Ratios and Key Performance Measures
Accounting Ratios and Ratio Analysis
Accounting (financial) ratios are used in accounting for measuring the efficiency and profitability of businesses based on their financial reports. Such ratios offer businesses a tool for expressing connections between different accounting data points, which is a useful comparison. Accounting ratios provide a basis for fundamental analysis. Essentially, ratios are derived numbers, and their efficacy relies on the basic numbers, with the help of which they are calculated.
Therefore, if financial statements of business have been calculated with errors, the derived numbers in ratio analysis will also be likely to be presented erroneously (ICWAI n.d.). Moreover, a ratio should be calculated with the use of numbers that are meaningfully correlated. Following this logic, a ratio that is calculated with the use of unrelated numbers will not serve any purpose to businesses.
Ratio analysis is an irreplaceable tool for interpreting the results of financial statements. Such an analysis provides managers with important financial information and areas that require further investigation (Lan 2012). Ratio analysis is a useful tool that includes the regrouping of data by applying arithmetical relationships. It is worth mentioning that ratio analysis requires managers to have an understanding of the rules of financial statements’ preparation. If done correctly, the analysis of ratios offers information that allows the manager to:
- Determine which business areas require more attention;
- Get detailed information about the profitability of the business, its liquidity, and levels of efficiency;
- Acquire information from financial statements that can be used for forecasting.
In the article “Role of ratio analysis in business decisions: a case study NBC Maiduguri Plant,” Nuhu (2014) found that ratio analysis is paramount for gaining information about the viability of the reporting entity since financial statements do not provide enough relevant data. It was concluded that ratio analysis is one of the useful tools for revealing, comparing, and interpreting salient features of financial statements presented by businesses. When effectively applied to the financial statements, financial ratios can be extremely helpful for highlighting important aspects of a financial position used for identifying strengths and weaknesses in performance (Nuhu 2014).
Ratio analysis helps businesses evaluate the past operation, the current position, and prospects. It enables managers and accountants to ask relevant questions about the direction of their business and become more efficient in control, planning, and forecasting.
Key Performance Measures
According to the article Velimirovic, Velimirovic, and Stankovic (2011), the current business conditions require companies to use the information for measuring their performance to make effective decisions. Key Performance Measures (indicators) are used for measuring the efficiency of operations within organizations. Through tracking and maintaining key performance indicators (KPIs), managers can find out about long- and short-term trends and issues for taking proactive measures for getting operations back to normal (Lindblad 2017).
KPIs are particularly important for accounting. Before identifying KPIs that can be used to the advantage of a company, a manager should understand the drivers of profitability. Among such drivers are accounts payable and account receivable. The division of accounts payable is associated with the creation of vendors’ accounts and paying their invoices. Examples of KPIs for the accounts payable group include the following:
- Time from the receipt of an invoice until its payment;
- Number of invoices with mistakes;
- Time is taken to fix the mistake;
- Number of discounts used for paying a vendor;
- Invoice amounts;
- The average value of invoices, etc.
Accounts receivable is a division associated with the funds that allow a business to run successfully. Managers can make forecasts with regards to cash flow through tracking time-bound key performance indicators, such as:
- Number of days for setting up new accounts;
- Credit requirements;
- Number of accounts supported by personal guarantees;
- Cases that go to litigation (Lindblad, 2017).
As to internal KPIs, they are used by accounting departments for measuring performance concerning the internal stakeholders. For instance, managers can measure the time that separate employees use to respond to various inquiries or fix arising issues. Through measuring these performance indicators, managers can acquire information on employees that may require training and coaching. An accounting organization can conduct surveys and ask their customers to rate the performance of its employees. Such surveys can be performed regularly for measuring the overall efficiency of the measures and changes they used for enhancing performance (Lindblad 2017).
Before formulating and analyzing KPIs, managers need to identify what they want to achieve with the help of the analysis. The aims of KPIs’ analysis can range from increasing revenue to improving customer satisfaction. The key difference between the aims is associated with the fact that metrics are used for tracking various aspects of an organization’s performance. In contrast, KPIs are linked to the identified strategic goals (Wise, 2010).
Consequently, the analysis of KPIs can incorporate a variety of components; however, the bottom line should lead to a range of indicators that reflect the overall goals of the organization, both long- and short-term. For example, to show the overlap between the long- and short-term goals, a business usually monitors sales since every company sets targets for sales based on region, product, or service.
Simultaneously, a business can also be interested in tracking metrics linked to how sales representatives are performing, which product lines are more profitable than others, or what are discrepancies between what the company invests into business and what profit it receives in return. Analyzing the mentioned metrics can be an effective tool for providing managers with in-depth information about the overall sales objectives and strategic goals (Wise 2010).
Competitiveness Reports
Global Competitiveness Reports (GCR) are annual reports issued by the World Economic Forum to rank countries based on their Global Competitiveness Indexes. Such reports are used for assessing the ability of countries to offer high prosperity levels to their citizens as well as how effectively countries use resources available to them. International competitiveness is defined as the “ability of a national economy to achieve sustained high rates of economic growth, as measured by the annual change in per-capita gross domestic product” (Halperin & Pagell 1998, p. 336). Measuring competitiveness of the economy is a complicated process since it implies the examination of a multi-dimensional concept that involves hard (e.g., the balance of trade) and soft (e.g., management quality) data.
GCR includes the following eight factors of economic competitiveness:
- How open an economy is to international finance and trade;
- What role does the government play in regulation and budgeting;
- How well the financial markets are developed;
- How high is the quality of infrastructure;
- How high is the quality of technology;
- Is the quality of business management low or high;
- Is the labor market flexible;
- Is the quality of political and judicial institutions high.
When reviewing relevant literature on the topic of competitiveness reports, it is crucial to mention the methodology developed by the World Economic Forum (2015) for a more in-depth view of how competitiveness is measured and assessed. The methodology for calculating the competitiveness index has remained unchanged for ten years. It combines one hundred and fourteen indicators that are linked to concepts and processes associated with the matter of productivity. The indicators are divided into twelve areas presented in the diagram below:
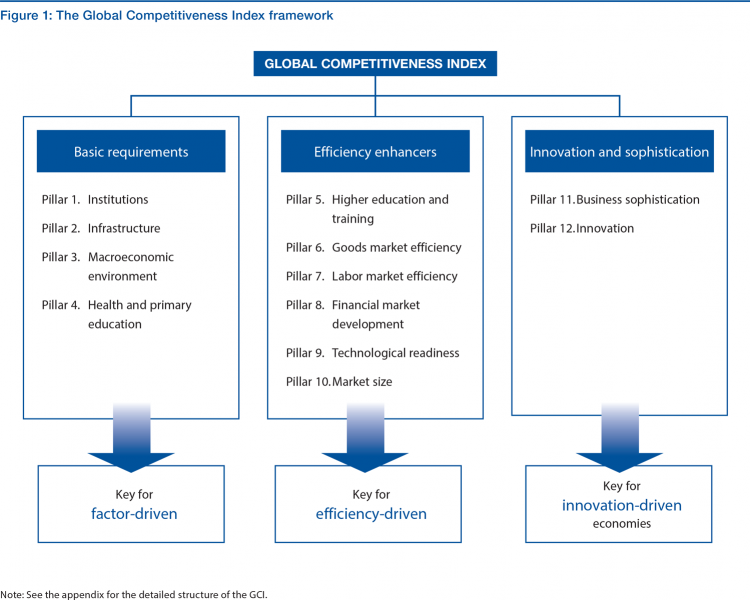
The GCI involves the usage of information of internationally acknowledged agencies such as the International Monetary Fund, the United Nations Educational, the World Health Organization, and Scientific and Cultural Organization (World Economic Forum 2015).
Financial Statements
Financial statements used by businesses are balanced sheets, income statements, cash flows, and retained earnings statements. It is a usual practice for companies to present their financial statements for maintaining the steady flow of information within the organization as well as organizational borders. Often, accountants, firms, government agencies, and other institutions audit financial statements for ensuring accuracy to investing, financing, and taxation. Financial statements are divided into four types, such as a statement of financial position, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of changes in equity.
Statement of Financial Position (the Balanced Sheet) is used for presenting financial positions of a business at a specific point in time. It is made up of assets, liabilities, and equity. Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement) is used for reporting on the financial performance of a company regarding the net loss and profit over a specific period. It is composed of income and expense. Companies use cash Flow Statement for determining the movement of cash and bank balance over a specific period. It is divided into segments, such as operating, investing, and financing activities.
Lastly, Statement of Changes in Equity (Statement of Retained Earnings) is a tool used for detailing the movement of equity over some time. It is derived from net profit or loss, share capital issues, divided payments, gains or losses, and implications of changes in policies or corrections of errors in accounting (What are financial statements n.d.). According to the article by John Bajkowski (1999), financial statement analysis is a process targeted at evaluating and reviewing the monetary statements to gain an understanding of a company’s stability and achieving a more efficient process of decision-making. While it is important to monitor financial data, without the analysis of such data, the gathered information will have no strategic value.
Lastly, it is important to mention benchmarking (industry analysis) that businesses use for comparing their current position to the position of key competitors for determining how well their business is doing financially. This type of analysis is quite effective for financial managers as it allows them to see if there is a need for any financial adjustments. In benchmarking, financial ratio analysis is often used: ratios of one company are compared to rations of another. This allows financial managers to be equipped with relevant data related to both the internal and external performance of their firms (Peavler 2016).
Reference List
Baikowski, J 1999, Financial statement analysis: a look at the balance sheet. Web.
Halperin, M & Pagell, R 1998, International business information, 2nd edn, Greenwood, Phoenix, AZ.
ICWAI n.d., Financial accounting. Web.
Lan, J 2012, 16 financial ratios for analyzing a company’s strengths and weaknesses. Web.
Lindblad, M 2017, Examples of KPIs for accounting department. Web.
Nuhu, M 2014, ‘Role of ratio analysis in business decisions: a case study NBC Maiduguri plant’, Journal of Educational and Social Research, vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 105-118.
Peavler, R 2016, How do you do financial statement analysis? Web.
The global competitiveness index framework 2015. Web.
Velimirovic, D, Velimirovic, M & Stankovic, R 2011, ‘Role and importance of key performance indicators measurement’, Serbian Journal of Management, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 63-72.
What are financial statements n.d.. Web.
Wise, L 2010, Using KPIs to identify trends in performance. Web.
World Economic Forum 2015, Methodology. Web.