Introduction
Etsy is an American e-commerce company focused on handmade, vintage, and creative goods. Founded in 2005, Etsy offers an online marketplace platform that connects artisans and crafters with buyers seeking unique and customized products. As of 2023, Etsy has over 90 million registered users and hosts over 100 million products spanning numerous categories, including jewelry, clothing, home décor, art, and craft supplies (Etsy, 2023). The company generated over $2.3 billion in gross merchandise sales in 2022.
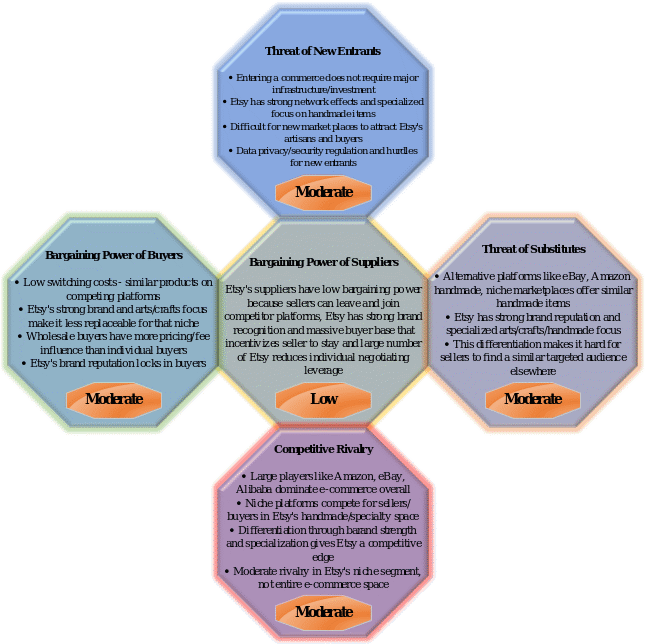
Etsy competes in the crowded online retail industry which includes e-commerce giants like Amazon and eBay. However, Etsy has carved out a niche for small-scale sellers of artisanal goods. This Five Force analysis evaluates Etsy’s competitiveness and position in the industry based on the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, and competitive rivalry.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Threat of New Entrants – Moderate
The threat of new entrants for Etsy is moderate. Launching an online marketplace does not require major infrastructure, inventory, or manufacturing investments, making entry relatively easy. The emergence of e-commerce platforms like Shopify has further reduced barriers to entering this market. However, building a strong brand and attracting artisans and buyers to a new marketplace takes significant time and effort (Porter, 2008).
Etsy benefits from strong network effects as the established marketplace for handmade and creative goods. New niche-focused marketplaces will struggle to divert artisans and buyers away from Etsy’s platform. Etsy’s specialized focus on unique, handmade items also makes it difficult for mass marketplaces to compete in Etsy’s niche (Etsy, 2023).
While the e-commerce industry overall has low barriers to entry, Etsy’s brand reputation, network of sellers and buyers, and niche focus make it challenging for new marketplaces to gain traction. Data privacy and security regulations create additional hurdles for new entrants. The e-commerce industry is easy to enter, but competing against Etsy’s entrenched position in the handmade/creative niche would prove difficult for newcomers.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers – Low
Etsy’s suppliers are the millions of independent crafters, artisans, and small merchants that operate shops on its marketplace platform. Individually, these sellers have very little bargaining power or leverage over Etsy. The company provides sellers access to a global base of buyers that would otherwise be difficult for small suppliers to reach independently.
While sellers can easily leave and move to competitor marketplaces or their own independent platforms like Shopify, Etsy’s strong brand recognition and massive buyer base create incentives for sellers to stay. The large number of sellers on Etsy ensures no single craftsperson or shop has significant negotiating leverage (Porter, 2008). For an individual seller, Etsy is replaceable, but for Etsy, any individual seller contributes a negligible fraction of overall revenue.
The abundance of sellers eager to access Etsy’s platform and buyers ensures low supplier power. However, while sellers have little individual leverage, organized collective action could increase negotiating power. The fragmented and individual nature of sellers on Etsy’s marketplace results in very limited bargaining power (Cho, Ke, & Han, 2019). The company can set policies and fees for sellers without much pushback, given the individual seller’s small size and lack of platform alternatives. This can easily replace Etsy’s built-up buyer base and brand recognition in the handmade segment.
Bargaining Power of Buyers – Moderate
The bargaining power of buyers on Etsy is moderate. Switching costs are low for buyers as unique handmade goods can also be found on competing marketplaces like eBay and Amazon Handmade or directly from individual seller websites. This availability of close substitute platforms limits Etsy’s pricing power (Zargartalebi, 2021). However, Etsy has built a strong brand reputation in the niche handmade segment that attracts buyers and provides some differentiation from competitors. While buyers can easily find product alternatives, Etsy’s brand recognition and specialized focus on arts/crafts make it less replaceable for buyers focused on that niche.
The large number of small, individual retail buyers on Etsy limits their negotiating leverage compared to Etsy’s total sales volume. However, larger wholesale buyers like big-box retailers have more influence over Etsy pricing and fees due to their bulk purchases. Low switching costs are balanced by Etsy’s strong brand in the handmade space.
Occasional buyers have limited influence but organized wholesale buyers can pressure for discounts and lower fees (Truong, Lang, & Conroy, 2021). This results in a moderate, balanced level of buyer bargaining power over Etsy. While alternatives exist, Etsy has created a niche ecosystem and loyal following that retains buyers despite low switching costs for individuals.
Threat of Substitutes – Moderate
The threat of substitutes for Etsy is moderate, as there are alternative platforms that facilitate transactions between artisans and buyers looking for unique handmade items. These include major e-commerce sites like eBay and Amazon, niche marketplaces like ArtFire focused on handmade goods, as well as direct sales channels like independent seller websites and social media platforms (Zargartalebi, 2021). Sellers can market to buyers directly through Facebook, Instagram, and their own sites, reducing reliance on a centralized marketplace like Etsy.
However, Etsy has cultivated a strong brand reputation and specialized focus specifically on arts, crafts, and handmade items. This provides differentiation as both sellers and buyers flock to Etsy for its niche community and product focus that other generalized marketplaces cannot easily replicate. Etsy’s large base of buyers interested in artisanal, vintage, and craft products makes it difficult for sellers to find that same targeted audience through independent websites or non-specialized e-commerce platforms. While consumers do have multiple substitute channels, Etsy’s network effects and concentrated marketplace for the handmade niche counteract the threat. The availability of e-commerce and direct sales substitutes poses a moderate threat to Etsy.
Competitive Rivalry – Moderate
The competitive rivalry among the major online marketplaces is moderate. The e-commerce space only has a handful of large players like Amazon, eBay and Alibaba that dominate the industry. However, competition is intensified in the handmade and specialty goods segment where Etsy operates.
Rival platforms like Amazon Handmade, ArtFire, and niche sites are vying for sellers and buyers in this space (Zargartalebi, 2021). The scope for differentiation is limited since marketplaces provide similar core functions like listings, payments, and reviews. Brand strength and specialization provide some competitive edge to Etsy.
While network effects and low switching costs increase rivalry, competitors are not yet posing an existential threat to Etsy’s market share. Etsy faces moderate threats across all five forces. Its brand recognition and specialty in handmade goods balance out the low barriers to entry and substitution in the e-commerce industry (Zhu & Liu, 2018). Etsy maintains a competitive position, though it needs to continue differentiating itself from rivals encroaching in its niche. Expanding its artisanal goods line-up and strengthening network effects will be key strategies going forward.
Conclusion
Thus, Etsy’s position in the existing market and the assessment of its competitiveness due to Porter’s five forces analysis can be considered as not entirely stable and has risks compared to other players. The overall situation has also been depicted in abbreviated form and graphically illustrated to provide readers with a full understanding of the situation and the analysis results. The risks are mainly expressed in the presence of many popular competitors in the industry and trade, some of which are difficult to counter. However, the company should not forget about digital marketing, sustainability, and innovation to build customer brand loyalty and expand operations.
References
Cho, W., Ke, J.-Y. F., & Han, C. (2019). An empirical examination of the use of bargaining power and its impacts on supply chain financial performance. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, 25(4). Web.
Etsy. (2023). Q4 and FY 2023 financial results. Web.
Porter, M. E. (2008). The five competitive forces that shape strategy. Harvard Business Review, 86(1), 78–93, 137. Web.
Truong, V. A., Lang, B., & Conroy, D. M. (2021). Are trust and consumption values important for buyers of organic food? A comparison of regular buyers, occasional buyers, and non-buyers. Appetite, 161. Web.
Zargartalebi, M. (2021). Sustainability as a competitiveness factor: A quantitative cross-country analysis. Economics and Environment, 76(1), 21–21. Web.
Zhu, F., & Liu, Q. (2018). Competing with complementors: An empirical look at Amazon.com. Strategic Management Journal, 39(10), 2618–2642. Web.