Introduction
Strategy refers to the “direction and scope of a firm over the long run”. It facilitates the creation of competitive advantages through configuration of the firm’s resources in a challenging business environment in order to meet the customers’ and stakeholders’ expectations. The strategy process begins with strategic analysis in which the internal and external environment of the firm is assessed.
This helps in identifying potential changes and the best responses to such changes. Having analyzed the environment, the firm must critically appraise all the strategic options at its disposal in order to choose the best strategy. The best strategy is usually implemented in order to overcome competition in the industry.
This paper will focus on the process of formulating and implementing business strategy. The first part of the paper focuses on the process of analyzing internal and external environment of the firm. In the second part, case studies will be used to illustrate the application of tools such as five forces in environmental analysis.
Steps in Environmental Analysis
The order in which environmental analyses are done is important. Analysis of the external environment should precede analysis of the internal environment. The importance of this order can be explained as follows. Analysis of the external environment serves three purposes. First, it facilitates understanding of the existing as well as potential changes in the business environment.
Second, it provides intelligence that informs strategic decisions of the firm. Finally, it facilitates strategic thinking within the firm. Internal environment analysis on the other hand, enables the firm to indentify its strengths and weaknesses.
Thus, it is apparent that external environment analysis serves as “an early-warning system” that enables the firm to predict opportunities and threats in its environment. This prediction enables the managers to formulate the best strategy to respond to the anticipated changes.
In order to respond to the expected changes, the firm must conduct an audit of its internal environment with the aim of identifying its capabilities or strengths and weaknesses. Consequently, the firm will be able to formulate the best strategy and utilize its resources as well as capabilities to exploit emerging opportunities. Additionally, the strategy will help the firm to mitigate the negative impacts of threats in the industry.
Thus, it is important to begin with external environment analysis in order to identify the factors that affect the competitive environment. The internal environment analysis should then be conducted in order to verify the firm’s ability to respond to the changes predicted by the external environment analysis.
Importance of Profits
As a manager of a large firm, I would focus on making superior profits due to the following reasons. To begin with, making profits is the main objective of every business. All other objectives of the business are meant to support the profit objective either directly or indirectly.
From the point of view of the stakeholders, profits represent returns on investments. All stakeholders invest their money in a company with the aim of realizing the highest possible returns. Non profitable businesses present a high opportunity cost to the investors. Thus, they are likely to channel their investments away from non-profitable firms, leading to the collapse of the business.
Profits are also fundamental for the sustenance of the business. They are used to finance implementation of strategies that improve the competitiveness of the firm. For example, a profitable firm will be able to hire the best talent in the industry in order to enhance its competitiveness.
High profits are also good for the employees. Hiring and retaining employees normally present high costs to the firm. Thus, when the firm is underperforming (financially), most cost-cutting measures are focused on reducing the number of employees or employees’ remuneration.
Thus, high profits represent some level of job security to the employees. A profitable firm will have the resources to invest in employee development in order to maintain its profitability.
For example, firms that make high profits are able to provide free staff training and mentorship programs. Besides, profitable firms tend to offer better pay in order to reduce staff turnover. Thus, it is in the interest of employees to work in profitable firms.
From the customers’ perspective, high profits reveals value received. In competitive industries, firms can only make superior profits if their products offer superior value to the customers. The high profits are normally used to enhance the firm’s marketing mix.
For instance, a profitable firm has the resources to produce high quality products and distribute them efficiently. Additionally, profitable firms are able to offer discounts and engage in promotional activities that offer valuable information to customers. Customers who receive value for their money are likely to be loyal to the firm.
High profit firms are good for the society. Good corporate citizenship requires firms to take care of the environment and societies in which they operate in. This objective is normally achieved through corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Such initiatives can only be undertaken if the firm makes high profits. Otherwise corporate social responsibility programs involve high costs that most firms can not afford. However, the corporate social responsibility programs are important since they enhance the image and acceptance of the firm in the society.
Five Forces Model
If several firms are aware of the threats associated with their competitive environment and make their strategic choices solely on this model, their performance is likely to be dismal. The low performance can be attributed to the following reasons. To begin with, the business environment can be categorized into three levels namely, the internal environment, the competitive environment and the external environment.
The five forces model provides only information about the competitive environment. In most cases, changes in the external environment usually affect the forces that shape competition in the industry. For example, regulation policies such as trade quotas can act as entry barriers to new firms.
In this context, it will be important to conduct an analysis of the external environment too in order to predict how the industry forces are likely to change in future. Additionally, the internal environment must be considered in order to formulate the best strategy, given the strengths and weaknesses of the firm.
Otherwise the information provided by the five forces model will be of little use if the managers are not aware of the firm’s ability to respond to industry threats.
As an analytical tool, the five forces model has its limitations which include the following. First, the model adopts an outside-in approach in strategy formulation. This means that analysis of the market dynamics precedes analysis of the firm’s capabilities. When several firms are using the five forces model, their strategies are likely to be more or less similar. Thus, they might not achieve competitive advantages.
In an industry with several firms, competitive advantage can only be achieved if strategy focuses on the core competencies of the firm. However, the five forces model does not allow firms to base their strategies on their core competence.
Second, the model focuses only on competition in the existing markets. It does not give firms the opportunity to develop blue ocean strategies. Blue ocean strategies are those that enable the firm to venture into markets that have not been exploited. Third, the five forces model “assumes relatively static market structures”. Consequently, the model can provide a framework for analyzing changes in the industry.
However, it does not provide valuable advice for preventive measures. In conclusion, the five forces model must be supported by other models such as the PESTEL and SWOT which analyses the external and internal environment respectively. This is because the external environmental factors affect the industry forces, while the internal environment determines the firm’s ability to respond to threats.
Consequently, different models must be used to obtain information from all levels of the business environment. Besides, the limitations of the five forces model can only be avoided by adopting supportive models.
Career Strategy
My career objective is to be a marketing director in the next five years. I particularly intend to work for a large firm within the fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry. The position of a marketing director is a challenging role, given the expected level of performance and the significance of the position.
The sales and marketing department of every company is very important since it determines the company’s ability to realize stable revenue streams. However, the position also provides exciting and rewarding opportunities to the holder. For instance, being a marketing director not only attracts a high pay, but also provides opportunities for gaining experience in handling marketing challenges.
I intend to pursue the following objectives in order to achieve the goal of being a marketing director. First, I intend to acquire more skills and knowledge in sales and marketing. Consequently, the objective will be to complete a Masters degree in Businesses Administration (MBA) in the next three years.
Second, I intend to gain more experience in the field of sales and marketing, especially, at managerial level. In this case, the objective is to move up the corporate ladder through promotions in the next four years. Finally, I intend to become a member of a recognized professional marketing body in the next two years.
Pursuing these objectives will enable me to acquire the necessary skills, qualifications and experience required for the position of marketing director.
How the Strategy Fits within my Capabilities, and External Environment
The external environment in the labor industry, especially, in the marketing field, is characterized by the following threats. Economic factors such as regulation, low economic growth, and high competition have resulted into poor performance of most businesses.
Consequently, businesses are reluctant to recruit new employees. As the business environment change, businesses also change, and thus, some roles are normally eliminated. Technological factors such as the use of computers and electronic linking of business activities have resulted into elimination of some roles.
For example, the use of e-commerce has reduced the number of sales staff needed in any sales and marketing department of firms that sell their products online. Finally, legal factors such as economic liberalization have allowed employers to hire employees on short-term contracts. Thus, job security is no longer guaranteed.
The competition in the job market is high due to the large number of graduates looking for jobs. Besides, employers have a high bargaining power due to the limited job opportunities. The opportunity in the labor industry is that the incumbent firms are constantly looking for talent in order to remain competitive.
Currently, my weaknesses include; lack of sufficient experience in marketing management, limited skills in marketing research and lack of recognition by a professional marketing body. My strengths include graduate training in sales and marketing, track record in achieving sales targets and experience in product promotion.
Thus, the objective of pursuing an MBA course and joining a professional marketing body will enable me to overcome the weakness of insufficient skills and lack of professional recognition. Seeking for promotions will enable me to overcome the weakness of insufficient experience.
Most importantly, these objectives will enable me to counter the competition in the job market. Given the threats presented by the external environment, gaining more skills, experience and new positions will enable me to adapt to the changing business environment. Consequently, I will not only stay employed, but also serve in positions in which I derive the greatest satisfaction.
Importance of Scenarios: South Africa Case Study
Scenarios are a “tool of analysis that improves the decision-making process, set against the background of a number of possible future environments”. Scenarios facilitate strategic thinking within organizations. Hence, it helps managers and business leaders to recognize possible changes in the business environment. The scenarios for South Africa were developed for the following reasons.
First, the scenarios were developed to facilitate strategic decision making by the government and business community. The scenarios provided the big picture of what the country’s future would be. This means that the leaders were aware of the looming changes in their country. Consequently, they were able to indentify the right strategies for each scenario. Second, the scenarios acted as an early warning mechanism.
The scenarios were a strategy for identifying possible crises and planning for a timely solution. For example, the icarus scenario was associated with unsustainable development. In this case, the country’s leaders were able to predict failure in time. This gave them ample time to mobilize enough resources and formulate the right strategies to prevent the predicted failure.
Third, the scenarios enhanced institutional learning. Since scenarios are based on past and current information, they enable leaders to avoid repeating mistakes.
In conclusion, the South African scenarios were meant to provide a context for decision-making. Additionally, the process of developing the scenarios facilitated communication throughout the country by bringing together various stakeholders to participate in strategy formulation.
Importance of Scenario Planning to Managers
Scenarios are an important tool for decision making under uncertain situations or environments. Several different possibilities are normally expected in uncertain business environments. Due to the underlying difficulty in predicting future changes under uncertainty, it is better to list all the possible changes and indentify a suitable strategy for each.
Additionally, scenario planning is important when capital and resources are likely to be adversely affected by uncertain risks. In this case, scenarios help in indentifying potential changes or risks that can lead to losses.
Comparative Impact Matrix Analysis: US Airline Industry
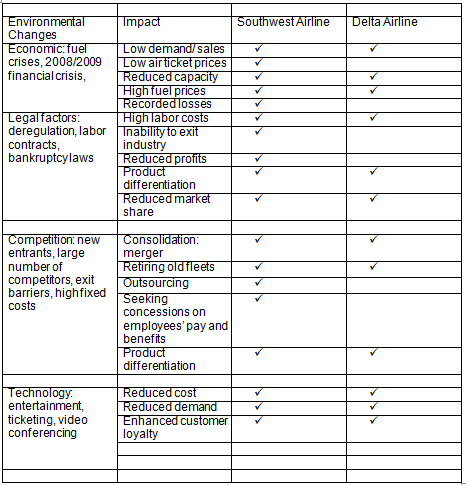
The above matrix indicates the environmental changes and how their impact on Delta Airline and Southwest Airline. The economic factors included the financial meltdown in United States and increase in jet fuel prices. The financial crisis had the effect of reducing demand for both passenger and cargo flights.
The high fuel prices led to an increase in operating costs. Consequently, both airlines experienced a reduction in sales, and reduced their capacities. Unlike Southwest Airline, Delta Airline did not manage to remain profitable. Delta Airline made losses and struggled to remain in the industry.
Stiff competition was brought about by the large number of competitors, high fixed costs, exit barriers and new entrants. Consequently, both firms merged with other airlines. They also retired their old fleets in order to reduce fuel costs. Like other legacy airlines, Delta Airline focused on outsourcing in order to reduce operating costs.
Legal factors included labor contracts between airlines and labor unions, deregulation and bankruptcy laws. Deregulation led to high competition in the industry. Labor contacts and bankruptcy laws served as exit barriers, thereby increasing competition.
Thus, both firms experienced high labor costs and reduced market share as more firms joined the industry. Non profitable firms such as Delta Airline found it difficult to exit the industry due to the exit barriers.
Technological factors included the use of modern information and communication technology to provide entertainment and ticketing services. These enhanced customer loyalty and reduced operating costs respectively. The introduction of video conferencing reduced participation in face-to-face meetings. This translated into a reduction in demand for passenger flights, especially, among the business class.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis for US Airline Industry
The five forces analysis framework enables managers to understand the dynamics of the competitive environment in which their businesses operate. It is an important tool for investigating the forces that determine the level of competition in a particular industry.
Consequently, it gives the managers information that forms the basis of strategic decision making. The industry forces that led to the mergers and acquisitions in the US airline industry include the following.
New Entrants
The USA airline industry is characterized with high levels of product differentiation. Differentiation was necessitated by the stiff competition that was experienced in the industry, following its deregulation in 1978. The deregulation allowed many firms to join the industry thereby, forcing the incumbents to compete on the basis of product differentiation. Joining the airline industry is also capital intensive.
A lot of financial resources are needed, especially, for the purchase of the aircrafts. Besides, the high levels of regulation in terms of safety and service quality present high costs to firms that intend to join the industry. Thus, the high costs acts as an entry barrier to new firms that intend to join the industry. The switching costs are high in the airline industry and this also discourages new firms from joining it.
After the deregulation of the industry in 1978, the incumbents’ control of routes reduced. This is because all firms were allowed to serve any route of their choice, thereby increasing competition. The incumbents also have vast propriety knowledge in the industry.
For instance, the United Airlines as well as American Airlines have been in operation since 1930s. Thus, they have the experience and expertise to counter any competition from new entrants. We can, thus, conclude that the threat attributed to new entrants is low in the US Airline industry.
Power of the Buyer
This refers to the bargaining power of the buyers, airline companies. There are very many airline companies (151 firms as at 2009) as compared to the suppliers such as aircraft manufacturers. However, the suppliers of products such as fuel are very many.
The switching costs are very high due to the contracts entered by the airlines and their suppliers. For instance, the purchase of aircrafts is based on contracts that last for several years. Some airlines also enter into contracts with fuel suppliers in order to reduce fuel costs. Thus, breaching of these contracts leads to high switching costs.
The suppliers’ products are highly differentiated. The US airline industry has two types of airlines namely; the low costs airlines and the legacy airlines. Since these two types of airlines have different capacity needs, the suppliers make aircrafts that meet the specific needs of their customers.
Since most airlines compete on the basis of differentiation, the suppliers have had to include additional features such as entertainment equipment in the aircrafts.
There is low threat of backward integration in the industry. Most airlines are relatively small compared to their suppliers. Besides, most of them are straggling to remain profitable, especially, after the 2008/ 2009 financial crisis. Consequently, the airlines can not afford to purchase their suppliers or invest in the production of their own aircrafts.
Finally, the suppliers’ inputs are very important to the quality of services rendered by the airlines. All aspects of the flight such as foodstuffs, entertainment and comfort within the aircraft directly affect the customers’ flight experience. Thus, all suppliers’ products must be of high quality in order to enhance all the aspects of every flight.
This leads to the conclusion that buyers have a low bargaining power in the industry. Low bargaining power means that airlines can not easily negotiate for low prices for their supplies. Thus, they can be exploited through high prices or low quality products.
Power of the Suppliers
The suppliers of aircrafts are very few as compared to the airline firms. In the last two decades, the number of manufacturers of large aircrafts reduced from four to only two. Additionally, there are only two leading suppliers of medium size aircrafts. This means that there is a potential constrain in the supply of aircrafts, especially, if there is a backlog of orders.
There are no substitutes for the suppliers’ products. For instance, jet fuel can not be substituted by any other form of energy. In this case, the airline companies are heavily dependent on their suppliers. As discussed earlier, the suppliers’ products are highly differentiated due to the capacity needs of airlines and the quality of service offered by the airlines.
Despite the high concentration of the aircraft industry relative to the airlines industry, the later remains very important to the former. This is because airlines are the main customers of the aircraft manufacturers. This is explained by the discounts and favorable terms of payment offered by the aircraft manufactures. However, the threat of forward integration is very high in the industry.
Most aircraft manufacturers are large in terms of capital and asset ownership. Thus, they can easily purchase the airlines or establish their own. Consequently, the suppliers have a high bargaining power in the industry. The implication of suppliers with a high bargaining power is that, the suppliers can exploit their clients through high prices.
Substitutes
Substitutes refer to other modes of transport that can be used as an alternative to air transport. These modes include buses, train and personal cars. The threat posed by the alternative modes of transport is relatively little. For instance, trains and buses accounted for only a small percentage of journeys that were more than one hundred miles.
This trend can perhaps be explained by the low differentiation and service quality associated with the train and bus transport industries. In most cases, buses and trains provide standardized services that do not meet the specific needs of their customers.
However, the trains and buses tend to be cheaper as compared to air transport. The low threat of substitute is an advantage to the airline industry since the level of competition will be low.
Competitive Rivalry
The US airline industry is characterized with cut-throat competition due to the following reasons. First, there are very many airlines competing in the industry. The increase in the number of airlines is mainly attributed to the liberalization of the industry.
Second, the growth rate of the industry is low. The low growth rate is attributed to poor economic performance of the US economy, especially, after the 2008/2009 financial crisis. Additionally, the industry is at its maturity stage and this limits potentials for faster growth.
Third, there are high fixed costs in the industry. Hiring labor presents the largest fixed costs to the airlines. The average pay for employees in the industry is about $ 55950, which is at least 40% more compared to labor costs in other private industries. Besides, the strong labor unions in the industry prevent airlines from reducing wages or the number of employees during periods of low demand.
As fixed costs rise, firms are left with little financial resources to enhance their competitiveness through expansion and introduction of new products. Besides, the high fixed costs directly impact profits negatively. As discussed earlier, switching costs are very high in the industry. Buyers can not easily change suppliers in order to achieve cost competitiveness.
Finally, the exit barriers in the industry also perpetuate stiff competition. The old airlines as well as the non profitable firms can not quit the industry due to the high exit costs. For example, the contracts between labor unions and airlines require the later to pay large sums of money to employees as terminal benefits.
This represents high costs of exit. Besides, firms that have filed for bankruptcy are expected to continue in operation as they service their depts. Thus, the competition in the industry presents a great threat to the survival of most airlines. The high competition, not only reduces profits, but also reduces market shares of the firms.
In conclusion, the forces that led to the mergers and acquisitions from 1981 to 2009 include the threat attributed to competitive rivalry, low power of the buyers and the high power of the buyers. These forces adversely affected the profitability of the airlines, thereby necessitating consolidation.
For example, a merge between two airlines helped to reduce competition. Additionally, the mergers enabled the firms to ensure economies of scale. Firms that were not able to withstand the effect of the aforementioned industry forces were acquired by their competitors.
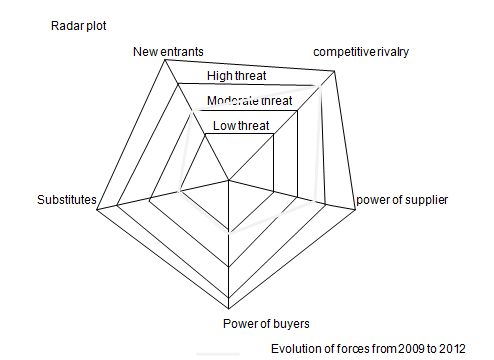
The Forces likely to Drive Change
Competitive Rivalry
The threat associated with competitive rivalry is likely to drive change in the US airline industry due to the following reasons. First, the economy of the United States of America is expected to recover in the near future. Thus, there will be an increase in demand for air transport. As the demand rises, most airlines are likely to embark on product and process innovation to attract customers.
Product innovation will involve improving the quality of existing products in order to make them attractive to the customers. Besides, new products are likely to emerge as airlines compete for customers. Since competition in the industry has always been characterized by price wars between the low cost airlines and the legacy airlines, most firms are likely to focus on cost reduction.
Thus, most firms are likely to embark on innovative strategies for reducing operating costs. Such strategies can include outsourcing non core business activities. As the demand for air transport increase within America and other parts of the world, new routes are likely to be introduced. The airlines are likely to deploy capacity to routes with relatively low competition.
New Entrants
As the industry grows in the future, new firms are likely to join it. With reduced regulation on entry, international flights are likely to join the industry, thereby, increasing competition. Currently, airlines from emerging economies in Asia and Africa are recording high profits. Thus, they are expanding both their route network and feet.
The Dubai-based Emirates Airline for example, has an ambitious plan of acquiring 90 new A380 jets. The threat attributed to new entrants will result into changes in the industry in the following ways. First, the incumbent firms are likely to work with the new entrants, especially, foreign airlines through airline alliances.
Such arrangements will not only enable the airlines to reduce costs, but will also enable them to maximize their profits. Second, competition is set to intensify in the industry as new firms join it. This has the implication of reducing the profitability of most incumbents. Thus, the airlines which are not able to survive the competition will either be acquired or they will merge with other firms.
Power of the Suppliers
The suppliers are likely to maintain a high bargaining power in the US airline industry. The high cost of joining the aircraft manufacturing industry is likely to discourage new firms from investing in the manufacture of aircrafts, especially, in USA.
However, the suppliers bargaining power might not be as high as it is at the moment. Newly industrialized countries such as China and India are likely to invest in aircraft manufacture. Besides, these countries have access to cheap labor and raw materials. Consequently, they are likely to manufacture aircrafts at low costs which will reduce the prices of aircrafts.
In this case, the competition from the low cost manufacturers will reduce the power of suppliers of aircrafts in the US airline industry. The suppliers of jet fuel are likely to maintain their high bargaining power through unions such as OPEC. As the power of suppliers reduces, there will be changes in fleet size and fleet age as more airlines find it easier to acquire new aircrafts.
Works Cited
Anderson, Peter. “Relationship Marketing and Brand Involvement of Professionals.” Industrial Marketing Management,36.6(2006): 285-297.Print.
Daraban, Ben and George Fournier. “Incumbent Responses to low-cost airline entry and exit: a Special Autoregressive Panel Data Analysis.” Research in Transport Economics 29.1(2008): 15-24. Print.
Duvan, Daniel. “Public/ Stakeholder Perception of Airline Alliances: the New Zealand Experience.” Journal of Airline Transport Management 11.6(2005): 448-454. Print.
Feiler, George and Timothy Goodoritch. “Decline and Growth, Privatization in Middle East Airline Industry.” Journal of Transport Geography 2.1 (2009): 55-64. Print.
Forsyth, Paul. “Environment and Financial Sustainability of Air Transport.” Journal of Air Transport Management 17.8(2010): 204-255. Print.
Groucutt, John. Marketing: Essential Principles. New York: Kogan, 2004. Print.
Kottler, Philip and Kevin Kelle. marketing Management. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2009. Print.
Sharma, Anthony. “Relationship Marketing.” Industrial Marketing Management, 36(2) (2005): 87-89. Print.