Many computer technologies are useful in communication of data or information that is essential for decision making pertaining to specific issues or concerns. The major technologies that find relevancies in technical communication are Global Positioning System (GPS) device, MP3 player, waste electrical and electronic equipment, automobile jack, and camera phone. This paper gives a general description of GPS device to enlighten the general public and other interested professionals.
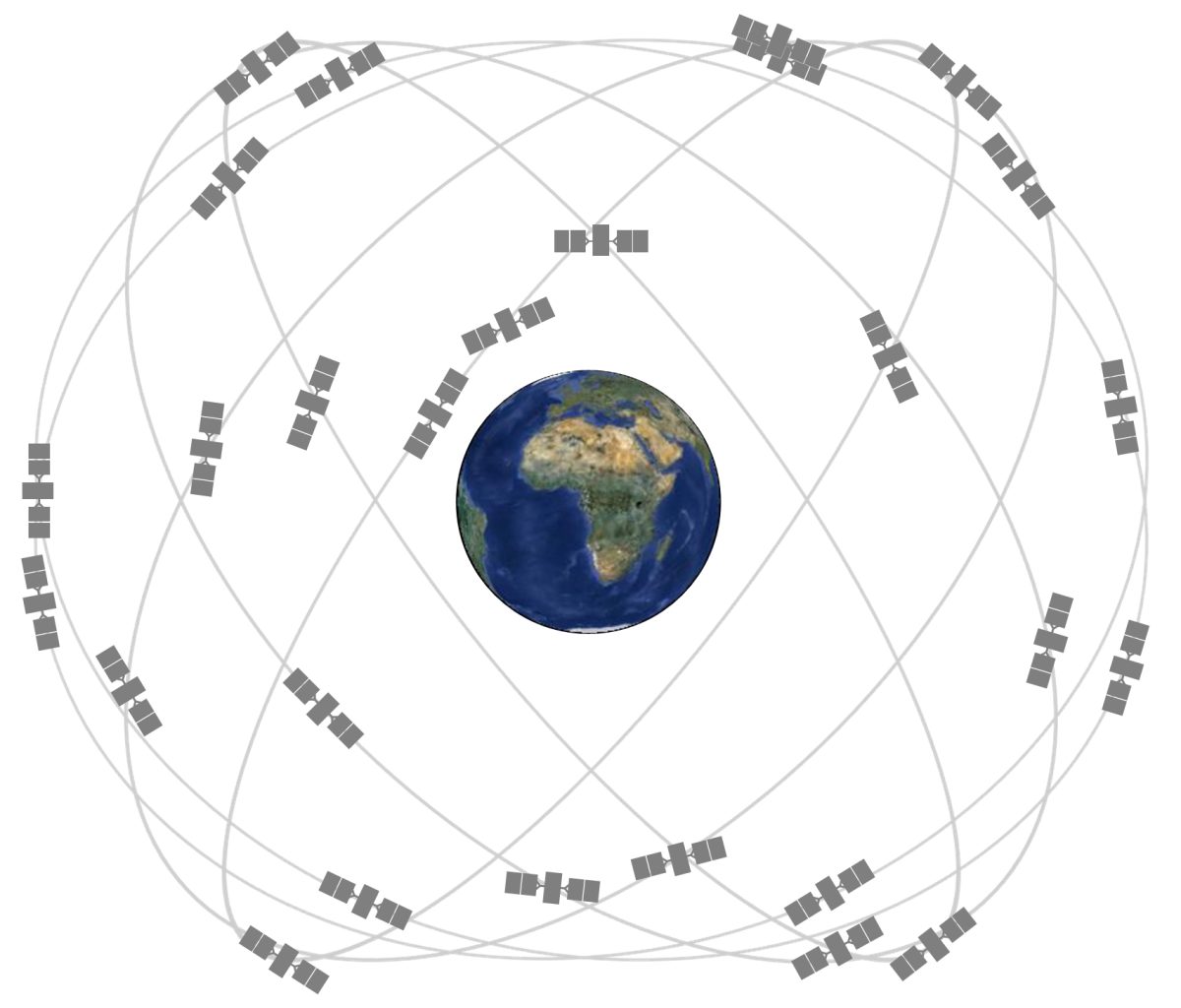
GPS is a radio-navigation system that is set in space and managed by the U.S. Department of Defense and Transportation. Image 1 shows the positions of the various satellites that constitute the GPS. It has been used for accurate determination of positions on the surface of the Earth (Combrink, Combrinck and Moraal 436).
It was initially invented as an enhancement system for the military forces and still serves this purpose as well as the others. Notwithstanding, it also has an adequate capacity to serve the civilian population in large numbers and variety of applications (Arnold, par. 16).
According to Arnold (par. 17), the GPS is comprised of three fragments, namely, space fragment, control fragment and user fragment. The space fragment uses 24 satellites suspending in 6 orbital planes. Each satellite rotates around a 20,200km orbit which is inclined at 55 degrees, and completes the rotation in 12 hours.
The configurations of the satellites in respective orbits are set in such a way that at least five are within the view of a user at any place on Earth in conjunction with Position Dilution of Precision (PDOP) of six satellites or less. PDOP is a quality measure of the relative configuration of the satellites as shown in figure 1. PDOP is inversely proportional to the degree of evenness in terms of spacing around the sky, so that the more evenly spaced the 24 satellite are, the lower PDOP is.
It can be said to be perfect when a satellite situates overhead the user with other three satellites located at 1200 intervals just over the horizon from the user (Arnold, par. 18). Combrink et al. (436) assert that thousands of stationary and mobile receivers also constitute the GPS.
The decrease in precision defines a root mean square estimation of the affect that position solution geometry imposes on positions’ faults. The experts managing the system can assess geometry affects in four different positions, namely, time position (TDOP), 3-D position (PDOP), vertical position (VDOP), and horizontal position (HDOP).
Arnold (par. 19) points out that the GPS control fragment comprises 5 monitoring stations and 3 ground antennas, which transmit radio or other signals to receivers in the communication satellites in space or aircraft within the atmosphere. The monitoring posts adopt GPS receivers to track every satellite within its scope of view and collect assorted data from the satellites’ signals. The information dispatched from the various monitoring posts is processed at a larger station, Master Control Station (MCS), located in proximity to the Colorado Springs Colo. It is done to establish satellite clock and orbits profiles in order to update the navigational information of individual satellite.

The user fragment of the GPS includes a range of integration and configurations architectures that encompass a receiver-pre-processor and an antenna to jointly receive and process navigational solutions to give a user positioning, velocity, and exact timing (Delaney 62).
Works Cited
Arnold, James A. “Surface Transportation and Global Positioning System Improvements: L5 and DGPS.” Public Roads 61.4 (1998): 2. Academic Search Complete. Web.
Combrink, A. Z. A., W. L. Combrinck, and H. Moraal. “Near Real-Time Detection of Atmospheric Water Vapour Using the SADC GPS Network.” South African Journal of Science 100.9/10 (2004): 436-442. Academic Search Complete. Web.
Delaney, John. “GPS: Yesterday and Tomorrow.” PC Magazine 20.7 (2001): 62. Academic Search Complete. Web.
“GPS Block II/IIA satellite“. 2014. JPEG file. Web.
“GPS Constellation (Expandable 24-slot configuration, as defined in SPS Performance Standard)“. 2014. Web.
“Satellite operators at the master control station, Schriever Air Force Base“. 2014. Web.