Sustainable Development
“Sustainability is refers to the indefinite use of available natural resources without ever causing depletion of the energy or material sources on which man depends; while, development is the continued improvement of living standards as a result of economic growth” (Dahir, 2010).
“Therefore, sustainable development refers to the development that meets the needs of the present generations without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (Dahir, 2010).
There are three main approaches that are used to categorise sustainable development: These include; the economic, ecological; and socio-cultural approaches. Figure 1.0 shows the interrelation between the social, environmental and economic aspects of sustainability and how they bring about a sustainable development.
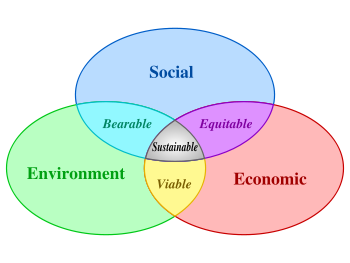
Economic Approach
From this approach, the idea of sustainability is that future living standards should not be prevented from further improvement or maintenance by current decisions. Therefore, the economic systems should allow for transition into the future without depletion of earlier investments and savings.
Ecological Approach
This approach holds that sustainable development involves ensuring that the following are achieved:
- Genetic diversity is preserved.
- Life support systems and essential ecological processes are maintained.
- Ecosystems and species are utilized in an efficient manner.
Socio-cultural Approach
This approach characterizes sustainable development in relation to developing and developed countries as a deep and profound change in the following:
- Political, Social, Economic;
- Institutional;
- And technological order.
The following are elements that can be used to measure achievement of a sustainable development:
- Living Standards: Access to clean drinking water which promotes healthy living.
- Proper Sanitation: Attributed to good drainage systems, clean latrines and toilets, and efficient waste management practices.
- Improved Infrastructure: The existence of good communication and transport systems helps in promoting tourism and reducing accidents.
- Political Stability: Allows for equitable distribution of resources.
- Population Numbers: There is a controlled growth rate which reduces overexploitation of resources like land, water and forests.
- High Literacy: High levels of literacy improve knowledge and impacts ability to utilize available resources in a sustainable manner.
Relevance of Sustainable Development
Humans as a Threat
Generally, man is considered as the greatest threat to realization of a sustainable environment.
- The rate at which man uses resources is higher than the rate of replacement of such resources (Accor, 2008).
- Globally, there is a heavy dependence on forests for wood, fuel and charcoal.
- Despite the high rate of tree harvesting, there are little efforts to replace them. Also, other types of tree species take many years to grow and mature.
- Therefore, since the rate of usage is very high, the numbers of trees are reduced by a certain percentage every year. These results in global warming and reduction in the amount of received rainfall (UNESCO, 2009): Hence, future generations are exposed to the risk of getting an unsustainable environment.
Ecosystem’s Lack of Self-sustainability
The ecosystem is not self sustainable, therefore, man has to play a major role in order to create a sustainable environment. For example, responsibilities should be assumed for every resources used in any development (UNESCO, 2009).
For instance, when a tree is cut, it is advisable to replace it with more than one. This would mean that future generation would have a chance to use the same species for own sustainable development.
Long-run Sustainability
A long-term sustainability can only be achieved through practice of a sustainable development (UNESCO, 2009). The use of resources in an irresponsible manner leads to environmental depreciation.
This results in depletion of resources, reduced productivity, global warming and many other negative effects. As such, a sustainable approach to development should be practiced for to realize long-term benefits.
Future Generations
A sustainable development is required in order for future generation to have a share of the current resources, and in a sustainable way (UNESCO, 2009). Therefore, a sustainable development ensures that all the necessary requirements for sustainable future are in at reach.
Depletion of resources is eliminated and the chances of future generations to suffer from unsustainable environment are reduced. Therefore, future generations will have accessibility to clean water, a green and productive environment, and resources like land will be available.
Challenges of Sustainable Development
Despite the urgent need for a sustainable development, there are many challenges that make its achievement difficult. Some of the challenges are; poverty, population sizes, poor policies, market failures, resource depletion, political instability, and lack of participation. These challenges are discussed in the following paragraphs.
Poverty
Poverty is characterised by a situation where people cannot afford the most basic needs for life (Dahir, 2010). It is one of the biggest challenges to achievement of a sustainable development. A poor society tends to over-depend on forests for sustainability.
As a result, depletion of forests which causes encroachment by deserts; thus, reduced annual rainfall, drying up of rivers, reduction in crop production, occurrence of famines and an unstable economy. However, poverty will continue to remain a major challenge since the number of poor people increases globally:
- Poverty is the overriding theme of sustainable development.
- Globally, 1.3 billion people live in absolute poverty (less than 1 dollar per day).
- Since the 1992 Rio Conference, the number of people living in absolute poverty has increased.
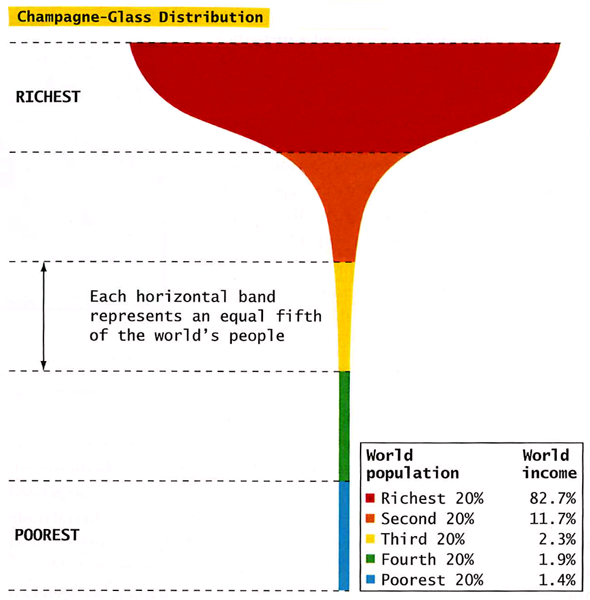
- As seen in figure 2.0, 82.7% of the global income goes to the 20% of the wealthiest global population (The Society Pages, 2009).
- Also, most of the investments are owned by this category of the wealthy as shown by the graph (Figure 2.0) associated to the richest global population.
Population
A high population results in increased pressure on the available resources (Accor, 2008). More people increase the demand for resources such as land, water, food, health facilities. As such, the fast increase in global population negatively impacts on achievement of a sustainable development (Dahir, 2010). The world’s population facts and its effects are as described below.
- World population is predicted to reach 8 billion people by the year 2020.
- This is stated as a fourfold increase as compared to 1920s growth rate.
- Will result in stiffer competition on land and water resources.
- These may result in conflicts, thus, hinder sustainable development.
- Also, threatens the survival and livelihood of people living at subsistence level.
Participation
The lack of participation in sustainable development activities negatively impacts on the realization of a sustainable development.
- Many people do not participate in designing of developmental programs.
- Important advice and opinions from potential people lack.
- The chief pioneers of such programs become demoralized.
- These may result in failure of important sustainability projects.
Policy & Market Failure
A sustainable development can be hindered from realization by poor policies and market failures in the following ways (ILO, 2008):
- Existing environmental laws and policies are undermined by some countries.
- Some see such policies as an extra cost to their economy, yet irrelevant.
- Omission – not intervening when necessary.
- Commission-stepping in when intervention is unnecessary or even detrimental.
Resource Depletion
The global rate of resource depletion is generally higher than the rate of replacement (Accor, 2008). This means that some resources cannot be produced at a rate that can fully support the demand. As a result, these resources are overexploited and some depleted.
This means that realization of a sustainable development is difficult, thus, impacting negatively on the current and future generations. Direct impacts are:
- Creation of forests.
- Leads to siltation and drying up of water bodies.
- Inadequate rainfall and land productivity.
- Finally, reduced harvest, hunger and famines.
Political Instability
Political instability which is rampant among Middle East and African countries such Afghanistan, Iraq, and Sudan make the realization of a sustainable development very difficult (Dahir, 2010):
- In such scenarios, forests and mountains are used as hideouts.
- Occurrence of many deaths that instill fear in people.
- Therefore, difficult to use resources for sustainability purposes.
- This results in low food production, poverty and unhealthy living.
Conclusions & Recommendations
In conclusion, the following recommendations are proposed in order to achieve a sustainable development for a healthy living of the present and future generations:
- Community participation: Participation in sustainable development projects will lead to increased motivation of pioneers, effective decisions, and success in realizing a sustainable development (Swanson & Laszlo, 2009).
- Poverty Eradication: A national agenda for poverty eradication will reduce depletion of resources such as forests and increase production, for example, through farming and animal rearing (ILO, 2008).
- Population Control: The local population should be educated on the importance of family planning so as to check the rate of population growth. This reduces overexploitation of resources such as land and water, thus, eliminates possible civil wars and famine.
- Use of Legal Policy Framework and Good Planning: Encouraging formation and use of policies that triggers a sustainable development is inevitable. Examples of such policies include; Conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA), Land use Planning, and Development Planning (Swanson & Laszlo, 2009).
- Alternative Energy Sources: It is advisable to use alternative sources of energy so as to reduce depletion of forest and other important resources. This may help to check the rate of global warming and realize a self sustainable development for long-term.
- Environmental Education: Creation of awareness on the need for a sustainable environment should be encouraged through environmental education. This will increase the knowledge for the need, thus, people will help in the achievement of the dream (Swanson & Laszlo, 2009).
References
Accor (2008) The Challenges of Sustainable Development. Web.
Dahir, H. (2010) The challenges of achieving sustainable development in both developed and developing countries, and their adjustments. Web. Free Online Articles Directory. Web.
ILO (2008) Global Challenges for Sustainable Development: Strategies for Green Jobs. Web. G8 Labor and Employment Ministers Conference. Niigata, Japan. Web.
Swanson, D., and Laszlo, P. (2009) National Strategies for Sustainable Development: Challenges, Approaches and Innovations in Strategic Co-ordinated Actions. Environmental Policy Research Centre, Frele University of Berlin. Web.
The Society Pages (2009) Graphic Sociology: Champagne Glass Distribution of Wealth. Web.
UNESCO (2009) Relevance of ESD for Key Sustainable Development Challenge. Web. ESD World Conference 2009. Web.
Wikipedia (2006) Scheme of Sustainable Development at the confluence of three constituent parts. The Free Encyclopedia Wikipedia. Web.