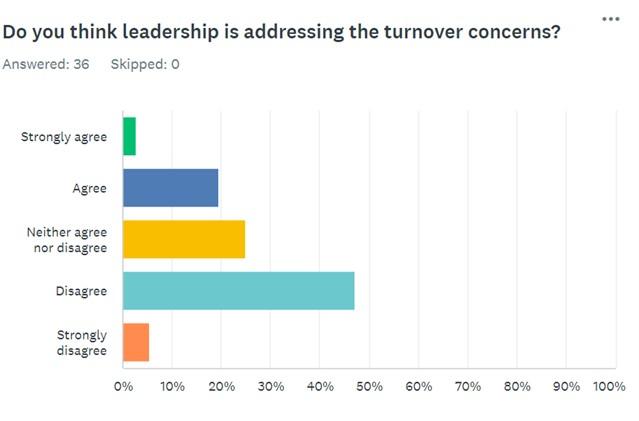
However, various scholarly articles stipulate that suitable leadership styles can successfully address the issue. For example, Jang and Kandampully (2018) acknowledge the positive effect of servant leadership, while Wang et al. (2018) emphasize the advantages of differential leadership and admit the harmful consequences of an authoritarian approach. Consequently, these findings demonstrate that leaders can effectively address turnover issues if they employ appropriate styles of managing their subordinates.
Furthermore, Question 8 was formulated to determine whether the respondents supported the idea of conducting skip-level meetings to address problems and retain employees. Almost all participants support this suggestion, as 54.29% strongly agreed and 40% agreed with the statement. Simultaneously, the remaining 5.71% neither agreed nor disagreed with the importance of these meetings.
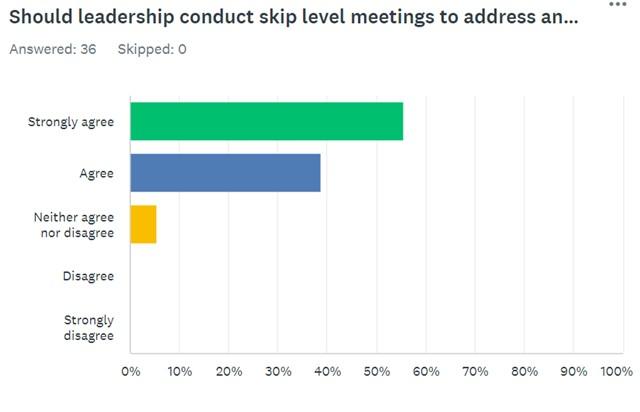
The literature review demonstrates that strong support for skip-level meetings is a justified phenomenon, as these events enable employees to raise concerns and express dissatisfaction with their manager’s performance (Goswami & Pandey, 2019). Simultaneously, these meetings are useful because they help workers feel heard and respected in the workplace. That is why it is not surprising that a significant part of the questioned employees advocated for holding such events because these individuals understand that it can be helpful to contact the manager’s supervisor.
The final subtopic is valuable because it reveals that it is insufficient to place all responsibility solely on a leader’s performance. As mentioned above, various factors contribute to the issue, and leaders are only one of many components. However, the responses demonstrate that skip-level meetings are an effective strategy for increasing employee satisfaction and achieving lower turnover rates. Therefore, leaders should take proactive steps to address the problem and achieve positive outcomes.
Conclusion
Data analysis reveals that people leave their employment places for several reasons, each carrying different weights. The analysis reveals that among those surveyed, 48% cited compensation and benefits as a reason for leaving their employment. 22% cited flexibility, 17% cited leadership, and 5% cited the nature of work and/or responsibilities and employee morale as the reasons why one would leave employment. At least one participant in the study cited a lack of training for the job as a possible reason for leaving employment.
When assessing the reasons why people stay in the same job, the results showed that individuals choose to remain in a job for various reasons, each carrying different weights. Some of the reasons people choose to stay in a job include comfort, leadership opportunities, and the nature of the work or responsibilities.
An analysis of whether working conditions in an organization can impact turnover reveals that a majority of those surveyed agreed that the working conditions in an organization have a significant impact on whether one stays or leaves the organization. When asked to rate the impact of working conditions on employee turnover, a majority of those surveyed rated it as high, indicating that it was one of the major factors employees considered when deciding whether to stay in employment.
In addition, the participants were asked their opinion on whether productivity could impact employee turnover. The majority of respondents rated productivity as low in relation to the factors that would influence an employee to leave their job, indicating that other factors are prioritized when considering whether to remain in an organization. However, when asked whether staff turnover impacted an organization’s performance, a majority of respondents believed that high staff turnover was detrimental to an organization’s performance, indicating recognition of the negative impact of high turnover on employees.
When asked whether leadership would address turnover issues, a majority of the respondents held a negative opinion. Their response was contrary to long-held beliefs that proper leadership can lead to lower employee turnover because it is inspirational and motivates employees to be more productive. Regarding suggestions on whether to hold skip-level meetings to address problems and retain workers, the surveyed employees supported holding these meetings regularly.
This indicates that failing to raise issues with managers at a platform, such as a skip-level meeting, could lead to employee frustrations and increased staff turnover. These meetings are also symbolic of the respect and dignity that management places on its employees. Thus, when held regularly, they give the impression that the management cares about and is concerned for the welfare of the employees. This perception creates goodwill and trust, which in turn reduces the rate of employee turnover.
Finally, when asked whether their organization addressed diversity and inclusion, an overwhelming majority of the respondents answered positively. However, a small majority of the respondents felt that the company was not doing enough to address diversity and inclusion issues. This indicates that a slim minority of employees feel dissatisfied with the organization’s stance and its efforts to address diversity and inclusion issues, and may consider departing the organization as a result.
In the grand scheme of things, any employee’s departure from an organization, regardless of the reason, has a negative impact on the organization and can lead to financial losses. Thus, data analysis gives insights into reasons why an employee would be inclined to stay or leave an organization. These insights should be taken into consideration when drawing conclusions and making recommendations based on the study’s results.
Employee turnover is a significant concern for the HR department and the organization as a whole. High turnover robs an organization of experienced and trained professionals, which could impact the performance and financial health of an organization (Soomro et al., 2018). Consequently, organizations spend a great deal of time searching for ways to attract and retain highly qualified employees (Hofmann and Strobel, 2020).
In recent years, organizations have turned to the scientific method to identify the reasons for high staff turnover and explore ways to minimize it (Dousin et al., 2021). The focus of this study was on the causes of high turnover at the customer service department in the corporation. After analysis, the following conclusions can be made:
- Most employees leave an organization because of compensation and benefits differences.
- Employees can leave an organization if they are not offered a flexible work schedule.
- The leadership of an organization can contribute to worker turnover.
- The nature of work and the responsibilities assigned to a particular employee significantly impact their decision to remain with an organization or leave.
- The lack of on-the-job training has little bearing on whether an employee leaves their job or not.
- The working conditions offered by an organization can have a positive or negative impact on a decision to stay or leave.
- Whether an organization is productive or not has a minimal impact on whether an employee leaves or stays.
- Skip-level meetings to address staff issues have an impact on an employee’s decision of whether to leave or stay with an organization.
- Properly addressing diversity and inclusion issues can encourage employees to remain committed to an organization.
These factors were found to influence the rate of employee turnover in the customer service department. Despite being specific to that corporation, these factors can apply to any organization because employees are generally affected by the same issues, regardless of the organization, department, or location they work in, globally. Thus, these factors can be generalized, and recommendations can be made on how to retain employees in a particular organization. These recommendations apply specifically to CAC and to any other organization in general.
Recommendations
When making personnel decisions, the HR department should prioritize attracting and retaining highly qualified personnel to the organization. With many organizations able to replicate other competitive advantages, the possession of highly qualified and motivated personnel is the only factor that maintains an organization’s competitive advantage (Aburumman et al., 2020).
Consequently, for an organization like Credit Acceptance Corporation, it is essential to consider several recommendations, such as offering above-market compensation and benefits. Salaries and benefits offered by an organization are the primary reasons why one chooses to leave or stay with the organization. Consequently, offering above-market pay and benefits would help attract and retain a highly qualified and productive workforce.
The second recommendation is offering employees flexible work schedules that balance work and life. Flexible work schedules are a significant factor in the decision to stay or leave (Choi, 2020). Consequently, an organization has several ways of ensuring flexible work schedules for its employees. The first is designating days when an employee can work from home and days when they would work from the office. The second option is to extend generous days off to all employees.
The third recommendation is that organizations should provide a better working environment for all their employees. Better working conditions do not exclusively mean physical conditions. On the contrary, a better working environment should be physically secure and provide employees with the peace of mind to complete their assigned tasks. Mental health is a major issue that could lead to higher staff turnover. Maintaining a conducive working environment means providing employees with conditions that support their mental health, rather than exacerbating it.
Finally, organizations should regularly conduct skip-level meetings to solve underlying issues with management. In skip-level meetings, employees can speak freely without fear of repercussions from management. This platform facilitates a candid conversation about the various issues they may be facing and provides ways to address them. Regular skip-level meetings give employees the impression that management is concerned about the issues affecting them, which fosters trust and goodwill in the relationship between management and employees, ultimately reducing staff turnover (Greenberg et al., 2018).
There are other recommendations that an organization should implement, including demonstrating exceptional leadership abilities, providing on-the-job training to employees, and effectively addressing concerns related to diversity and inclusivity. By implementing these strategic changes, an organization should be better placed to attract and retain the most qualified personnel. Retaining personnel is especially critical because it saves a company recruitment costs and ensures that employees with years of experience apply their skills for the benefit of the company and its stakeholders.
References
2020 Employee care report: The hidden causes of employee turnover. (2020). Limeade. Web.
Aburumman, O., Salleh, A., Omar, K., & Abadi, M. (2020). The Impact of Human Resource Management Practices and Career Satisfaction on Employee Turnover Intention. Management Science Letters, 10(3), 641-652.
Al Karim, R. (2019). Impact of different training and development programs on employee performance in Bangladesh perspective. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Research, 2(1), 8-14. Web.
Arifin, Z., Nirwanto, N., & Manan, A. (2019). Improving the effect of work satisfaction on job performance through employee engagement. International Journal of Multi-Discipline Science (IJ-MDS), 2(1), 1-9.
Belete, A. K. (2018). Turnover intention influencing factors of employees: An empirical work review. Journal of Entrepreneurship & Organization Management, 7(3), 1-7. Web.
Bhattacharya, S., Momaya, K. S., & Iyer, K. C. (2020). Benchmarking enablers to achieve growth performance: a conceptual framework. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 27(4), 1475-1501. Web.
Burke, R. J., & Cooper, C. L. (Eds.). (2007). Building more effective organizations: HR
Choi, S. (2020). Flexible work arrangements and employee retention: A longitudinal analysis of the federal workforces. Public Personnel Management, 49(3), 470-495.
Credit acceptance: Number of employees 2010-2022. (n.d.). Microtrends. Web.
De Winne, S., Marescaux, E., Sels, L., Van Beveren, I., & Vanormelingen, S. (2019). The impact of employee turnover and turnover volatility on labor productivity: A flexible non-linear approach. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 30(21), 3049-3079. Web.
Dousin, O., Collins, N., Bartram, T., & Stanton, P. (2021). The relationship between work‐life balance, the need for achievement, and intention to leave: Mixed‐method study. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 77(3), 1478-1489. Web.
Goswami, A., & Pandey, J. (2019). Credit attribution bias and its impact on employee morale and retention. Strategic HR Review, 18(2), 80-83. Web.
Greenberg, P., Johnson, P. T., Fishman, E. K., & Horton, K. M. (2018). Navigating the rapidly changing business landscape: Managing and motivating your team. Journal of the American College of Radiology, 15(8), 1190-1192.
Hofmann, Y. E., & Strobel, M. (2020). Transparency goes a long way: Information transparency and its effect on job satisfaction and turnover intentions of the professoriate. Journal of Business Economics, 90(5), 713-732. Web.
Holliday, M. (2022). 50 employee turnover statistics to know today. Oracle NetSuite. Web.
Indeed Editorial Team. (2021). 21 of the most competitive jobs right now. Indeed. Web.
Jang, J., & Kandampully, J. (2018). Reducing employee turnover intention through servant leadership in the restaurant context: A mediation study of affective organizational commitment. International Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Administration, 19(2), 125-141. Web.
Jordan’s Banking Sector (scirp.org)
Kothari, C. R. (2003). Research methodology: Methods & Techniques. First Edition, New Age International Publishers
Kurniawaty, K., Ramly, M., & Ramlawati, R. (2019). The effect of work environment, stress, and job satisfaction on employee turnover intention. Management Science Letters, 9(6), 877-886. Web.
Lagacé, M., Firzly, N., & Zhang, A. (2020). Self-report measures of ageism in the workplace: A scoping review. Researching Ageing, 41-55.
Lebreton, M., Langdon, S., Slieker, M.J., Nooitgedacht, J.S., Goudriaan, A.E., Denys, D., Van Holst, R.J., & Luigjes, J. (2018). Two sides of the same coin: Monetary incentives concurrently improve and bias confidence judgments. Science Advances, 4(5). Web.
Lovering, C. (2022). How personality can affect your stress levels. Psych Central. Web.
Macrotrends. (2022). Credit Acceptance: Number of employees 2010-2022 / CACC. Web.
Milosevic, I., Maric, S., & Lončar, D. (2020). Defeating the toxic boss: The nature of toxic leadership and the role of followers. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 27(2), 117-137. Web.
Mugenda & Mugenda, (2003), Research Methods, (4th Ed), Longman Publishers
Peil, S., (2005). Research Methodology and Design. 5th Edition, Macmillan. Publishers, U.S.A. New York
Rajhans, K. (2018). Effective communication management: A key to stakeholder relationship management in project-based organizations. IUP Journal of Soft Skills, 12(4), 47-66.
Sabuhari, R., Sudiro, A., Irawanto, D., & Rahayu, M. (2020). The effects of human resource flexibility, employee competency, organizational culture adaptation, and job satisfaction on employee performance. Management Science Letters, 10(8), 1775-1786. Web.
Sadiq, M. (2022). Policing in pandemic: Is perception of workload causing work-family conflict, job dissatisfaction, and job stress?Journal of Public Affairs, 22(2), e2486. Web.
Saeed, B. B., Afsar, B., Hafeez, S., Khan, I., Tahir, M., & Afridi, M. A. (2019). Promoting employee’s proenvironmental behavior through green human resource management practices. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 26(2), 424-438. Web.
Schaerer, M., Kern, M., Berger, G., Medvec, V., & Swaab, R. I. (2018). The illusion of transparency in performance appraisals: When and why accuracy motivation explains unintentional feedback inflation. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 144, 171-186. Web.
Singh, D. (2019). A literature review on employee retention with focus on recent trends. International Journal of Scientific Research in Science and Technology, 6(1), 425-431. Web.
Soomro, A. A., Breitenecker, R. J., & Shah, S. A. M. (2018). Relation of work-life balance, work-family conflict, and family-work conflict with the employee performance-moderating role of job satisfaction. South Asian Journal of Business Studies, 7(1), 129-146. Web.
Viegas, V., & Henriques, J. (2021). Job stress and work-family conflict as correlates of job satisfaction among police officials. Journal of Police and Criminal Psychology, 36(2), 227-235. Web.
Wang, L., Cheng, M. Y., & Wang, S. (2018). Carrot or stick? The role of in-group/out-group on the multilevel relationship between authoritarian and differential leadership and employee turnover intention. Journal of Business Ethics, 152(4), 1069-1084. Web.
Zhang, H., Sun, L., & Zhang, Q. (2022). How workplace social capital affects turnover intention: the mediating role of job satisfaction and burnout. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(15), 9587. Web.
Zimmerman, R. D., Swider, B. W., & Boswell, W. R. (2019). Synthesizing content models of employee turnover. Human Resource Management, 58(1), 99-114. Web.
Žnidaršič, J., & Bernik, M. (2021). Impact of work-family balance results on employee work engagement within the organization: The case of Slovenia. Plos One, 16(1), e0245078. Web.