Introduction
Six Sigma is a lean methodology for problem-solving through defining and eliminating defects. The DMAIN process is an integral part of a Six Sigma model that consists of five phases: definition, measurement, analysis, improvement, and control (Selvi & Majumdar, 2014). An Abu Dhabi hospital faces client dissatisfaction because of the high waiting time (45 minutes) for patients. The Six Sigma DMAIC method helps the hospital analyze, improve, and control the shortage of general or specialist staff and the lack of triage rooms and registration counters.
Analyze Phase
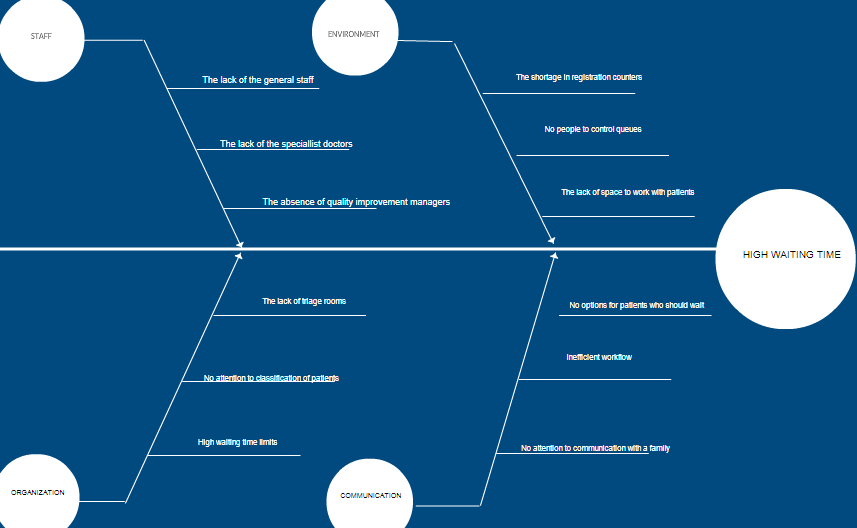
The goal is to investigate the root causes of the already defined problems in a working process. A fishbone diagram is a Six Sigma tool for data analysis. In this case, the major errors occur in the wrong organization of a hospital, poor administration, and the lack of people and space for cooperation with patients. As it is shown in Figure 1, there are four sectors where improvements and innovations may be needed.
First, the staffing sector (human resources) should be restructured because of the evident lack of specialists who are on calls and the absence of the general staff who could support effective cooperation and communication with patients. In addition, the hospital in Abu Dhabi does not have enough triage rooms and registration counters where patients have to be served. Such outcomes are explained due to the absence of quality improvement or strategic managers who predict the possible number of patients per day. As a result, the environment is poor to promote an effective working flow.
Improve Phase
The objective is to understand how to implement changes to the already existing system and offer solutions to specific hospital areas. First, new staffing requirements have to be developed, including the level of education and working experience. Second, new stakeholders must be invited as effective sponsors to create additional triage rooms and registration counters to work with patients.
Finally, an overall reorganization of the staff work is expected, including the norms to identify patients’ conditions, an automatic controller of waiting time queues, and a new phone call system in terms of which patients may plan their visits and reduce the time for waiting. The peculiar feature of these solutions is their connection and the impossibility of neglecting neither of them. On the one hand, re-structuring strongly depends on the number of employees in a hospital. On the other hand, additional people can hardly work effectively in case the number of triage rooms and registration counters remains the same.
Control Phase
The aim is to control and monitor solutions offered to the problem of high waiting time. It is expected to ensure long-term success and quality control for a certain period. In other words, the offered project plan that includes staff and organizational improvements has to be checked and proved as an effective one. A monitoring plan is a tool to be used for process control in the hospital. It helps to identify all the changes in the working process and the possibility to continue improvements in the same way. As it can be observed in Table 1, a monitoring plan includes the measures identified during the second phase of the Six Sigma approach.
Table 1. Monitoring plan.
Conclusion
The identification of defects, a properly developed plan, and monitoring are the key points for the Abu Dhabi hospital where the high waiting time is a major problem. Regarding the inability to predict the number of potential clients, the hospital fails to create an effective environment and hire enough people. The recommendation is to find additional sponsorship to increase the staff and the number of triage rooms for patients, which results in waiting time reduction.
Reference
Selvi, K., & Majumdar, R. (2014). Six sigma – Overview of DMAIC and DMADV. International Journal of Innovative Science and Modern Engineering, 2(5), 16-19. Web.