Summary of the Company (FedEx)
FedEx was established in 1971 in Little Rock, Arkansas (FedEx Corporation 1). Today, FedEx is a global corporation in the transportation and logistics industry. The sector has evolved as businesses strive to create new products and services to meet the diverse demands of their customers. As such, the industry is now characterized by transportation and logistics, e-commerce, and business services worldwide. It is highly competitive with intense competition emanating from both global actors and well established local players and peers. FedEx generally faces competition from TNT Express N.V, United Parcel Service Inc., Deutsche Post DHL Group, Expeditors International of Washington Inc., XPO Logistics Inc., Royal Mail PLC, and Aramex among other global competitors and peers.
FedEx offers a wide range of solutions products and services for millions of its customers globally. The company delivers nearly 3.5 million packages every day to over 220 countries and territories from its 1,800 FedEx Office shops spread across the world. FedEx focuses on common sales, marketing, revenue management, customer service, and information technology support for revenue generation and profitability. The company has created different business segments including, FedEx Express, FedEx Ground, FedEx Office, FedEx Freight, FedEx Custom Critical, FedEx Trade Networks, FedEx Cross Border, and FedEx Supply Chain.
The financial reports for FedEx cover the year 2015 and 2014 for comparison. The company has realized increased revenues, increased total costs, but a decline in profitability between the fiscal year 2014 and 2015. This variation could be perhaps linked to increased costs.
These strong financial results have made FedEx the most successful firm in the sector.
Countries in which FedEx does Business
Countries in which FedEx does Business are spread across the world. The company asserts that it does business across 220 countries and territories through its 1,800 FedEx Office shops. These countries and territories are served by a global network managed by the company. They include the U.S; Canada; Asia Pacific (APAC); Europe; the Middle East, Indian Subcontinent and Africa (MEISA); and Latin America, Caribbean (LAC).
It is imperative to note that FedEx can now be found almost in any country globally. As such, the company has focused on geographical segmentation for ease of performance assessment.
Percentages of Overseas Earnings, Costs, and Profits
As shown in the table below, FedEx has consistently reported its financial performances on the US and international operations. The US is the major market of FedEx, outdoing all other regions by far superior margins over the years (FedEx Corporation 43).
Core costs
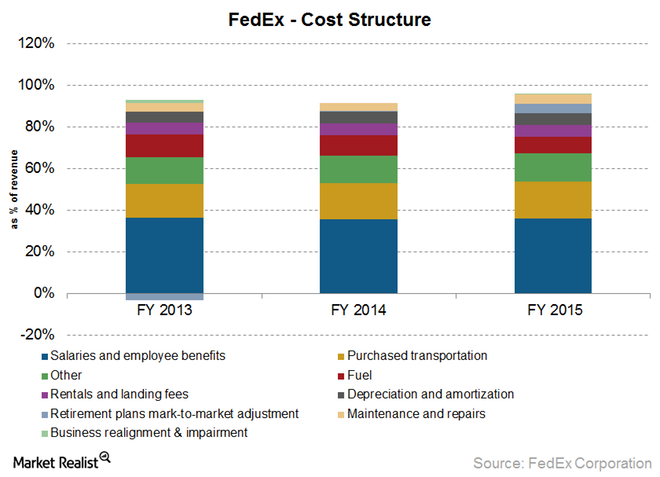
FedEx is grappling with huge fixed costs. For instance, the company earned $ 47,453 million in the fiscal year 2015 and incurred costs amounting to $ 45,586 million, leaving it with an extremely small profit margin.
It is noted that FedEx was hardly hit by the 2009 global financial crisis (Schmidt 1). There were notable declines in revenues and net incomes. The business model runs on high costs operations. As such, any external forces negatively impact the company’s earnings and profits. However, the company has attempted to react by cost reduction measures, lean operations, and sustained investment and acquisition. Consequently, it is now stronger relative to competitors.
From the figure above, FedEx has continued to spend more financial resources on salaries and employee benefits, which account for about 36 percent of the total revenues. Moreover, during the fiscal year 2015, the company spent an additional six percent salaries relative to the previous year. FedEx has also noted an increase in costs associated with purchase transportation because of growth in volumes, increased usage of third party transport service providers, and global expansion of operations. During the fiscal year 2014, the company spent an additional 10% on purchased transportation and a further six percent in the subsequent fiscal year 2015. However, given the global drop in oil and gas prices, the company noted a reduction in cost by 18% on jet and vehicle fuel costs.
During the fiscal year 2015, FedEx realized increased costs associated with mark-to-market pension. The company had to spend about $ 2,190 million on retirement plans associated with mark-to-market (Schmidt 1).
One major obstacle for analysts of FedEx financial performance is that the company does not provide a detailed performance for country or region-specific. As mentioned, FedEx serves 220 countries and territories. However, there are no specific financial data provided by the company related to country earnings, costs, and profits. Thus, country reports are not available for comparison. Nevertheless, FedEx provides figures for international intra-country operations as consolidated totals by business segments. Prominently, the US and international fiscal performance feature in the reports.
The company generally focuses on its different business segments previously mentioned to report performances.
Global Challenges and Opportunities
Multinational businesses irrespective of the industry face both global Challenges and opportunities. Some of these aspects of global operations present both opportunities and challenges for FedEx. For instance, the company must deal with intense competition from its peers and other local, small firms found all over the world. Factors related to interest rates and foreign currencies affect FedEx revenues, costs, and earnings because its business is based on dollars.
Moreover, the company must face changes related to the state of the economy across different countries and territories. In such instances, growth in economies presents favorable opportunities while declines in economies slow down the business. In the recent past, the company recorded significant cost-savings associated with low commodity prices (jet and vehicle fuel). It realized these savings after the global prices of oil and gas dropped to unprecedented levels.
Further, FedEx has to deal with various labor laws and regulations found in over 220 countries and territories. These laws and regulations rarely present any favorable conditions for operations. While the company has been successfully leveraging its IT resources, any disruptions can significantly hamper operations. Besides, country business laws and regulations related to ownership and renewal of licenses could be costly.
Customer preferences and habits generally differ across the globe based on various cultures. On this note, FedEx must always strive to meet different expectations of customers based on cultural variations. Current environmental changes have significantly affected packaging practices. Moreover, global aviation and other transportation regulations continue to influence FedEx in a way that increases the costs of compliance. Terrorists have also become bolder and now target transport systems and networks. As such, FedEx strives to control such threats through its safety measures.
While the company operates in more than 200 countries, China is extremely important for the company because of its uniqueness in terms of culture, growth, and work practices. Hence, diversity management is vital for the company. Besides, the Asia-Pacific region offers massive market opportunities for expansion (Chao 1).
A Country that would present the Most Management Challenges
The Chinese market offers a competitive landscape specifically from several strong local firms. Those companies have emerged and grown in the local market. They understand Chinese culture with established strong relations in local communities. Besides, all efforts are directed toward the success of local firms. Hence, the domestic market is tough for foreign firms (Nelson 1).
China’s geography also presents management challenges to FedEx because of its size and market complexity. While China is generally large relative to the US in terms of size and population, its population of more than one billion people is mainly concentrated in small regions. The company currently experiences the challenge of capacity related to a lack of slot at the transportation hubs, road and railways congestions, and others. Moreover, these facilities are not well developed in regions outside major Chinese cities. Hence, local delivery is extremely difficult.
Variations in habits and preferences related to business practices are also noted. For instance, FedEx must adhere to local regulations of trucking, which is majorly local. This implies that the company cannot develop and operate nationally without challenges. Moreover, it is observed that the country is made up of a collection of regional distinct markets, but not a single national market.
Infrastructure presents critical management issues to the company. While physical infrastructure continues to a major hurdle for nationwide operations, regulatory structures are equally impeding business activities. China continues to implement some restrictive regulations, specifically for foreign firms. Consequently, it remains difficult to create a competitive landscape with multiple barriers that restrict physical, customer, partner, and supplier access (Birla 13). Only the elimination of these barriers in trade and market will create favorable market conditions.
FedEx suffered a setback because of the inability to replicate the “hub and spokes” distribution model, which is extremely successful in the US. In the US, the company had developed a system in which service delivery was managed through a model linked to the central hub. While the company has successfully executed the model in other international markets, China is a different market. It is observed that the Chinese current airports cannot be used to implement the ‘spoke’ for the local market.
The country has a low density at airports. The country has about 1.6 airports for about 100,000 km sq. (Nelson 1). Also, most of these facilities are not optimally used. As a result, the company has experienced airspace challenges and issues associated with developing and running regional air operations for local markets. These issues are associated with critical unwanted airport downtimes. Hence, the company’s airfreight segment will not be optimal in operations and service delivery. Nevertheless, FedEx continues to work closely with various government agencies to address major obstacles and exploit available market opportunities.
Conclusion
Domestic market and international market performances significantly differ for FedEx.
Works Cited
Birla, Madan. FedEx Delivers: How the World’s Leading Shipping Company Keeps Innovating and Outperforming the Competition. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. Print.
Chao, Loretta. “FedEx to Expand E-Commerce Reach in China, Japan.” Wall Street Journal. 2016. Web.
FedEx Corporation. FedEx 2015 Annual Report. 2015. Web.
—. About FedEx. 2016. Web.
Nelson, Christina. “FedEx Delivers in China.” China Business Review. 2012. Web.
Schmidt, Ally. What Are FedEx’s Major Costs? 2015. Web.