Introduction
Planning of medical facilities and amenities calls for extra care and caution to ensure adherence to all the laid down procedures, regulations, and certification. This in turn ensures conduct of work within the budget limits and the stakeholders achieve their targeted goals.
The research paper examines an in-depth analysis of the creation of a medical care amenity, while examining the laid down regulations, all important parameters, and time required for finishing the project, the total cost of the project and the equipment needed in the project.
Concerning this, the equipments used in the medical field are highly regulated. They are under a high level of maintenance and safety than most of the machines and equipments found in the market. This is because there are those patients who respond very slowly or are unable to respond to hazardous conditions.
Some of the medical equipment in use today act as life support and their failure lead to loss of life. Before designing the phase of any equipment, it is important to understand its regulatory requirements and the certification required of it. This is advantageous in that it not only reduces the costs, but it also increases the safety of the product and the turn around time required for certification.
Regulatory requirements
The licensing regulations of each State lay down the specific design on the use of medical facility within its premises. These are the FGI guidelines used in the construction of and design of medical facilities Kunders (2004). The different states call for the use of codes in International Building.
In addition, the states get accreditation from the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare organizations Kunders (2004). The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) provides guidelines ensuring compliance with fire codes within the health facility.
This is to protect patients from fire outbreaks within the health centers. The guidance of fire safety within the facilities requires adherence to the standards contained in the NFPA 101 and NFPA 99.
Health facility must also follow the American Disability Act in order to protect the physically challenged patients. The facilities must also follow the OSHA regulations especially in the design of their laboratories. Medical facilities should be accessible to those seeking medical care. Therefore, they should have designs that enhance care to patients. This is especially in tall buildings, which should have lifts, and they should be accessible to people with disability.
The design of the medical facility should ensure that there are fire assembly points in case of fire outbreak within the premises. The design of the facility is environmental friendly to avoid polluting the environment. Patients’ experiences within a health facility are many and varied. To take good care and ensure wellbeing of patients, health facilities apply aesthetics that ensure comfort of the patient while in the facility.
Additionally, the medical facilities need to be sustainable and environmental friendly because they make use of a lot of human power, raw materials, water, and energy. Therefore, the designs must follow the laid down regulations.
Color and noise issues
It is important to choose the best color for the medical facility. The colors used in the medical facility aims at capturing, coordinating and calming the best mood and mental state of the patients and providing a serene environment for the patient so that they recover fast Kunders (2004). The ambiance provided by colors makes it fast for patients to recover.
When the colors are not calm, they interfere with the health and the recovery process of the patient. Therefore, they threaten the recovery process of the patient. There should be enough signboards in and around hospitals to ensure maximum silence Kunders (2004). There should be no hooting by cars in and around hospitals.
This ensures that noise is at minimum to enable patients have ample time for rest and sleep and this makes them feel secure. The privacy of the patient is very important, medical facilities should guarantee the patient’s privacy, and there should be no disclosure of private and confidential information of the patient without the consent of the patient Kunders (2004).
Equipment needed
Medical facilities across the board have similar health care equipment. The equipments in use in our medical facility are; trolleys, sinks, room dividers, heating and ventilation systems, lavatories, X-ray machines, wheel chairs and tables, laboratory kits, waste containers, examination beds, desks and chairs. The National Clearing House for Educational Facilities (NCHEF) provides for these lists of equipment (clark, 2009).
Electronic items needed
Medical facilities require electronic items to fasten the process of service delivery and to ensure that patients have the best care and diagnoses, and administration of best treatment. Electrically modified devices are the best to conform to the hospital safety standards.
The devices also assist patients in the recovery process. They include fans, electronic beds, computers, DVD players, play station, blood pressure monitors, ultrasound systems, emergency oxygen systems, and dental instruments among others (clark, 2009).
Budget planning and Cost estimates
Buildings in use require conversion to medical facility, which marks the start of budget planning. The budget should take care of materials, wages, transport, and architectural costs. Installation of medical equipments is after completion of the conversion process.
The role of stakeholders
The stakeholders of a medical facility are the community and inside stakeholders Tregunno (2004). People working in the facility such as doctors, nurses and cooks forms part of the inside stakeholder. Physicians ensure design of medical facilities in a way that not only promotes the wellbeing of the patient but also their own wellbeing.
Nurses require a facility that will enable them provide the best care to patients Kunders (2004). Doctors provide medical care and they prescribe medicine to patients. The community stakeholders ensure that there is enough supply of medicine, food, security and there is adherence to government policies.
The care personnel make sure the facility ensures maximum interaction between nurses and physicians. The facility should ensure outside stakeholders like emergency personnel have easy access to the facility to enhance patient care.
The outside stakeholders look forward to a facility that is responsive to their needs and a facility that does not harm them. The facility should meet the needs of the surrounding stakeholders Kunders (2004)
Gantt chart
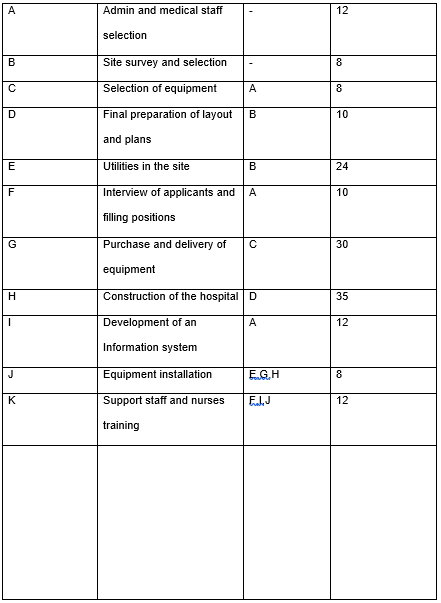
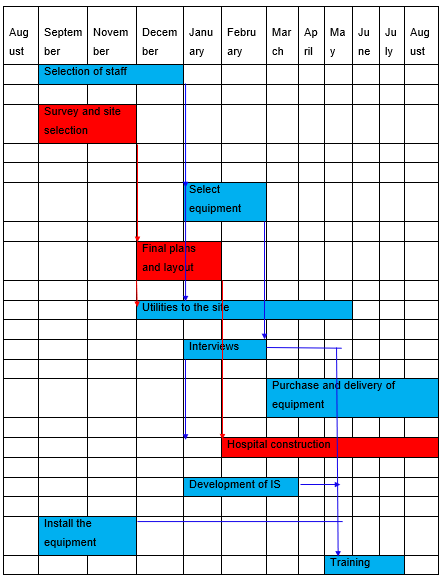
References
Clark, W. (2009). The Gantt chart:a working tool of management. London: Pitman. Web.
Kunders, G. (2004). Hospitals: Facilities Planning and Management. New York: Tata McGraw-Hill Education. Web.
Tregunno, D. (2004). Health, Nursing & Environmental Studies. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. Web.