Introduction
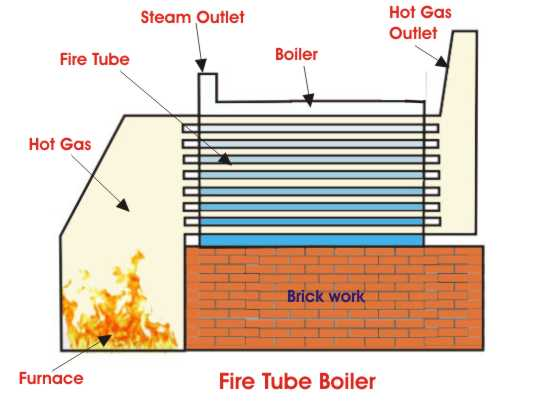
Boilers are mainly classified based on their mode of operation. One of the most common types of boilers is the fire tube boiler. This boiler operates by passing hot gases through tubes that run from the water inlet. The tubes pass through a container filled with water that is heated by heat from the gases. The boiler operates through many processes. For example, thermal conduction is the process through which the heat of the gases is absorbed by the water in the tank. The heat is used to produce steam from the water. The fire tube boiler is one of the four main types of boilers. Other types of boilers include the low-pressure tank boiler and the flued boiler. The boiler comprises pipes, a tank of water, and a source of fire. The fire tube boiler was very common during the 18th century (Electrical Engineering par1). However, its popularity waned as more advanced boilers emerged.
How it operates
Hot gases are passed through pipes that run through a tank of water. The tank is inside the boiler. As these gases pass through the fire pipes, heat is absorbed and then used to raise the temperature of the water until it evaporates. As the water absorbs more heat, its temperature rises to a point that it turns into steam (Heselton 274). The buildup of steam in the steam vessel increases the amount of pressure thus raising the boiling point of water. An increase in the boiling point of water reduces the amount of steam produced because water takes longer to boil and produce steam (Heselton 274). The steam is then stored in the vessel after which it is released for the intended purpose. The steam is released through an outlet on the vessel. After the steam is released, more water is added to the boiler through a water inlet. The boiler does not produce high-pressure steam because the steam and water are stored together. The boiler should be constructed professionally because it can cause serious accidents in case it explodes due to pressure buildup.
Advantages of fire tube boiler
The fire tube boiler has several advantages. First, it is cheaper than other types of boilers such as the water tube boiler (Electrical Engineering par4). Secondly, it is compact because it has distinct parts that are assembled together to make up the boiler. These parts include the furnace, pipes, fire tubes, and steam and hot gases outlets. The fire tube boiler is not as complex as other types of boilers. Therefore, it is easy to operate and maintain. On the other hand, its ease of use means that it can be used by both small scale and large-scale industries. The boiler is safer than other types because the supply of water and transfer of gases is executed separately. Water is fed to the boiler through a shell and outside tubes while gases are carried trough the water tank by fire tubes. Finally, it is easy to control steam fluctuations by regulating the amount of water that flows through the fire tubes. If more steam is needed, more water is fed into the boiler and vice versa.
Disadvantages of the fire tube boiler
The boiler requires high amounts of water to generate the requisite amount of steam. Therefore, it takes some time for the pressure to build up to levels that can be used to execute certain operations. In addition, there is limited production of steam. As mentioned earlier, water and steam are stored in the same vessel. This prevents the production of high-pressure steam unless the two are stored in different vessels. On the other hand, the steam that is released from the boiler is wet because it is stored together with water. The boiler is inefficient with regard to heat transfer. The heat exchanger uses the process of thermal conduction instead of the more efficient process of thermal radiation. Finally, the boiler is a health hazard because it can explode due to pressure buildup in the steam vessel.
Types
There are many types of fire tube boiler. They include Cornish boiler, Lancashire boiler, Scotch marine boiler, Locomotive boiler, vertical fire tub boiler, horizontal return tubular boiler, admiralty-type direct tube boiler, and the immersion fired boiler (Heselton 76). The Cornish boiler was initially developed as a low-pressure boiler. However, the use of a cylindrical boiler shell improved the operation of the boiler and thus enabled it to produce high-pressure steam. The Lancashire boiler possesses two flues that act as the furnaces.

The Scotch marine boiler has a large heating surface because it comprises many small-diameter tubes (Heselton 275). The locomotive boiler comprises three main parts: a firebox, a boiler barrel, and a smoke box. These types of coilers are used in steamrollers, portable engines, and traction engines. The horizontal return tubular boiler is characterized by a horizontal cylindrical shell that holds flue tubes. The furnace is located below the cylindrical shell. The admiralty-type direct tube boiler was common among the Britons. This type of boiler is uncommon because of the unequal expansion of certain boiler parts. This phenomenon reduces the life of the boiler.
Variations
A water tube boiler has three main variations that include water tubes, reverse flame, and package boiler. Fire tube boilers are sometimes fitted with water tubes in order to increase surface area for more heating. Other boilers have internal rifling that is found inside the fire tubes. Modern fire tube boilers use the reverse flame design. This design reduces the need for many fire tubes to transport gases. These variations usually affect how a boiler operates with regard to the pressure of steam generated and its efficiency in heat conservation.
Conclusion
The most common types of boilers include the flued boiler and the fire tube boiler. Each of these boilers has a unique method of operation. The fire tube boiler operates by absorbing heat from hot gases and using it to raise the temperature of water until it evaporates. Heat is passed to the water through the process of thermal conduction. This process renders the boiler less efficient with regard to heat efficiency. Types of fire tube boilers include the Cornish boiler, Lancashire boiler, Scotch marine boiler, Locomotive boiler, vertical fire tube boiler, horizontal return tubular boiler, admiralty-type direct tube boiler, and the immersion fired boiler. The advantages of the boiler include ease of operation and maintenance, cheaper, and safer compared to other types. It has disadvantages too that include high risk of explosions due to pressure buildups, production of low-pressure gas, and limited production of steam. The fire tube boiler has three main variations that include water tubes, reverse flame, and package boiler.
Works Cited
Electrical Engineering: Fire tube Boiler: Operation and Types of Fire Tube Boiler. N.d. Web.
Heselton, Kenneth. Boilers Operator’s Handbook. New York: The Fairmont Press, 2005. Print.