Introduction
This is a case study about operations management with a specific focus on Faber-Castell, the oldest pencil company in the world (1761).
Mission Statement
Faber-Castell does not clearly state its mission statement. Nevertheless, the company is known for its quality experiences in all areas of business. For over 250 years since its inception, Faber-Castell has promoted the legacy of its founder in the following statement:
“From the start, I was determined to raise myself to the highest rank by making the best that can be made in the world” (Faber-Castell 1).
This statement indicates that Faber-Castell aims to develop high-quality products through innovation and maintain its tradition.
Internal Forces
Resources
One major resource of the company is its people. Employees of Faber-Castell have been able to sustain the company’s vision of “quality, innovation in the present and future time, as well as its tradition” (Faber-Castell 1). As a result, its basic design of the graphite encased wood pencil still reflects the tradition and is unlikely to change much, at least in the present time. Today, senior management has been instrumental in developing new products and steering international growth in emerging economies like India.
Faber-Castell team takes delight in developing new products, recreating past products by relying on “design and modern technology, as well as its massive resources for expansion” (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1).
Core Competencies or Capabilities
From the case study of Faber-Castell, as well as knowledge of the business and its products, it is evident that the company has various core competencies. These core competencies have resulted from the company’s resources and strategic directions that are executed in different subsidiaries worldwide. Faber-Castell’s core competencies result in a culture of innovation, creativity, competitiveness and sustainable profitability in the competitive world of creative design, writing and drawing. Core competencies are in areas of the company’s tradition and heritage, the team, brand, products, innovation, globalisation, customer benefits, environment and social responsibility, organisation, and a long-term orientation.
Culture
Faber-Castell promotes a culture of innovation, creativity, competitiveness and sustainable profitability in the competitive world of creative design, writing and drawing. At the same time, the company focuses on the welfare of its customers, especially children, and therefore, it has adopted environmentally friendly materials for manufacturing its products.
Through innovation, Faber-Castell has ventured into manufacturing “eye pencils, lip pencils and other products for some of the leading cosmetic brands” (Chamikutty 1).
Other than the resource and strategic core competencies, the brand is a major aspect that gives Faber-Castell its identity. The business develops a brand based on four critical factors. The four factors stipulate guidelines on the conduction of operations at the firm, both in the internal environment and external environments in dealing with business partners, customers, the environment and the community. Through effective operations management, the management does not just define and publicise the brand core competencies; rather, there is an effective implementation of the core competencies in daily operations and encouraging employees to be proactive. In this regard, the four aspects that enhance brand core competence are competence and tradition, outstanding quality, innovation and quality as well as social and environmental responsibility. These factors have reinforced the company’s culture.
Weakness
Chamikutty cited von Faber Castell, saying that distribution was a major challenge for the company, particularly its high-end luxury pencils and fountain pens (Chamikutty 1).
von Faber Castell also commented that the company needed highly sophisticated salespersons who were, however, difficult to get in the labour market. Faber-Castell aims to improve brand visibility and market penetration (Chamikutty, 1).
External Force
Environmental
As consumers became aware of the toxins found in some pencils, parents and teachers raised issues that children would “swallow toxins as they chew their pencils and they, therefore, preferred plain wooden ones” (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1). On the contrary, brighter colours appealed to children. As a result, Faber-Castell had to change its processes in order to introduce environmental-friendly paints and use new paints without dangerous chemicals. Today, teachers encourage parents to buy such pencils.
Competitors
The Economist notes that nearly “15 billion – 20 billion pencils are made each year, roughly half of them in China”, and Faber-Castell produces about 2.2 billion” (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1). This suggests that Faber-Castell faces fierce competition from other organisations that manufacture pencils and other related products globally. In addition, technology has introduced substitute products, which the company must compete against to acquire new markets. The Economist notes that majorities thought that pencils would become obsolete in the computer age, but this has not happened to date (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1).
Technology
Technology has been one major source of threat to the company. Many thought that the computer age would eliminate pencils and other writing materials. Conversely, Faber-Castell has used technologies to innovate and develop some of the best luxurious pencils and other writing materials in the world.
Customers
As populations increase globally, users of pencils and other writing materials increase too. For instance, pencils have found many consumers, especially children, in both developed and emerging nations. In addition, the company has developed a wide range of products to meet the needs of different customers.
Today, Faber-Castell believes that the future of its brand lies in emerging economies like Turkey, China, Brazil, and India, where there are high growth rates of populations and education. It hopes that children will make a smooth transition from using pencils to its premium range of products later in life.
Business Strategy and Strategy for the Company
Based on the company’s long-standing statement, Faber-Castell business strategy focuses on innovative, high-end products. In developed nations, Faber-Castell promotes its premium products while in emerging economies like India, the company focuses on Tier I & Tier II markets.
The company’s boutique retail outlets reflect premium products and high-end consumers its targets. The business strategy aims to spearhead “direct consumer contacts and trade promotion” (Chamikutty 1). In this regard, Faber-Castell aims to create a brand for the mass market through digital media strategies.
As Faber-Castell emphasises environmentally friendly products, it also recognises that the future of its business lies on emerging economies like Turkey, India, Brazil, and China, which have experienced high rates of population growth and focus on education. Faber-Castell believes that it will create brand loyalty and help its customers during the transition from pencils to a wide variety of premium products. Although the company acknowledges that transition could be a challenging process, Faber-Castell strives to create brand loyalty by defining their products as ‘customers’ friend for life’, which are life partner from the beginning of the journey to the end.
The local management teams of Faber-Castell must determine their priority and set annual targets in their respective markets. In most cases, local managers have emphasised the need to promote their premium products across various cities.
Mass Customisation Strategies
Faber-Castell has adopted a transparent customisation strategy to develop its products. The company customises products without informing the customer. Although Faber-Castell relies on transparent customisation, it listens to customers’ responses about their experiences with the products. For several years, the company embarked on research to develop “firm lead and the type of wood that would protect pencils when dropped” (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1).
Over the years, the company has customised its pencils to meet the needs of scribblers. First, Faber-Castell introduced “water-based environmentally friendly paints to its pencils to eliminate fears in parents and teachers that children would swallow toxins as they chew pencils” (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1). Instead of introducing plain wooden pencils as parents and teachers would have preferred, the company introduced safe, bright colours for children in the 1990s. Faber-Castell reworked, therefore, its production processes to introduce and accommodate new paints with no harmful elements in paints.
Today, teachers encourage parents to purchase such safe pencils. Second, elements of transparent customisation at the company involved the introduction of an ergonomic triangular shape in pencils. This was a popular shape among children. Third, the company “added rubbery dots to keep pencils in sweaty hands of users, and they would therefore not slip out of little hands” (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1). Finally, the company is yet to determine the exact customisation it would introduce to pencils. Nevertheless, the company believes that there is further room for refining its pencils. It will perhaps focus on tougher pencils, easier on the eye with the basic design that uses the wood to encase the graphite (Chamikutty 1).
Categories of Business Strategies
Faber-Castell uses two business strategies, which include first-to-market strategy and market segmentation strategy. In the first-to-market strategy, the company introduces its products before the competition. Faber-Castell is the oldest known pencil company in the world. In 1883, artists like Vincent van Gogh and Anthon van Rappard had already discovered Faber-Castell pencils, and today, the company continues to introduce new products for various segments of the market (Chamikutty 1).
Faber-Castell engages in research to develop products that appeal to the market, including children, teachers and parents. It has also introduced modern technologies to facilitate processes in order to develop the best products. Given that Faber-Castell was the first in the market and has always led with innovative products, the company had developed luxury products with high prices to skim the market, particularly in the developed nations and emerging economies.
Another critical strategy that Faber-Castell uses is market segmentation. In the emerging economies, Faber-Castell has segmented its markets into Tier I & Tier II. The first tier serves high-end customers in boutique-designed outlets, while the second tier focuses on the mass market to grow the market share globally.
The Life Cycle of Product
Faber-Castell is over 250 years old, and one may be forgiven to think that its products are obsolete. This is, however, not the case with the company’s products. In fact, the company’s products have matured over time, but have not reached the stage of decline.
At one time, many thought that the Computer Age would eliminate the need for pencils and other writing materials (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1). Faber-Castell realised this threat from substitute products. Consequently, it embarked on reworking its production processes through innovation and inculcating customers’ experiences into the design to develop the best premium products for the market and restore handwriting culture in its customers. Today, Faber-Castell focuses on international expansion strategies as its global activities, sales and profitability surge.
A table showing the growth of sales of the firm in the last ten years
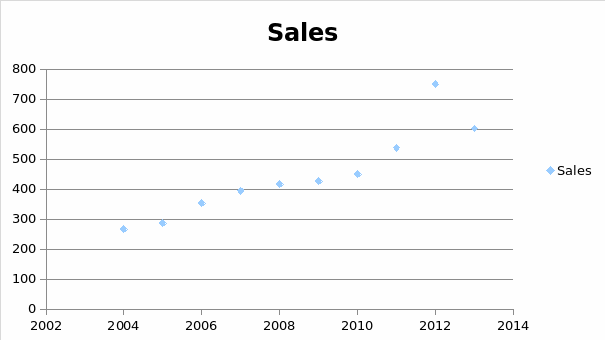
Globalisation and customer benefits are at the core of organisational strategies. Following the opening of the first branch in New York in the mid – 19th century, there was an established basis for global expansion of the business. The world forms the global market and products are designed to accommodate regional and local needs. Globalisation presents a major platform for the establishment of Faber-Castell as an international brand. Thinking global and acting on local results in the design of products ensures that customers benefit through being responsive to market needs. Customer feedback and perspectives are the points of focus in product design and development. It is the mission of Faber-Castell to enhance customer benefits through continuous product development and improvement trends while ensuring adequate differentiation to ensure that customers recognise the extra value in using the products.
Challenges Faced in the Digital Era
The digital era presents major challenges, mainly because of the conveniences people associate with technological advancements. Furthermore, the world is in a period of the rapid proliferation of personal computers and mobile devices that are acquired at relatively low costs. Personal computers are portable and are used for verbal and non-verbal communications, which pose challenges to Faber-Castell. Through palm computers, technological advancements seek to combine the computer and pencil technologies, which present major challenges to Faber-Castell (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1).
With many people embracing technology in their communications, the company may lose a significant share of the market. The loss of a market share would result in a decline in revenues and profitability with negative implications for employees and other organisational functions. Computers have tools and applications that enable students to draw, write and exercise their creativity, which take away a key market segment from the organisation. Using the pencil for calculations is no longer applicable, as technology led to the development of calculators. In view of the challenges brought by digitisation, the company has to embrace innovation and use it as a platform to develop creative products, especially in areas with limited impacts of digitisation (Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil 1).
Conclusion
The case study of Faber-Castell shows major competencies that saw the business grow from the time it was founded to the current years of market leadership in the industry. The core competencies discussed in this paper fall in the broad categories of competence and tradition, outstanding quality, innovation and creativity as well as environmental and social responsibility. The core competencies, especially innovation and creativity, contributed to the development of new ideas and products such as luxury pencils, which ensured the survival of the company. Such competencies support the development of solutions to the challenges of digitisation.
Through its traditional heritage, the company focuses its operations on experience to offer expertise for effective leadership, communication and distribution of products in the global market. Outstanding quality is fundamental in product differentiation, performance improvement and development of timeless designs. Responsible management of resources ensures satisfaction and support from stakeholders both in the internal and external environments.
Works Cited
Chamikutty, Preethi. Distribution one of the major challenges for brand, says von Faber Castell. 2011. Web.
“Company Report: Faber-Castell AG.” Hoovers. n.d. Web.
Faber-Castell. About Us. n.d. Web.
“Faber-Castell: The future of the pencil.” The Economist. 2010. Web.