Introduction
General Electric (GE) is a profitable corporation that operates in different sectors such as technology, financial services, healthcare, and media. The company uses a diversified strategy to meet the changing needs and demands of its global customers. Some of its products include medical imaging technologies, industrial chemicals, machines, and aircraft engines. It also markets a wide range of services such as medical imaging solutions, financing, power, lighting, transportation, software development, and renewable energy. The American multinational corporation markets its superior products in more than 100 nations across the globe. In 2016, GE was ranked among the top 20 most profitable corporations. The company has its headquarters in Boston, Massachusetts. This report gives a detailed analysis of GE’s background, business structure, human resources, financial performance, and business marketing plan, and product development.
Founders, Mission, and Vision
GE is an organization that has a complex history. The story of this company started in 1889. During this time, Thomas Edison owned several companies that produced electricity-related products. These included Bergmann & Company, Edison Electric Light Company, Edison Lamp Company, and Edison Machine Works. Drexel, Morgan & Co. decided to finance most of the researches and inventions pursued by Edison in 1889. This company was founded by Anthony Drexel and J. P. Morgan. The new agreement led to the formation of the Edison General Electric Company. This organization emerged after all the founders agreed to combine their efforts (Kumar, Arora, & Bansal, 2015). The new company was incorporated during the same year. It also managed to acquire the Sprague Electric Railway & Motor Company in 1889 (Agarwal, 2015). In 1892, GE would be formed after Thomson-Houston Electric Company (owned by Gerald Hart) merged with Edison General Electric Company. The founders of GE, therefore, included Thomas Edison, Edwin Houston, J. P. Morgan, and Charles Coffin.
General Electric would be one of the first companies to be listed on the Dow Jones Industrial Average in 1896 (Kumar et al., 2015). Over the years, GE managed to acquire or absorb several companies such as Marconi Wireless Telegraph Company of America. The organization also supported the establishment of the Radio Corporation of America (RCA) in the year 1919. It also considered the need to diversify its operations by investing in different segments such as power generation, computing, television, health care, gas, weapons, wind turbines, lighting, water, and software (Kumar et al., 2015). The corporation has continued to use exemplary business strategies and approaches to remain successful in the global market.
At the heart of GE’s positive performance is its mission statement. The company’s mission is to “usher in the next industrial era and to build, move, power, and cure the world” (Stephans, 2016, para. 1). This statement captures the company’s business agenda by ensuring that its major diversifications or segments are taken into consideration. The company’s products are also engineered and designed in such a way that they resonate with the demands of the targeted customers. The corporation’s decision to operate in different regions has made it possible to market and deliver exemplary services and products to many customers.
On top of this mission is a powerful vision statement that makes it easier for GE to achieve its potential. GE’s vision statement is to “focus on businesses that connect to its core competences” (Stephans, 2016, para. 1). The vision guides the corporation to identify new markets and segments that can transform its competitiveness or performance. The mission and vision statements are used to guide the company’s business model and encourage different stakeholders to support the strategy. Underperforming segments are also identified to ensure the company remains sustainable and profitable.
With this vision and mission, it is quite clear that GE will continue to dominate its major segments, attract more customers, and satisfy their needs. Additionally, the company has come up with some core values that are embraced to drive organizational performance. Some of the values include a passion for every customer, excellence, speed, hallmarks of General Electric leadership, and meritocracy. The employees at the organization are guided, empowered, and encouraged to focus on such statements and core values (Agarwal, 2015). Such measures have created the best environment whereby revolutionary ideas can emerge and eventually meet the needs of the company’s stakeholders.
Business Structure
General Electric is known to have a complex business structure. This is the case because it has managed to merge with or acquire numerous companies within the past century. The move has created a complex corporate empire that is supported by many segments or departments (Agarwal, 2015). After acquiring a new company, the leaders at GE come up with appropriate strategies to integrate it within the existing corporate structure. The next important thing is implementing powerful changes to support the corporation’s business activities and goals.
The current organizational structure implemented by GE is composed of six segments. Such divisions are connected to support the company’s objectives. The first division is that of energy. This has remained the company’s cash cow for many years. The energy division is subdivided further into three segments. These include power and water, energy services, and oil and gas (Kumar et al., 2015). The second segment is that of capital. It is the largest in the company and supports its business goals. The other remaining divisions include home and business solutions, aviation, transportation, and healthcare (see Fig 1).
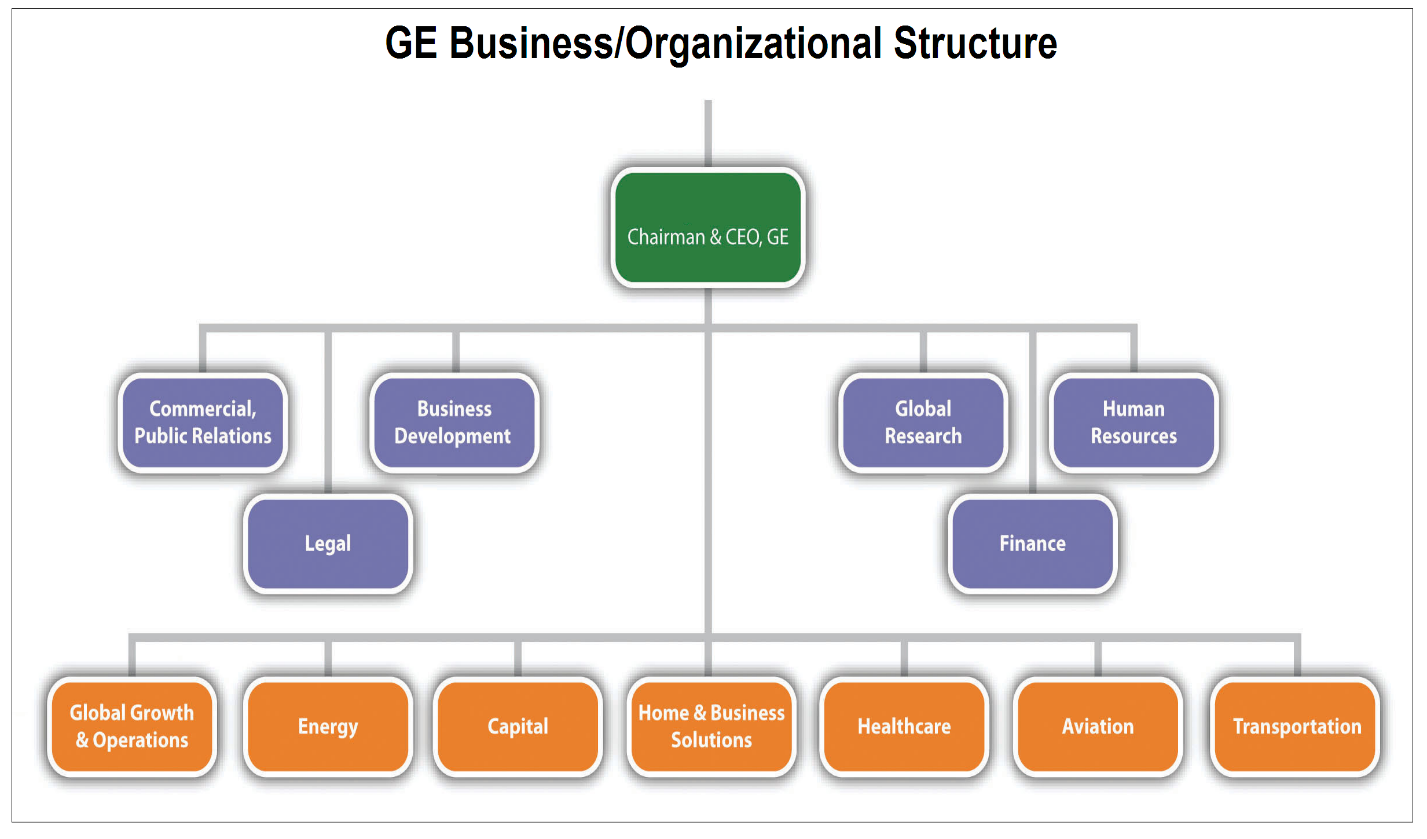
On top of these six divisions, the company’s structure has a segment known as Global Growth and Operations (Rothaermel, 2015). This department is relevant for GE since it has been responsible for its business operations outside America. The division has also been focusing on the company’s marketing processes and activities. The segment has been subdivided further to respond to the emerging needs of local customers in every geographic region across the globe. Such regions include Africa, the Middle East, Japan, Europe, Australia, Canada, Russia, South America, Southeast Asia, India, and China.
In an attempt to support the effectiveness of the company, the leaders at GE have come up with centralized functions that complete their business structure. These supportive functions or services include global research, finance, human resources, legal, business development, and public relations (Agarwal, 2015). The roles undertaken by these functional departments have made it possible for GE to minimize its operational costs or expenses. The centralized services have also increased the level of consistency across various segments within the multinational corporation.
This business structure empowers the organization’s leaders to make timely decisions and share ideas with different stakeholders. The corporate empire has benefited from the structure since managerial practices are completed efficiently by the relevant individuals. The needs of different customers are identified and addressed inefficiently. Consequently, the company has managed to develop a powerful mission and vision statements that empower and guide every employee. After GE acquires a new company, a powerful change process is implemented in an attempt to streamline or merge its operations with the existing ones (Rothaermel, 2015). Different employees and leaders and guided in an attempt to make the acquisition process seamless. These initiatives explain why GE’s corporate structure has been effective for every business operation.
Business Human Resources
Many successful companies tend to have efficient human resources. Their human resources (HR) departments implement powerful policies, programs, and interventions to support the performance of the targeted workers. HR managers possess adequate competencies and skills that make it easier for them to address the challenges affecting their workers, empower them, and offer the right resources in an attempt to improve performance (Kumar et al., 2015). General Electric is a company whose HR team is known to focus on this description. The first activity undertaken by GE’s HR team is to find, attract, and develop skilled persons to ensure the mission of the company is realized. The HR department has come up with a powerful mission that is aimed at empowering different workers. The mission is associated with unique attributes such as the ability to empower one another, build meaningful teams, and deliver results effectively.
Every division replicates the above aspects and attributes of HR. This is a clear indication that the company has developed and managed powerful business practices that are aimed at fulfilling the changing demands of different employees. The department is tasked with numerous roles such as identifying causes of disagreements, addressing conflicts, implementing the company’s code of ethics, and empowering employees using a wide range of programs (Agarwal, 2015). These initiatives have created the best environment whereby the targeted employees are satisfied with their working conditions and willing to support the company’s goals.
General Electric has come up with a Human Resources Leadership Program (HRLP) to empower its workers and ensure every objective is realized within the stipulated period. The HR department uses the program to work with leaders in different divisions, regions, and industries. The ultimate goal is to develop every person and build competent leaders who can make a significant difference (Power, 2014). The HR department is always keen to support the organizational culture by making it vibrant. The team liaises with different leaders and professionals at the company to achieve the company’s objectives.
Power (2014) indicates clearly that GE has appropriate mechanisms for dealing with disagreements and conflicts. Such initiatives are undertaken by the corporation’s HR department. HR managers use their competencies to address such issues since they have the potential to affect business performance. The department goes further to propose several action plans that can be implemented to empower different employees and make the company successful (“Our culture,” n.d.). HR practices are executed in such a way that they bring together different stakeholders at the company. This approach is critical since GE is a corporation that operates in diverse segments or industries. Industrial relationships are monitored and managed by the HR team.
With over 295,000 employees, GE’s HR team has managed to develop and maintain the best environment whereby different goals can be achieved (Agarwal, 2015). To improve efficiency, HR managers promote a sense of diversity and simplicity. These aspects guide the company’s workers to collaborate, share ideas, make timely decisions, and focus on the outlined business aims. The team believes strongly that ideas can be initiated or proposed by every employee (“Our culture,” n.d.). When the workers receive adequate support, it becomes possible to collaborate and support every agenda implemented at the company.
Marketing Plan and Product development
Marketing Plan
In 2005, the leaders at General Electric (GE) restructured its model to form six segments. This approach made it possible for the company to implement a powerful marketing plan and achieve its goals. The first aspect of the plan is a powerful 4Ps marketing mix. The mix begins by ensuring that superior products are produced to address the needs of different customers (Agarwal, 2015). Such products (and services) are segmented by the company’s six divisions. With a wide range of options, the targeted customers are always able to purchase quality products and eventually realize their goals.
When it comes to pricing, the company considers the changes experienced in the global economy and marketplace situations. The Power by the Hour program is used to market GE’s aircraft engines. The program means that such engines are usually powerful and easy to maintain. The concept of place is supported by having different geographic locations. The approach makes it easier for the company to address the needs of more customers across the globe. The fourth aspect of the marketing mix is a promotion (Rothaermel, 2015). The corporation has selected different marketing agencies such as Responsys Incorporation to implement powerful initiatives and online platforms. The company uses the slogan “Bringing Good Things To Life” to ensure its products are appreciated in every part of the world (Rothaermel, 2015). Rebranding and co-branding approaches are used for different products.
GE’s marketing plan is supported using a powerful mix of psychographic and demographic segmentation. For instance, people’s lifestyles, interests, and activities are considered to understand the needs of a given market segment (Krumholz, 2014). The behaviors of different customers are analyzed in an attempt to improve the organization’s marketing model. These initiatives have made it easier for General Electric to meet its global customers’ needs.
Product Development
It is agreeable that GE innovates and markets numerous products across the globe. The company has been keen to develop such products and make them more competitive and useful to its customers. Consequently, it has developed a research and development (R&D) team that has supported innovation within the past 100 years. The company also collaborates with many technicians working in its global research centers and business outlines. These professionals focus on emerging trends, changing consumer needs, and global expectations (Power, 2014). The team is provided with adequate resources and tools. This approach makes it easier for its technicians to solve existing puzzles and come up with superior products (and improve existing ones) that can empower more clients.
The company also partners with start-ups in an attempt to identify new products that can support its business goals. In the future, the company plans to liaise with upcoming innovators to develop new offerings and disrupt existing businesses (Power, 2014). This analysis shows conclusively that GE’s product development model is sustainable and capable of supporting its current and future business performance.
Financial Analysis
General Electric’s financial records and performance are promising. For instance, the company’s market cap stands at 141,000 million US dollars. This makes GE a good choice for investment. The organization’s earnings trend has increased steadily within the past decade (Kumar et al., 2015). The company’s return on equity (ROE) is 11.4 percent (Krumholz, 2014). This means that minimal structural flaws are experienced in the organization. GE’s profit margin is around 7.53 percent. The organization’s return on assets (ROA) is 2.2 percent (“Financial highlights,” n.d.). In 2016, the company’s operating income was 9.03 billion US dollars (“Financial highlights,” n.d.). GE’s total assets during the same year stood at 365 billion dollars. With over 295,000 workers, the company has been able to compete in different sectors, thereby making it successful.
GE’s gross profit margin for 2017 was around 21 percent. This analysis shows conclusively that the company remains one of the profitable organizations in the industry. The company’s return on invested capital (RIC) stands at 7.2 percent. Interest coverage (IC) has averaged 1.9 percent for the last three years (“Financial highlights,” n.d.). The organization’s average financial leverage for 2017 was 6.8 percent. GE’s asset turnover (AT) has remained below 0.23 percent within the past eight years. These statistics show conclusively that GE is a giant corporation that has remained profitable over the years.
The company’s consolidated liquidity is adequate due to its consistent profits and earnings. This is a clear indication that GE is capable of settling its debts within the specified period. The company’s revenues have remained consistent within the past two decades. Its operating margin has been increasing significantly. The current margin is around 29 percent (“Financial highlights,” n.d.).
GE’s price-to-book ratio is around 7 while that of the industry is 8.5 (“Financial highlights,” n.d.). Although this ratio appears to affect investor confidence, the undeniable fact is that the company’s stock price has been undervalued. Interestingly, the stock has remained attractive to many investors. Consequently, the company has become a leading player and competitor in the industry.
From 2014 to 2016, General Electric has recorded commendable results from its segments. For instance, profits from different products have continued to increase significantly. This achievement has made it possible for the organization to embrace the concept of research and development (R&D). This move has led to increased profits at the company. GE has managed to deliver 1.49 US dollars per share in 2017 (“Financial highlights,” n.d.). The company also returned around 30.5 billion dollars to its shareholders by its dividends policy (website). The leaders at the company also acknowledged that similar approaches will be considered in the future to maximize productivity, profitability, and business performance.
Conclusion
This discussion shows clearly that General Electric is a competitive multinational corporation that meets the needs of many customers across the globe. The company has six unique business segments that sustain its model. Research is done continuously to develop better products and models that can support different organizational activities such as marketing. Additionally, the company is associated with exemplary human resources that resonate with the emerging needs of different workers. Its financial performance is also attractive, thereby making it a competitive corporation in its six business divisions. The company should continue to support its current business model and engage in R&D to remain relevant in its industry.
References
Agarwal, N. (2015). Strategic business transformation through technology convergence: Implications from General Electric’s industrial internet initiative. International Journal of Technology Management, 67(2-4), 196-214.
Financial highlights. (n.d.). Web.
Krumholz, W. L. (2014). General Electric’s tax liability: The case for corporate tax reform. University of St. Thomas Journal of Law and Public Policy, 8(2), 194-221.
Kumar, B. R., Arora, D., & Bansal, A. (2015). Valuation of General Electric: A case analysis. International Journal of Teaching and Case Studies, 6(3), 1-12. Web.
Our culture. (n.d.). Web.
Power, B. (2014). How GE stays young.Harvard Business Review. Web.
Rothaermel, F. T. (2015). General Electric after GE capital. Harvard Business Review. Web.
Stephans, J. (2016). General Electric’s mission, vision, and strategy.Market Realist. Web.