Introduction
In today’s society, the role that financial management plays in all facets of life cannot be overstated. Man’s ability to plan for the present and future is purely based on the basic fundamentals and methodologies applied when managing their finances. As such, financial management in whatever capacity is the key determinant to the success or failure of any proposed venture or activity.
In the business world, financial management is divided into various capacities all of which contributes to the smooth running and success of the business. However, due to the dynamicity and rapid change in interactions, technology and overall development, there has emerged various factors that subject the management system adopted to change.
Such factors include but are not limited to politics, the environment, society, culture and technology among others. This paper shall discuss the Federal Reserve System adopted by America in 1931 as a key concept in the development and survival of the nation’s economical well being. It shall focus on the structure, board of governors and the federal open market committee as the major factors that influences the financial decisions made by financial institutions as relating to global competition, investments and market share.
Also the roles of the Federal Reserve under different circumstances shall also be mentioned and their effects on the economic growth highlighted. An analysis of the various sectors which have over the years been affected by the presence of the Federal Reserve shall be carried out in a bid to further provide insight as to the importance of such a system to the financial stability of any given nation.
Brief Summary of the Federal Reserve
According to Wells (2004), the Federal Reserve was established in 1931 soon after the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act. Its establishment was mostly influenced by a series of financial mishaps and irregularities that were experienced in America (financial panic of 1907 among others).
Since then, the Federal Reserve has continually expanded and changed over the year. Much of the change experienced has been due to the diverse nature of the economy, industrialization/development, financial crisis (great depression) among others. The expansion on the other hand refers to the structural changes and the number of functions that the Federal Reserve has. Today, the Federal Reserve is chaired by Ben Bernanke and its headquarters is located in Washington DC.
Structure of the Federal Reserve
As per the Federal Reserve website (federalreserve.gov, 2010), the Federal Reserve is made up of five very important parts. These five segments all play an important role in the coordination, control and management of financial assets in the United States.
They include; the board of governors, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), twelve federal reserve banks that are privately owned and located in major cities, other banks with non transferable stocks in their regional federal banks and finally, a number of councils which partake an advisory role. However, it should be noted that the federal banks that are involved with the Federal Reserve are strategically located such that they divide the nation into twelve federal districts.
The board of governors
Through out their existence, organizations and businesses are considerably pressured to raise their levels of performance and productivity. This is especially so in the modern day business environment which is characterized by aggression and excessive competition thereby constantly forcing businesses to exhibit innovation and enhanced performance so as to remain relevant and profitable in the ever increasingly competitive arena.
To achieve the organizational goals of increased productivity, the input of both the individual and groups in the organization remains invaluable. However, for these inputs to make optimal impact there must be a strong leadership to steer the individual and group effort in the right direction. This being the case, the presence of a board of governors is indeed necessary for the survival and continued success of the Federal Reserve.
According to Longley (2008), the president is responsible for the appointments of the seven members who constitute to the board of governors of the Federal Reserve System. The selected board is tasked with the duty of overseeing the system’s operations.
This means that they are in charge of controlling the activities of the twelve selected federal banks, the advisory committees and the numerous member banks spread across the United States. Simply put, the board of governors of the Federal Reserve plays a pivotal role in the monetary policies adopted in the United States and also controls the amount of money in circulation within the United States economy (Grey, 2002).
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
An article posted on the InvestorWords website (2010) defines FOMC as a committee comprising of twelve members which is responsible for controlling and dictating the credit and interest rate policies utilized by the Federal Reserve System. It dictates these rates to member banks in two main ways. It can influence these rates directly by changing the discount rates or indirectly by buying or selling government securities (open market operations).
Functions of the Federal Reserve
According to Longley (2008), the functions of the Federal Reserve are classified into four main categories. Firstly, it is responsible for formulating the nation’s monetary policies. It does this by influencing the financial and credit atmosphere within the economy by monitoring and balancing the employment rates, prices and the interest rates offered on long-term loans. The graph below represents the interest rates at the beginning of the year (Jan) on the federal fund target since the year 2000.
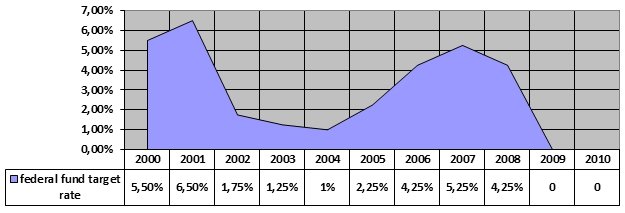
Secondly, the Federal Reserve oversees the operations of banking institutions through regulatory measures which are implemented to ensure ethical and efficient banking systems as well as protecting consumer’s credit rights within the economy. Thirdly, it ensures that the financial system adopted is stable by managing risks and eventualities that may crop up in the economy due to systemic errors. Lastly, it acts as the main bank for the government, depository institutions and foreign financial institutions by offering financial services.
Conclusion
This paper set out to explore the various aspects that constitute to the Federal Reserve System. To this end, the paper has highlighted the structure, functions and importance of this entity to the American economy. The study has subsequently articulated how these aspects impact on the success and survival of the US economy. It has been seen that the adoption of this system in the economy will yield to higher productivity which will subsequently result in the attainment of the nation’s goals of increased productivity and financial stability.
From the discussions forwarded in this paper, it has been noted that a lack of such a system can lead to a total collapse of the economy leading to uncontrollable side effects. It can therefore be authoritatively stated that the Federal Reserve System is imperative for the increased profitability and indeed the future survival of the economy as it gives the nation a means by which to competitively deal with the market forces that may threaten it
References
Grey, G. B. (2002). Federal Reserve System: background, analyses and bibliography. USA: Nova Publishers.
InvestorWords. (2010). Federal Open Market Committee. Web.
Longley, R. (2008). The Federal Reserve System: History, Function & Organization. Web.
The Federal Reserve Board. (2010). The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. Web.
Wells, D. R. (2004). The Federal Reserve System: a history. USA: McFarland.