Introduction
- Businesses that prosper have their core values and purpose.
- The core values support the vision of the company.
- Hewlett-Packard Company (HP) mainly focuses on the technical competencies but often forget what makes the company runs smoothly.
- Some of the recommended core values for the company are as discussed below.
The core values remain fixed even as the organizations’ strategies and practices continuously adapt to the changing world. Such dynamics of conserving the core values while stimulating progress is the main reason bigger companies become elites and able to redeem themselves to achieving superior long term-performance (Waldman and Javida, 2009). They help in shaping the culture and reflecting the company’s values. Core values are currently gaining popularity in becoming recruiting and retention tools (Wolf and Egelhoff, 2002).

Trust and respect for individuals
This core value encourages the company to work closely with all the stakeholders to allow creation of culture inclusion built on belief, respect, and dignity for all.
The company takes into account the views of the employees in trying to serve their customers properly.

Achievement and contribution
The Company aspires to strive in excellence in all the activities it does.
In order to achieve this as a core value, the HP has to ensure integration of individuals’ view and thoughts into the development process since they are critical to its success (Waldman and Javida, 2009).

Results through teamwork
- The aim of having the core values in every company is mainly help achieve appropriate results.
- The HP Company should value expertise beyond its own, and proactively look for ideas and advice from colleagues and support them.
The HP Company should effectively collaborate with all the stakeholders and employees to receive broader views and alternatives of what to implement. This will help it to look for efficient ways to serve its customers and ensure implementation of goals oriented core values.
The company is humble enough to rely on others, and trustworthy enough to deliver when others rely on us. The core value aims at ensuring all the stakeholders receive equal treat (Wolf and Egelhoff, 2002).

Meaningful innovation
As company that deals electronics, the main aim of this core value is to ensure that any of the company’s innovative product, has positive impact on the market as well as taste.
The company can achieve this through ensuring that it involves the views of the customers while developing any of their products to reduce any probability of poor outcome.

Uncompromising integrity
The company must ensure it earns customer respect and loyalty by providing the highest quality and value, which meets the expectations of the customers consistently.
It has to ensure honesty, openness, and ensure direct dealing with the customers.
To gain customers’ trust, the company must ensure that it upholds all the matters of integrity at all levels of their production process. It has to value culture of inclusion where everyone is treated fairly and have an opportunity to contribute his/her mind (Wolf and Egelhoff, 2002).

Stakeholders’ success
The core value should focus on rewarding the investors with growing shareholder value.
Through operating profitably and with higher integrity, the company should focus on core values that provide its customers with best-value innovation and a competitive edge in their individual markets (Young, 2008).
This core value enables employees to work in a secure, ethical environment with attractive and competitive mix of pay and remuneration.

Cultural Core Values
- Culture is the compilation of internalized rules of performance for those in a company.
- Cultural Core Values also establishes the basis for consistent decision making for the company.
- HP Company employees strive to produce outstanding work that improves the company as their culture.
These rules form the basis for the company’s Core Values; hence, through identifying company’s Core Values and making them clear, one shapes organizational culture. This is significant crucial since company’s Core Values and culture enables the company to provide a moral compass for its employees for helping in decision-making regardless of the challenge the company face.
- Employees embrace their duties, enjoy the problem solving process, and provide effective solutions and benefit to customers (Waldman and Javida, 2009).
- They formulate well-thought-out decisions leading to the right changes for the right reasons.
- Creativity culture among the employees forms the fountain of new ideas, propelling better products, and processes. HP Company embraces having fun while working toward a general goal.
This is in companies’ bid to champion the principles of organizational quality, presentation excellence, and continuous development. The culture of accountability in HP Company ensures dedication of employees to their work and takes full responsibility for their responsibilities (Waldman and Javida, 2009). Employees care about the company and its constituents as a result always acting in the best interest of all stakeholders involved. It pools a varied set of perspectives and skill by assembling cross-functional teams to work together on projects. As its core value culture, the company often holds brainstorming meetings around new themes and objectives.


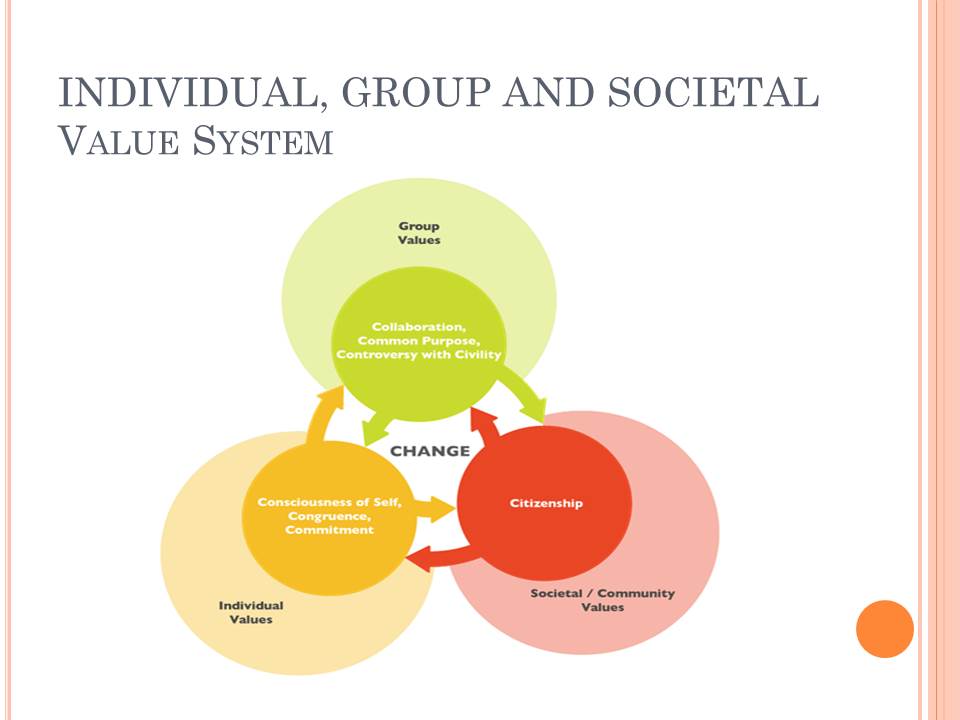
Individual, Group and Societal
Value System
Research-based models
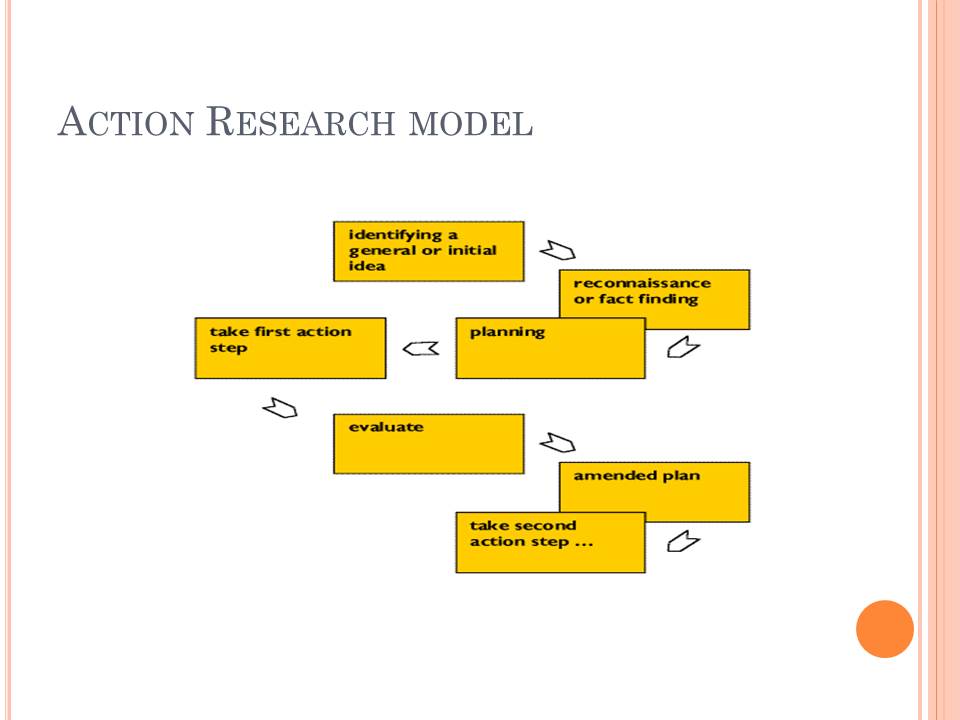
Action Research model
Action Research model used by the company aimed at creating useful knowledge.
Considered as the participatory action research method, the Action Research model mainly brings together all the stakeholders and the public to ensure that the report considers their views (Young, 2008).
The main feature of the model is its constitution of well-defined processes, which attach the elements of the model systematically to one (Stahl and Voigt, 2008).
In successive studies, data gathering continued to provide two purposes: the surfacing and theory testing, and provision of diagnostic data a contribution into an Action Research Cycle in the HP Company (Stahl and Voigt, 2008). This cycle often leads to redesigning of the products in line with the company’s core values. The teamwork included combined interpretation and collaboration in achievement planning. Most company’s studies are longitudinal in nature, allowing examination of the dynamics and impacts of change eventually, hence, leading to a permutation approach. It focuses on the reflection, collection of data, and actions that aims at improving the efficiency of the company through the people whose responsibility involves improving the quality of its services and products. The company’s model of culture is of particular interest to investigate cultural phenomena and change over time. An important aspect that clearly comes out of the model includes consideration of two factors during its development stage: company’s values considerably differ from one to another and organizational values, which influence the society.

How Cultural, Research-Based Models Help Clarify the Core Values
The company’s culture and research based model ensure efficient skills, attributes and behaviors that directly relates to successful performance on the work.
Core values provide a sound basis for reliable and objective performance standards through creation of shared language about what the company needs and expects.
They are important for the structuring of the company staff regardless of their levels. They depict the skills and attributes staff and managers require in building a new HP Company’s culture and meeting future challenges (Stahl and Voigt, 2008). They assist the company in clarifying its expectations, describe future development needs, and apply more focused recruitment and development planning.

References
Stahl, G. K., & Voigt, A. (2008). Do cultural differences matter in mergers and acquisitions? A tentative model and examination. Organization Science, 19(5), 160-176.
Waldman, D. A., & Javida, M. (2009). Alternative forms of charismatic leadership in the integration of mergers and acquisitions. Leadership Quarterly, 20(1), 130-142.
Wolf J, J., & Egelhoff, W. G. (2002). A reexamination and extension of international strategy-structure theory. Strategic Management Journal, 23(4), 181-189.
Young, P. A. (2008). The Culture Based Model: Constructing a Model of Culture. Educational Technology & Society, 11(2), 107-118. Web.