This treatise looks at various aspects of a strategic plan for a four star hotel. First, it compares several marketing niche planning strategies using the competing values framework.
Secondly, it discusses key factors that will be critical in the hotel’s performance in short and long term to best ensures it supports the strategic goals. Third it proposes an audience strategy use when preparing to reorganize facilities and financials. Finally, recommendations for technology tools that can be used in the planning are discussed.
In planning strategy, culture defines all aspects of a business, both internal and external relationships. First, the management should consider having intranet for the new hotel. This is a secured internal or private network of an organization that connects all computers to ingress that access the internet.
An intranet is restricted to an organization and its associates (customers, employees, members and suppliers among others) and is protected from unauthorized access with security systems and firewalls. Such security encryption put a stop to abuses of the system like social networking, inapt use of web, among others. As a result, the costs of operation will be minimised (Slack, Chambers, Johnston, & Betts, 2005).
The first dimension places the values of “flexibility, discretion, and dynamism at one end of the scale while stability, order, and control on the other. This indicates that some organizations values adaptation, change and organic processes while others are effective in emphasizing stable, predictable and mechanistic processes” (Tharp, 2009).
The second dimension looks at “internal orientation, integration and unity on one side while external orientation, differentiation and rivalry on the other end” (Tharp, 2009). This implies that the hotel should focus on their internal processes for success while others perform well by focusing on market and competition. The diagram below summarizes the two dimension of completing values framework.
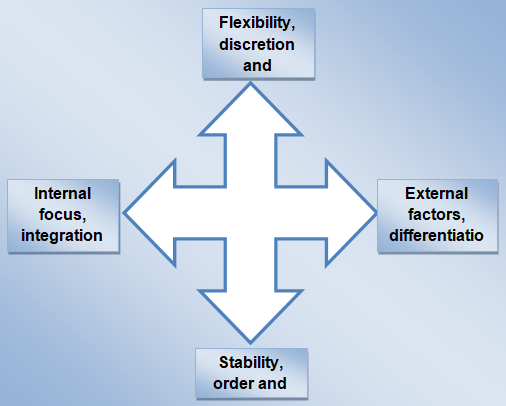
The internal and external reporting channels are then cascaded down to the rest of the structures. The two structures differ in the sense that there is an indication of unity, integration and internal orientation in line with the SWOT results (Cheverton, 2004).
The hotel should put out most of the documents such as policies, procedure manuals and new rules through the intranet Web pages. This saves the company costs relating to printing, maintaining and circulating such documents. Also, intranet makes it easy for communication across the organization.
Secondly, the management should consider using internet tools such as VoIP and Groupware. These technology tools would provide a good avenue for interaction of the staff members and ease of integrating administrative applications of the hotel (Laudon & Laudon, 2007).
Based on the first dimension of the competing values framework, the hotel already has a flexible business model and with the reserve funds, it is possible to adjust the size of the business or eliminate projects that do not reach the fund-raising goal (Cameron & Quinn, 2011).
Also, we are informed that for operation to thrive it must always be looking at new ways to survive, that is, “new way for fund raising, marketing, reaching out to the community and communicating with the public, therefore it is much quicker to adapt to change” (Samson & Singh, 2008). It can be deduced that there is a lot of hierarchical (control) and competition culture at the hotel (Morrison, 2003).
Technological transformations and the global market are the two major factors that will define changes that happen in the hotel’s financial performance. Therefore, there is need for staff members to adapt quickly to change, work smarter, increase productivity and carry out duties that are outside their job description for them to remain relevant in the job market.
References List
Cameron, K. C., & Quinn, R. E 2011, Diagnosing and Changing Organizational Culture, Kogan Page, London.
Cheverton,P 2004, Key Marketing skills: strategies, tools, and techniques for marketing success, Sterling, VA: Kogan Page, London.
Laudon, K. C., & Laudon, J. P 2007, “Using internet tools to increase efficiency and productivity,” Essentials of Management Information System, Vol. 8, pp. 300-410.
Morrison, D 2003, E-learning Strategies: How to get Implementation and Delivery Right first time. New York: Wiley.
Samson, D, & Singh, P 2008 Operations Management: An Integrated Approach, Cambridge University Press, London.
Slack, N., Chambers, S., Johnston, R., & Betts, A 2005, Operations and Process Management: Principles and Practice for Strategic Impact, Prentice Hall, Benin.
Tharp, B 2009, Organizational Culture White Paper. Web.