Audit Task Description
Management of effective workflow in the audit process is critical as it allows the identification of issues within the organization and the prompt implementation of appropriate measures. Furthermore, defining the time frame for the internal audit is essential as it allows for establishing clear time goals for completing each key step of the audit process. Several tools can be used during the audit execution to describe the scope, format, and content of the audit assignment (Stamatis, 2021). The creation of the Gantt chart provides substantial assistance in organizing the audit process by helping with visualizing the possible time frames for each task.
Audit Steps
Firstly, the case details identified seven prominent steps in the future internal audit process. Considering that the internal audit process generally takes approximately three months and must be performed yearly, the chart sets a four-month time frame for completing all identified steps. While the first internal audit process can take four months, in future cases, the time for each task can be reduced proportionally to ensure the completion of the audit in a one-month frame. Furthermore, the chart separates the steps into three categories: the preparation stage, the audit performance stage, and the implementation of recommendations based on audit findings.
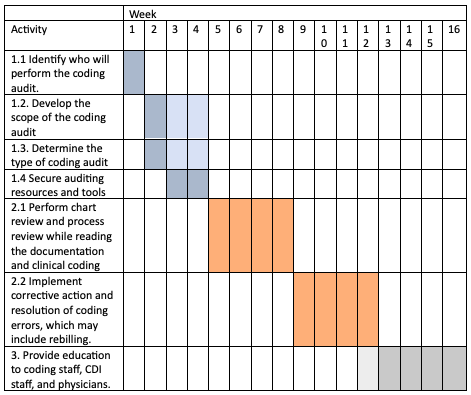
Planning
The first essential step of identifying who will perform the audit plays an important role and, therefore, has a strictly defined period of one week. Further steps in the planning process can have slight deviations depending on the complexity of the task, which is reflected in the graph. The last step of the planning secures the availability of auditing resources and tools, which marks the beginning of the audit performance stage.
Execution
Next, the two phases of the performance stage have an extended duration to ensure that the audit notes all the critical details. Lastly, the stage where findings identified by the audit are implemented in the education of coding staff, CDI staff, and physicians requires some level of organizational work. Therefore, the chart reflects that the organizational work can be planned in advance during the audit stage.
Reference
Stamatis, D. H. (2021). Automotive audits: Principles and practices. CRC Press.