Epithelial tissue is composed of cells that are laid together in sheets, with its cells being closely connected to one another. The epithelial layers are avascular but innervated. The cells of the epithelium have two surfaces, the structure, and function of which can vary1. Such glands as the exocrine and endocrine are made up of epithelial tissue and are differentiated based on the manner of secretions’ release. There are eight types of epithelia, with six of them being identified on the basis of the number of cells and their shape and two being named by the type of cells found in them. They include simple squamous epithelium, simple cuboidal epithelium, simple columnar epithelium, pseudostratified columnar epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, stratified cuboidal epithelium, stratified columnar epithelium, and transitional epithelium. Among the mentioned types of epithelia, the simple squamous epithelium will be discussed further.
Simple squamous epithelium represents a single layer of flat cells that have the shape of scales. This type of epithelial lines the inner surfaces of all blood vessels make up the wall of alveolar sacs in the lungs and lines the cavities in the body2. The cells of the epithelium have a flat shape and are arranged using a single layer. This layer is thin enough that it allows forming of a membrane through which the compounds can move with the help of diffusion. Simple squamous epithelia allow for facilitating gas diffusion as well as small molecules.
Simple squamous epithelium tends to be permeable and occurs where small molecules require passing quickly through membranes through diffusion or filtration. The epithelium falls under the physiological category of exchange epithelium because of its capacity to transport molecules promptly across the tissue level. To enable this movement, some kinds of simple squamous epithelium can be porous, which allows molecules to pass through it, thus enabling a leaky epithelium. Simple squamous epithelium is best located in the air sacs of the lungs, the lining of the heart, as well as lymphatic and blood vessels. Therefore, the primary function of this type of epithelium entails allowing materials to pass by means of diffusion and filtration and secrete lubricating substances.
Because simple squamous epithelium is involved in the composition of the lungs, the heart, blood, and lymphatic vessels, it plays crucial functions in the body. The lungs are a vital body organ, which is a part of the respiratory system, allowing a person to breathe. They will enable the inflow of oxygen into the body (inhalation) and send carbon dioxide out (exhalation), while the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide is called respiration. Besides, the simple squamous epithelium is included in the composition of the heart, which is the most critical organ in the body which sends blood around it. Blood functions as the key provider of the body with oxygen and much-needed nutrients and also carries waste.
The blood and lymphatic vessels also play vital roles in the human organism, with simple squamous epithelium representing their core component. The lymphatic system represents the component of the immune system, helping maintain the balance of fluid in the body and playing a part in the absorption of fats and fat-soluble nutrients3. It encompasses an extensive vessel network passing through the majority of the tissues to allow for the movement of lymph. When it comes to the importance of blood vessels, their function entails the delivery of blood to organs and tissues in the body. The blood supplies the organs and tissues with oxygen and nutrients needed for the functioning of the organism.
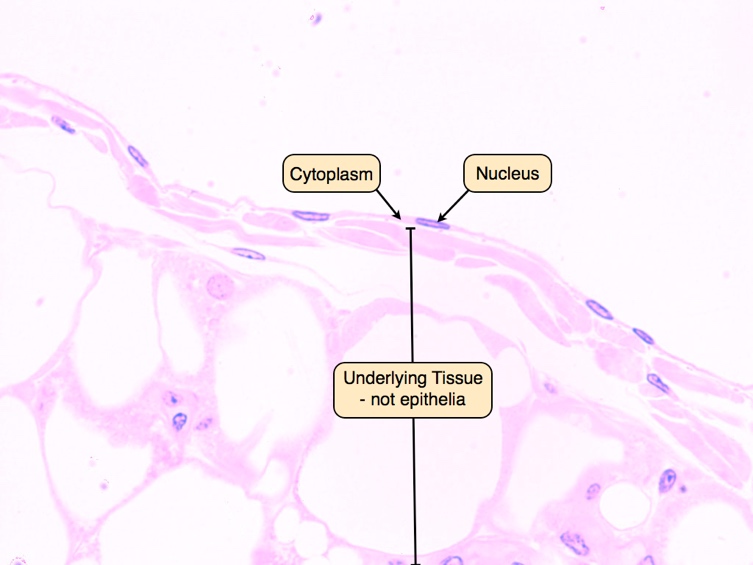
The image of the simple squamous epithelium is represented in the longitudinal section, which is done by achieving a plane along the long axis of the structure. It represents a section done by a plane along the long axis of a structure as opposed to a cross-section, which is also referred to as the transverse section. In histology, the longitudinal section is achieved by making a cut that is made parallel to the longest dimension of an organ or a specimen. This is because many anatomical structures are significantly longer in one direction than the other. Therefore, the tissue cut in the long direction, the longitudinal section of the simple epithelium will mean that the image should show that every cell touches the basement membrane. In contrast, in a stratified epithelium, some cells should be shown resting on top of other cells without being in contact with the basement membrane.
The examination of simple epithelial cells is usually possible through a biopsy. After a sample is collected, it is being fixed in formalin and embedded in a medium such as paraffin. Then, it is sectioned and stained to fit the further examination. Besides, in histology, it is notable that keratin can be used for defining tissue as epithelial cells and differentiate between the different types. In terms of visualization of cells, light microscopy is usually used; it can also help determine the epithelium’s morphology present in the tissue specimen.
Reference List
- Kurn H, Daly DT. Histology, Epithelial cell. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Web.
- Xiong F, Ma W, Hiscock TW, et al. Interplay of cell shape and division orientation promotes robust morphogenesis of developing epithelia. Cell. 2014;159(2):415-427. Web.
- Null M, Agarwal M. Anatomy, Lymphatic System. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021.