Introduction
From the study and the financial data, Capstan Autos is dealing with serious financial difficulties. Potential financial hardship is portrayed by the rapid increases in the debt-to-equity and debt-to-asset ratios, as well as the variation in the interest coverage ratio (Melan et al., 2023).
The Company’s primary problem came when it started offering free credit for six months. Considering the declining revenues, this was an essential action to increase sales. However, the credit duration was excessively long, which made receivables accumulate (Zymovets, 2019). Due to the Company’s inability to pay its receivables, there is a significant liquidity issue. According to the presented summary of the balance sheet, the receivables increased from 0 at the end of Q3 2012 to $10,500 by Q1 2013. Growing accounts receivable indicate a lack of liquidity in the organization, suggesting that sales have yet to be turned into cash.
Additionally, there is a chance that the Company would accrue large quantities of bad debts, which might reduce its earnings. The bank loan amount has grown from $230 in 2012 to $9731 in 2013. The outcome has been a significant interest load for the business. According to the income statement, interest expenditure increased from $4,000 to $178,000. This is even though the EBIT increased from $220,000 in 2018 to $320,000 in 2013. As a result, net earnings decreased from $140,000 to $92,000.
Justification for the Bank’s Decision to Withhold Further Credit
The bank’s decision to refuse to offer further loans is reasonable. The provided financial analysis offers support for this decision using several indicators. The Interest Coverage Ratio dropped sharply from 55 (EBIT/Interest) in 2012 to 1.79 in 2013. This decline implies that for the Company to cover interest expenses, there must be greater Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) (Raimo et al., 2021). A ratio of 1.79 suggests that the Company is struggling to make its interest payments. Banks would be exposed to non-performing assets (NPAs) if credit was extended since the Company would find it challenging to repay its existing debt and any new loans.
The debt-to-equity ratio is another factor that backs the bank’s denying extra loans. It increased from 0.15 at the end of the third quarter of 2012 to 0.17 at the end of the first quarter of 2013. This better-than-average ratio shows that the Company is heavily leveraged and indebted to finance its operations. Given the Company’s high debt levels, additional funding would raise its financial risk, making it a risky decision for the banks.
Reasons for Capstan’s Rising Indebtedness Despite Higher Profits
Several factors might be responsible for Capstan’s increasing debt despite higher revenues. Although the Company has increased its income, it has also significantly increased its debt. The rise in debt has caused higher interest rates. Despite the revenue growth, there has been a commensurate increase in the interest cost. Moreover, the Company’s growing revenues need to be more significant to balance the higher interest costs brought on by its growing debt load. As a result, the Company’s debt load increases, indicating that many increased revenues are used to settle the higher interest rates rather than to lower debt.
Problem Definition
The presented financial analysis poses a problem as it depicts a considerable growth in the Company’s debt-to-asset ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and interest coverage ratio throughout the chosen years. Between 2012 and 2013, the Debt/Equity Ratio—which measures the Company’s reliance on debt financing concerning shareholders’ equity—rose significantly, from 0.15 in the third quarter to 4.73 in the first. This steep increase raises the likelihood of financial instability by pointing to a potentially hazardous reliance on debt as a source of support.
Similarly, the Debt/Asset Ratio, which indicates the proportion of assets funded by debt, increased from 0.04 to 0.57 during the same time, indicating a notable increase in debt relative to total assets. This points to a too-broad financial structure that might jeopardize the organization’s capacity to maintain a stable financial position. Furthermore, the fact that the Interest Coverage Ratio fluctuates raises concerns. In the first quarter of 2013, the ratio dropped to zero, meaning the Company’s earnings were not high enough to cover its interest expenses. It remained low despite increasing in the following quarters, casting doubt on the Company’s ability to settle its debt.
The primary issues facing the Company are its mounting debt burdens and its inability to turn a profit large enough to cover its interest expenses. This challenge might have several root reasons, such as inadequate management, declining profitability, or rising interest rates. Protecting the long-term profitability and financial health of the Company requires identifying and addressing the precise causes of these financial imbalances (Skocdopole, 2021). Therefore, the real issues that need to be addressed are the Company’s highly leveraged financial situation and ability to make a profit to pay its obligations.
Alternative Solutions
Debt Restructuring
Lower interest rates and longer payback terms are two possible strengths of restructuring the Company’s debt, which would lessen the burden of interest costs. Nevertheless, there are drawbacks to this strategy because it frequently entails complex talks with creditors, which may result in extra expenses and obligations. The Company’s creditworthiness determines whether debt restructuring is feasible; it is often a good idea when the credit rating is high. Thoughtful assessment and preparation are necessary when contemplating this approach to financial difficulties.
Increase Sales and Profitability
Prioritizing growth in sales and profitability offers significant benefits, as it may yield the extra cash flow required to cover interest costs and lower debt. This project has difficulties, in any case, because it can be challenging to achieve notable increases in sales and profitability, especially in a market that is very competitive and may take patience and persistent work. The competitive environment and market dynamics might make it difficult to see results quickly, so the firm has to plan carefully and consistently in order to see significant financial gain.
Cost Reduction Measures
By lowering operational costs and streamlining manufacturing procedures, cost-cutting strategies can boost profitability while freeing up funds for debt repayment. Nevertheless, these cost-cutting measures could lower staff morale and jeopardize the caliber of the goods or services. To ensure that the Company’s financial health is not attained at the price of customer happiness and staff engagement, it is imperative to balance cost reductions and preserving employee motivation and product/service quality.
Effective Solutions
It is crucial to offer a practical solution to the primary challenges in the prior research, especially in light of Capstan Autos’ significant financial struggles. While there are several reasons for the Company’s issues, its highly leveraged financial structure is the primary cause, as seen by the steep increase in the Debt/Equity Ratio and growing interest expenses. Using a range of strategies, including debt restructuring, cost-cutting measures, and a focus on increasing sales and profitability, is the best approach to deal with this.
Debt Restructuring
Capstan must take the crucial initial step of debt restructuring. The debt-to-equity ratio of the Company rose sharply from 0.15 in 2012 to 4.73 in 2013. This sudden increase highlights the Company’s high reliance on debt financing, which adds to its precarious financial position. Restructuring the existing debt can mitigate the challenge. It can include negotiating with creditors for better terms, including longer payback durations or cheaper interest rates.
Securing more favorable financing conditions might result in lower interest expenses, which will ultimately decrease the financial strain on the Company (Acker et al., 2020). With greater flexibility, Capstan Autos may allocate resources more effectively to operations, investments, and debt repayment. The Company’s debt should be redistributed to ensure it can pay off its present debt without financial troubles.
Cost Reduction Measures
Restructuring the debt must be combined with cost-cutting initiatives. The Company has to look closely at its operating expenses and optimize its manufacturing processes to increase efficiency. Reducing wasteful spending can free up funds that can be utilized to settle debt. Reducing expenses may entail assessing employee productivity, reducing overhead, and streamlining the supply chain. Capstan Autos needs to strike a balance while implementing these security measures so as not to compromise the quality of its products or services. By effectively carrying out cost-cutting measures, the Company may boost profitability and fortify its financial stability.
Increasing Sales and Profitability
Increasing sales and profitability is a crucial goal for Capstan Autos. According to the report, despite the Company’s best attempts to increase sales, it still requires assistance paying mounting interest charges. To solve this problem, the Company should focus on expanding into new customer categories, enhancing its product offerings, and strengthening its market presence. Among the strategies that might increase profitability are forging strategic relationships, venturing into uncharted territory, and introducing advanced product lines (Joshi et al., 2020). By improving sales and profitability, Capstan Autos could produce more significant cash flow, making it easier for the Company to pay its interest expenses and minimize its reliance on debt.
Monitoring and Control
Capstan Autos must put up a strict monitoring and control system to ensure that these recommended solutions are implemented. Tracking progress and making any plan modifications requires regular financial evaluations and monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs). Within the Company, openness and effective communication are also essential (Li et al., 2021). Employees should be informed about the Company’s financial situation and eager to participate in activities to boost revenue and moderate costs.
Restructuring the debt, increasing sales and profitability, and implementing cost-cutting measures are generally the best ways to address Capstan Autos’ financial issues. The Company can stabilize its financial position by lowering its immediate interest expenditure burden through debt restructuring. Putting cost-cutting measures into action boosts revenue and frees up money for debt payments. By increasing sales and profitability, the Company may generate the necessary cash flow to pay down its obligations.
Conclusion and Circumvention of Potential Problems
As the Company’s case analysis illustrates, Capstan Autos is facing a severe financial crisis due to its highly leveraged position and growing interest expenses. The Debt/Equity Ratio grew dramatically from 0.15 in 2012 to 4.73 in 2013, indicating a risky reliance on debt. The dramatic rise in interest expenses impacts net earnings. To effectively handle these issues, a comprehensive plan that incorporates cost-cutting measures, debt restructuring, and raising sales and profitability is suggested.
Even if the recommended repairs offer a means of financial recovery, problems and difficulties can arise. The first is change aversion, which happens when employees and supervisors disagree on changes that must be made in order to decrease costs or implement the latest strategies. In order to solve this, effective communication and employee involvement are essential. Establish training and reward programs to ensure a commitment to change.
Barriers to expanding sales and profitability include market circumstances, competitive pressures, and unanticipated economic downturns. A backup plan should include diversification strategies and ongoing market research to adapt to changing conditions. The last consideration is how well or poorly new product lines or geographical market receives expansions. Pilot studies and market research should be part of a contingency plan before new techniques are applied widely.
References
Acker, K., Bräutigam, D., & Huang, Y. (2020). Debt relief with Chinese characteristics. Social Science Research Network, 39. Web.
Joshi, S. K., Singh, R., & Sharma, M. (2020). Sustainable agri-food supply chain practices: Few empirical evidence from a developing economy. Global Business Review, 24(3), 451–474. Web.
Li, J., Sun, R., Tao, W., & Lee, Y. (2021). Employee coping with organizational change in the face of a pandemic: The role of transparent internal communication. Public Relations Review, 47(1). Web.
Melan, M. F., Lisetyati, E., & Safriliana, R. (2023). Ratio analysis of financials and stock price of heavy construction and civil engineering companies. Journal of Research on Business and Tourism, 3(1), 44-54. Web.
Raimo, N., Caragnano, A., Zito, M., Vitolla, F., & Mariani, M. (2021). Extending the benefits of ESG disclosure: The effect on the cost of debt financing. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 28(4), 1412–1421. Web.
Skocdopole, P. (2021). Financial analysis as a basis for creation of the financial plan of the selected business entity – case study. SHS Web of Conferences, 92. Web.
Zymovets, V. (2019). The excessive receivables of the enterprises: causes and consequences for the financial system of Ukraine. Economy and Forecasting, 5–18. Web.
Appendix
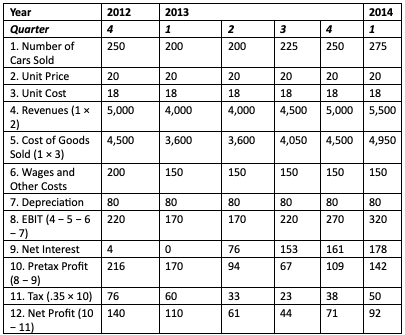
Note: All figures except unit sales in thousands of dollars.
Table 2 – Summary Balance Sheets.
Note: Figures in thousands of dollars.
Now, to understand if the Company was really in trouble, specific ratios are calculated as follows:
Debt/equity ratio = bank loan/shareholder’s equity
For 2012, Quarter 3:
Debt/Equity Ratio = 230 / 1,540 = 0.15
For 2013, Quarter 1:
Debt/Equity Ratio = 9,731 / 2,059 = 4.73
Debt asset ratio = bank loan/assets
For 2012, Quarter 3:
Debt/Asset Ratio = 230 / 6,270 = 0.04
For 2013, Quarter 1:
Debt/Asset Ratio = 9,731 / 17,190 = 0.57
Interest coverage ratio = EBIT/Interest
For 2012, Quarter 3:
Interest Coverage Ratio = 220 / 4 = 55
For 2013, Quarter 1:
Interest Coverage Ratio = 170 / 0 = 0 (as there is no interest expense in this quarter)
For 2013, Quarter 2:
Interest Coverage Ratio = 170 / 76 = 2.24
For 2013, Quarter 3:
Interest Coverage Ratio = 220 / 153 = 1.44
For 2013, Quarter 4:
Interest Coverage Ratio = 270 / 161 = 1.68
For 2014, Quarter 1:
Interest Coverage Ratio = 320 / 178 = 1.79
Table 3 – Debt Equity and Debt Assets Ratio.
Table 4 – Interest Coverage Ratio.