Introduction
Each generation has significant differences in how they perceive and react to the world around them. This aspect may be influenced by indicators such as access to technology, information, the conditions in which individuals grew up, and societal values. At the center of this analysis is the study of test results for representatives of millennials, generation Z, and generation Y. Scores obtained after completing the questionnaire provide a more complete understanding of how people of different generations react to fake news and help to identify the factors that influence it.
Intergenerational Analysis of Fake News Perception
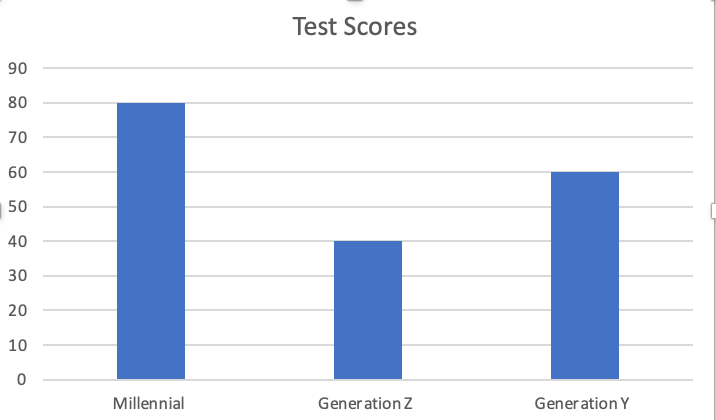
When comparing how millennials, generation Z, and Generation Y perceive false information, it is necessary to consider the conditions and factors that most affect it. Hence, when passing the test from the perspective of the millennium, relatively high results were obtained. This may be because this generation has broad access to technology and much information.
Thus, these individuals have high skills in analysis, media literacy, and critical thinking. These characteristics contribute to highlighting common sense in the information they receive. It is vital to mention such aspects as exposure to social media and the Internet for millennial representatives (Ana & Istudor, 2019). Under these conditions, individuals have a clear idea of the possible veracity of the source and how it can be supported or refuted.
Generation Z significantly differs from millennials regarding their attitude toward fake news. This group includes individuals born after 2000 (Szymkowiak et al., 2021). They are believed to have even greater exposure to the internet as they grow up, with smartphones and social media as integral parts of their lives.
The main problem in this context is that they can only receive information that corresponds to their interests and needs. In other words, due to the high skill required to filter data, representatives of this generation can remove information they do not need, which may limit their perception of fake news. This aspect supports that during testing, a representative of this generation scored lower than millennials and Generation Y.
The Generation Y representative showed promising results when passing the test for fake news. People of this type were born in 1965-1979, and the main characteristic of this generation is low exposure to social networks and the internet in general. Before disseminating these sources of knowledge, the leading news and knowledge that individuals received from newspapers or magazines.
Because they were the first generation to have access to Internet technologies at a sufficiently mature age, it came to them to adapt to it. Consequently, they have much less skill in criticizing news and resisting false knowledge. Moreover, in this age category, personal bias is of great importance, on which most of the judgments are based.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the testing offers a deeper insight into the ways individuals perceive and analyze the information they receive from various sources. As part of the study, data were obtained from millennials, generation Z, and Generation Y representatives. The results showed that the former are more skilled at criticizing the information received and are able to dissect the truthfulness and reliability of the data.
References
Ana, M. I., & Istudor, L. G. (2019). The role of Social Media and user-generated-content in Millennials travel behavior. Management Dynamics in the Knowledge Economy, 7(1/23), 87-104.
Szymkowiak, A., Melović, B., Dabić, M., Jeganathan, K., & Kundi, G. S. (2021). Information technology and Gen Z: The role of teachers, the internet, and technology in the education of young people. Technology in Society, 65. Web.