Summary
The healthcare management system offers healthcare consumers a wide set of choices by providing life-enhancing treatments and enormous benefits. The system is continually working towards reforms that reduce costs, enhance quality, and increase consumer access to healthcare services. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines six key building blocks of a health system, including service delivery, health workforce, medical products, information, financing, stewardship, and vaccines and technologies (Kumar et al., 2022). These blocks outline the entirety of the healthcare system’s agenda, including its essential functions. Healthcare management systems in different countries collaborate with the WHO, utilizing various building blocks to enhance their performance and address the health needs of their populations.
The demand for health among individuals in both developed and developing countries remains high due to its role in facilitating and promoting happiness within a population. Health is one of the most essential components of human capital investment (Purnell et al., 2019). Both national and global healthcare institutions are investing heavily to promote quality of life and productivity. Despite these efforts, persistent deep inequalities in health status persist across countries, with developing countries reporting lower health outcomes than developed nations (Martin-Howard & Farmbry, 2020). Failing or inadequate healthcare systems have been a significant cause of these inequalities.
The WHO targets access to healthcare, a critical social determinant of health, aiming to enhance the timeliness and quality of healthcare. With the global rapid growth of aging populations, life expectancy has remained a critical metric of overall health quality. Studies have revealed links between life expectancy and various measures, including health expenditure, national gross domestic product (GDP), country status, population, and health-related variables, among others (Catillon et al., 2018; Hao et al., 2020; Sopina et al., 2021). This report aims to identify the factors that influence improvements in life expectancy in both developed and developing countries.
Problem Statement
International organizations continue to make significant efforts to address life expectancy disparities across countries. Data collected by various institutions indicate the importance of several socioeconomic and health factors as key determinants of life expectancy. Business analytics has excellent potential in deriving meaningful information from data concerning life expectancy and its determinants. Consequently, it improves the health quality of countries and enhances the productivity of the people. This report uses descriptive, predictive, and perspective analytics to provide insight into life expectancy improvement. The questions addressed by this report include:
- Does life expectancy differ by country status?
- Is GDP a factor influencing life expectancy?
- Is population related to life expectancy?
- Is health expenditure a factor influencing life expectancy?
Motivation
Business analytics is a growing field that continues to increase the significance of data by creating value in businesses, healthcare systems, and government organizations. Business analytics involves extensive use of data in both qualitative and quantitative analysis to address specific problems. Improved life expectancy is one of the major healthcare problems that business analytics can address.
An improvement in life expectancy indicates enhanced health and well-being of a population. It causes an increase in demand for healthcare services, creating new business opportunities for medical technology companies and healthcare providers. The longevity of a population translates to greater workforce participation and enhanced economic growth.
Enhanced life expectancy leads to increased consumer spending, benefiting a wide range of businesses. Promoting life expectancy reduces long-term health costs because healthier populations require less medical intervention. Global and national efforts by the business world towards improved life expectancy through initiatives that promote health and wellness demonstrate their commitment to corporate social responsibility.
Approach
The report employed several descriptive analytics to assess variations in life expectancy from 2000 to 2015 across different nations. Several variables, including average life expectancy, GDP, country status, and year, were of interest in the analytics. A line graph was used to analyze the trend in life expectancy over 15 years. The line graph was used to show the overall life expectancy pattern between the study periods. Graphs are essential descriptive analytics as they provide critical insights into patterns and trends by examining the data (El Morr et al., 2019).
Another descriptive analysis used was the clustered bar chart to visualize the changes in life expectancy between developed and developing countries over 15 years. Additionally, a pie chart showed the average life expectancy of the country’s population. Finally, a two-line graph showed the average GDP and life expectancy trend from 2000 to 2015.
A multiple linear regression model was used to predict changes in life expectancy. The predictor variables used in the model included GDP, percentage expenditure, and population. The model coefficient estimates showed the effect of each independent variable on life expectancy. The adjusted R-squared value explained how much variation in life expectancy was accounted for by the studied variables.
Prescriptive analytics employs data-driven decisions from descriptive and predictive analytics. At this stage, recommending the specific course of action is critical to improving health quality and enhancing business value. Economic, demographic, and healthcare factors were employed to provide significant insight into life expectancy.
Tools Used
MS Excel was used to generate the descriptive and predictive analytics. A dashboard created in Excel was used to present graphs generated in Descriptive. Descriptive analytics were presented in tables. The prescriptive analysis was derived from both descriptive and predictive analytics.
Analytics Analysis and Visualizations
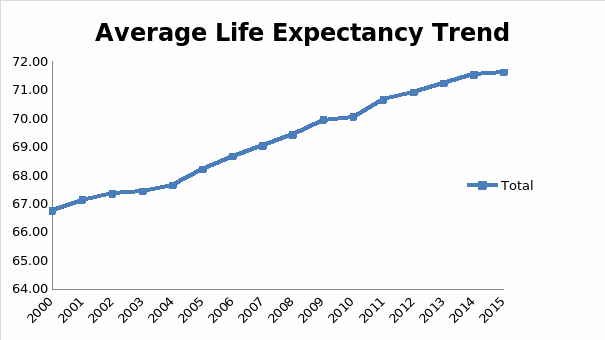
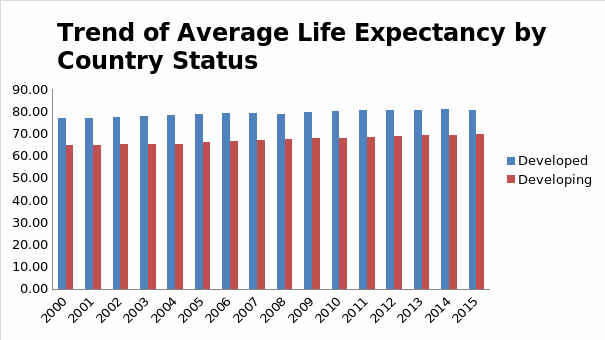
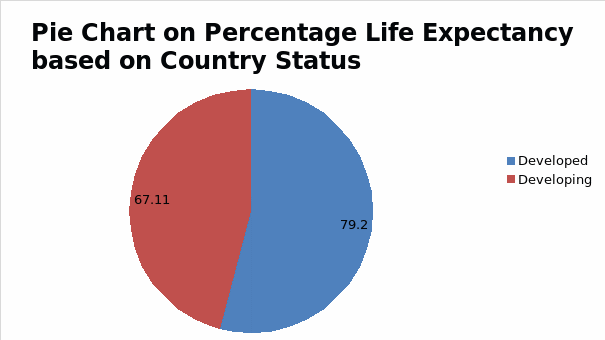
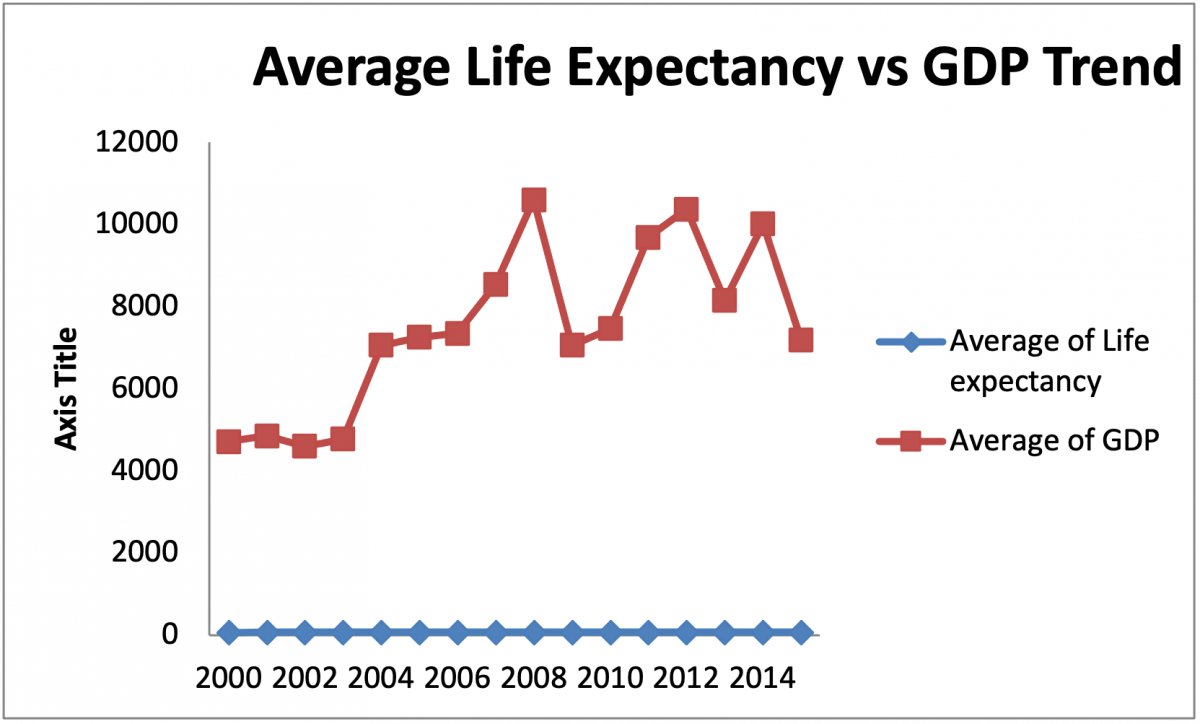
Table 1: Factors influencing Life Expectancy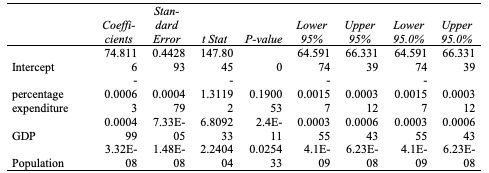
Analysis of Results
Results indicated an exponential growth in the average life expectancy between 2000 and 2015. This implies that a significant increase in life expectancy is recorded every year. However, developed countries, compared to developing countries, registered a higher average life expectancy for all 15 years, at 79.20 and 67.11, respectively.
Both countries showed a steady rise in average life expectancy for the period. Freeman et al. (2020) state that wealthier countries report higher average life expectancy than their poorer counterparts. The results indicated fluctuations in the average GDP between 2000 and 2015. There was no clear pattern in the changes in GDP, as the changes seemed random.
Holding all other factors constant, the average life expectancy from the data is 74.81 years. The life expectancy of 74.81 years is statistically significant at a 5% significance level. The average life expectancy in this report is slightly above the current life expectancy in 2023, which is 73.16 years (Macrotrends, 2023).
Health expenditures substantially reduce life expectancy. The results showed that a unit increase in expenditure on health as a percentage of GDP per capita results in a 0.00063 decline in life expectancy in years. The population has a significant impact on a country’s life expectancy.
Empirical evidence shows a conflicting relationship between several factors and life expectancy. Research by Bunyaminu et al. (2022) suggests that investing in the health sector has a minimal impact on enhancing health outcomes, such as life expectancy. A dollar increase in GDP per capita results in a 0.000499 unit increase in a person’s life expectancy. An improvement in a country’s GDP is associated with a significant increase in its life expectancy. The level of economic development is a critical determinant of the citizenry’s life expectancy.
Developing countries generally have lower life expectancies compared to developed countries. There is a significant disparity in life expectancy between developing and developed countries. The four variables used in the regression model explained 23% of the variation in life expectancy, with 77% variation remaining unexplained. According to Lelieveld et al. (2020), a wide range of factors affect a population’s life expectancy. The overall model was significant in predicting the influence of the four variables on life expectancy (F(3, 2934) = 59.49, p < 0.05).
Decisions Taken from the Results
Expenditure on health has a significant adverse effect on life expectancy; the healthcare management should direct its resources to other areas that promote the longevity of its population. Governments should strike a balance between healthcare spending and other critical areas to ensure improved health and increased life expectancy. Health expenditure per capita does not necessarily indicate efficiency in healthcare spending, as it does not directly improve life expectancy. Therefore, management should consider other expenditure metrics in decision-making, such as general government expenditure on health as a percentage of total government expenditure.
There is no clear cause-and-effect relationship between a country’s population and life expectancy. Decisions to improve life expectancy should focus on significant factors, excluding those such as population. Some of these important factors include a country’s GDP and its overall status. Governments should invest more in increasing GDP by encouraging foreign investment to ensure the country has access to new expertise and capital. Leaders should promote policies that enhance economic growth, such as investing in infrastructure and removing trade barriers, to help with GDP growth.
Developing countries should strive to narrow the significant development gap between them and their more developed counterparts, which have better access to economic opportunities, education, and healthcare. Developing countries should consider making resources and infrastructure available to support their health system. Most developed countries have robust healthcare systems that address any health inequalities. Governments in developing nations should prioritize improving the social determinants of health in their countries to contribute to longer and healthier lives. However, because of the complexity associated with development, developing countries should first understand their priorities and adopt sustainable strategies that prioritize their citizens’ health and life expectancy.
Value Derived from Results
The results enhance decision-making by providing valuable insights to inform effective choices on improved life expectancy. An improvement in life expectancy due to increased GDP has several benefits for businesses. Businesses in countries with high life expectancy and high GDP have larger market sizes to consume products and services sold.
With high GDP and improved life expectancy, people lead healthier lives and are more productive at work, resulting in greater productivity. High life expectancies imply an improved reputation for a country and thus, increased consumer trust. Countries need to invest significantly in their economic growth to promote life expectancy and long-term stability.
The results provide a basis for healthcare management to evaluate performance and hold organizations and individuals accountable for actions toward improving life expectancy. The results demonstrate the impact of several factors on life expectancy, increasing transparency, and enhancing resource allocation among management. Having identified non-significant factors and those significant in predicting improved life expectancy, resources are likely to be allocated more effectively. These results promote improved communication between stakeholders, valuable insights, and learning opportunities to support improvements in life expectancy.
Recommendations
Based on the business analytics conducted in this report, the following recommendations were made;
- Resources used to promote increased health expenditure should be redirected to a wide range of other areas rather than being used alone in healthcare to enhance life expectancy.
- Invest more in the country’s GDP to increase access to quality healthcare and promote improved life expectancy.
- Address the factors causing the significant socioeconomic disparity between developed and developing economies to enhance the implementation of policies that focus on economic development and, thus, promote greater population longevity.
Reference List
Bunyaminu, A. et al. (2022) ‘The effect of health expenditure on average life expectancy: does government effectiveness play a moderating role?’. International Journal of Health Governance, (ahead-of-print). Web.
Catillon, M., Cutler, D., & Getzen, T. (2018) ‘Two hundred years of health and medical care: the importance of medical care for life expectancy gains’. National Bureau of Economic Research. Web.
El Morr, C. et al. (2019) ‘Descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics’, Analytics in healthcare: a practical introduction, pp. 31-55. Web.
Freeman, T. et al. (2020) ‘Why do some countries do better or worse in life expectancy relative to income? An analysis of Brazil, Ethiopia, and the United States of America’, International journal for equity in health, 19(1), pp. 1-19. Web.
Hao, L. et al. (2020) ‘Adequate access to healthcare and added life expectancy among older adults in China’, BMC geriatrics, p.1-15. Web.
Kumar, S., Mangal, A., & Mangal, D. K. (2022) ‘Health policy and health system. in healthcare system management: methods and techniques’, Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, pp. 19-45. Web.
Macrotrends (2023). World life expectancy 1950-2023. Web.
Martin‐Howard, S., & Farmbry, K. (2020) ‘Framing a needed discourse on health disparities and social inequities: drawing lessons from a pandemic,’ Public Administration Review, p. 839-844. Web.
Purnell, L. D. et al. (2019) ‘Transcultural diversity and health care’, Handbook for culturally competent care, pp.1-6. Web.
Sopina, E., Toffolutti, V., & Lenart, A. (2021) ‘Health care system efficiency and life expectancy: A 140-country study’, Web.